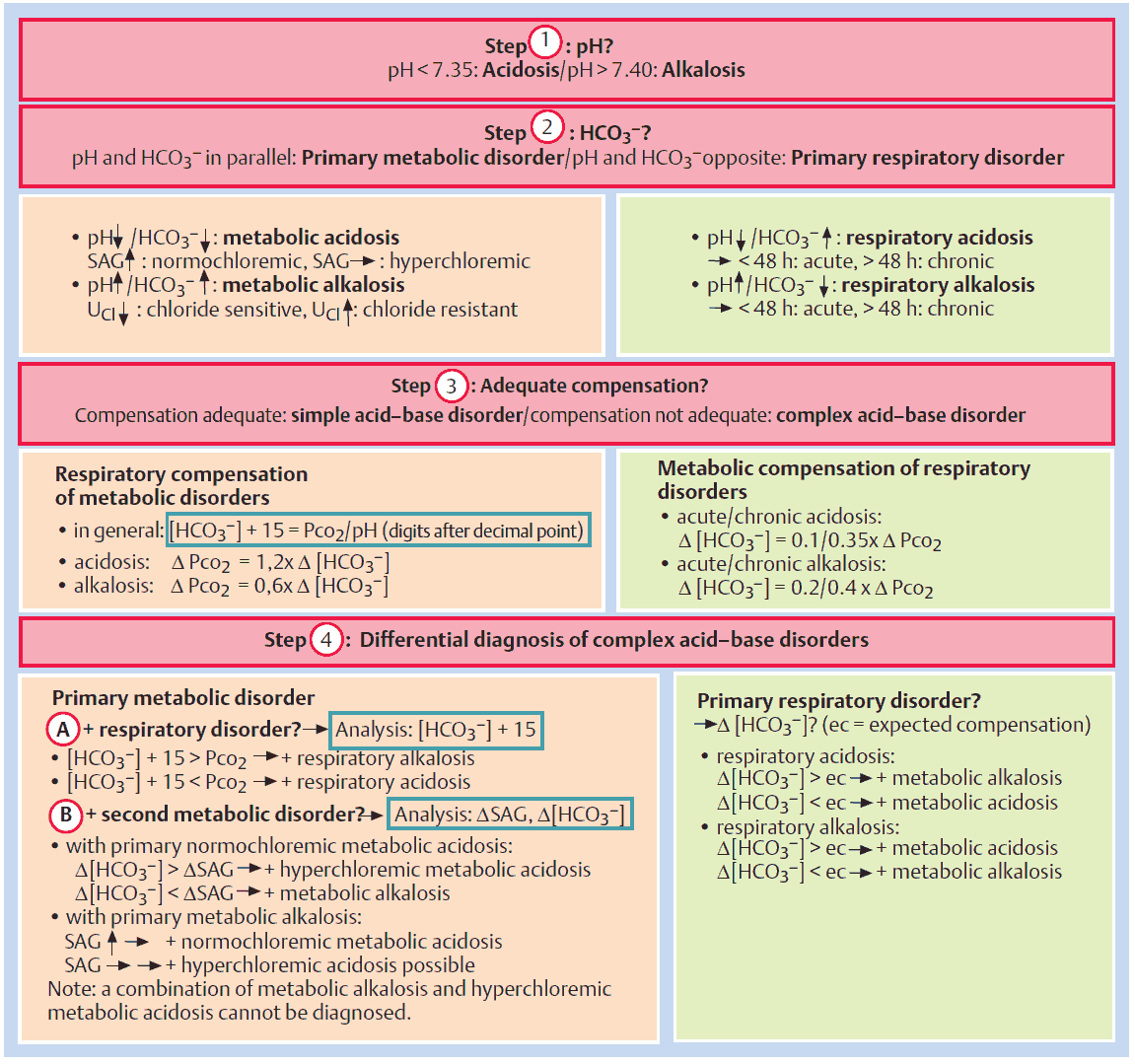
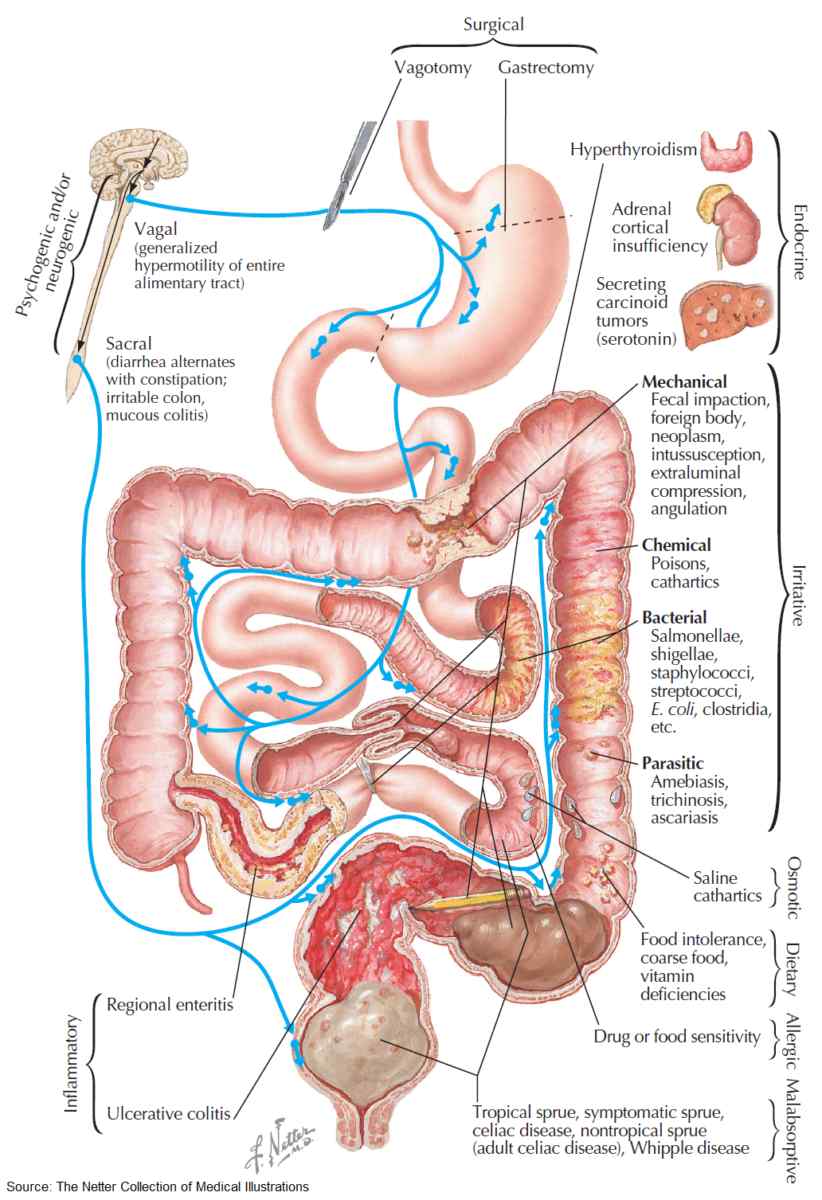
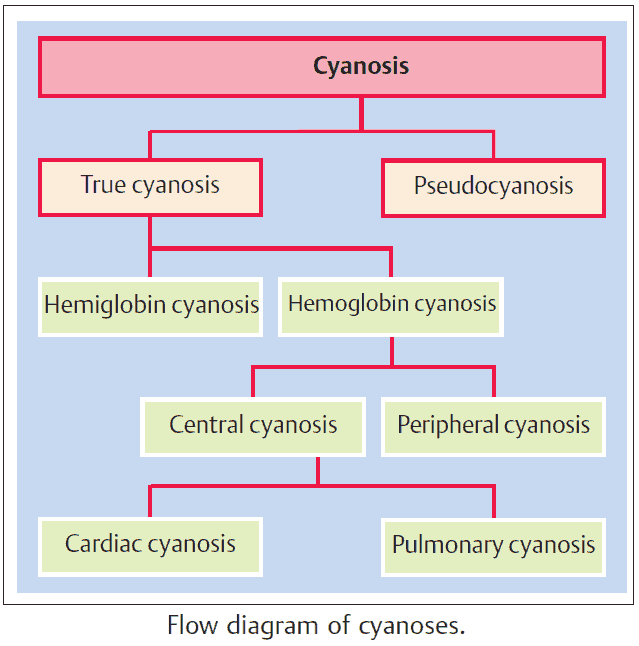
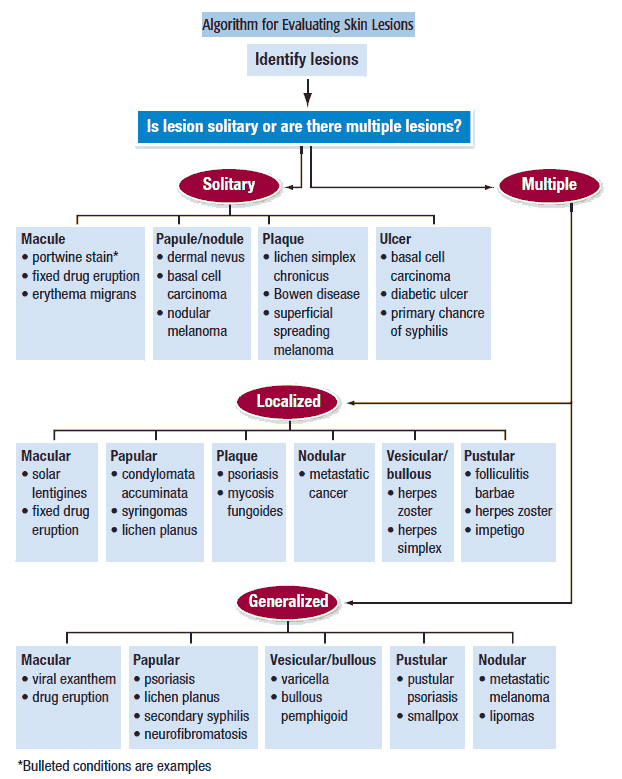
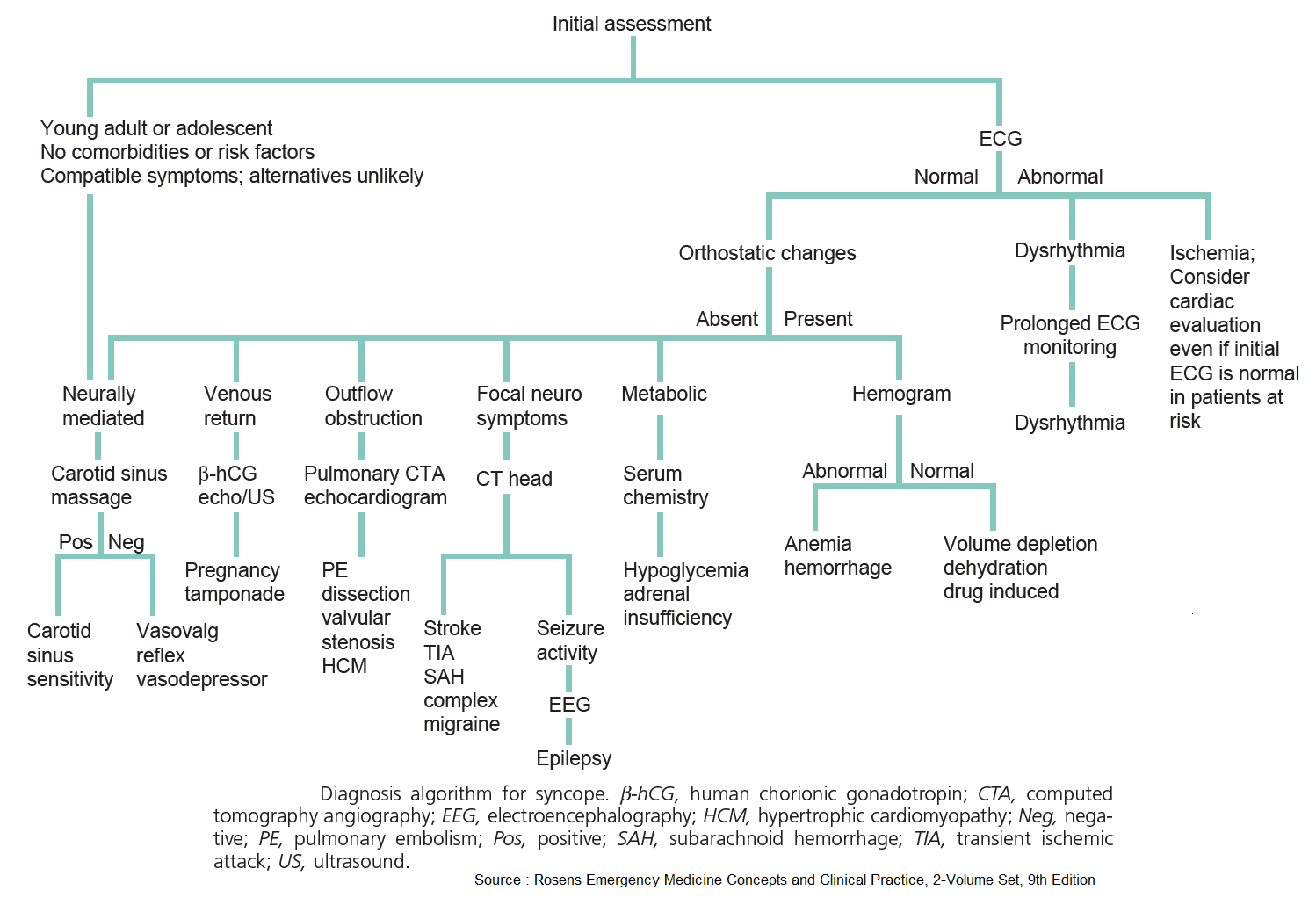
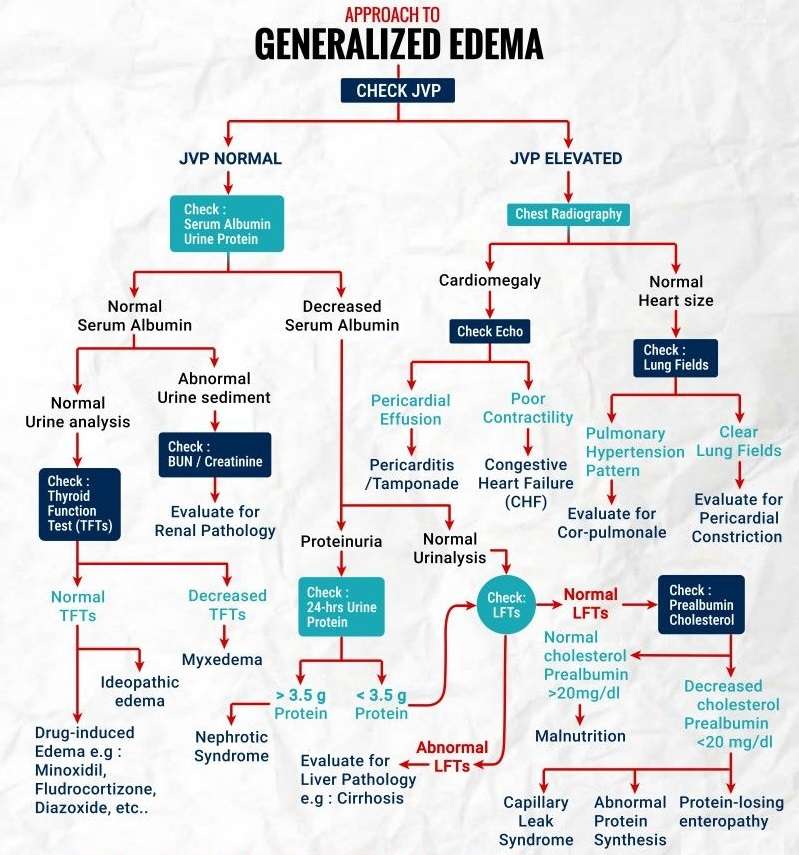
Driving Better Results in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension
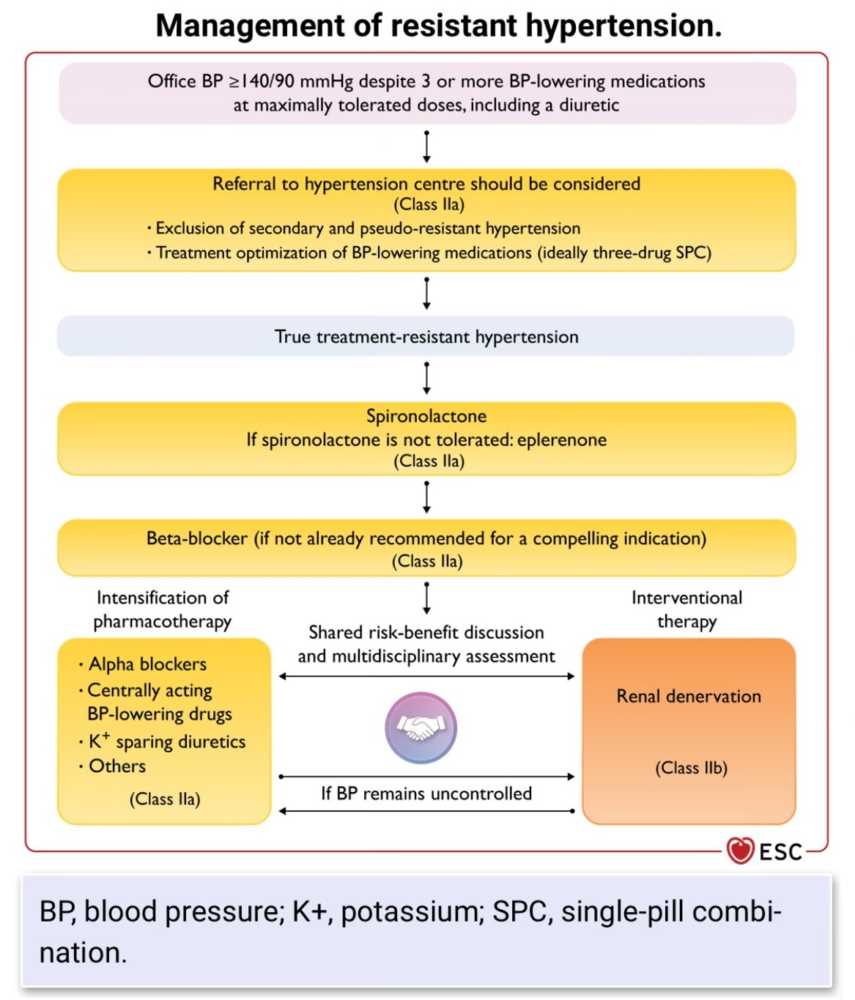
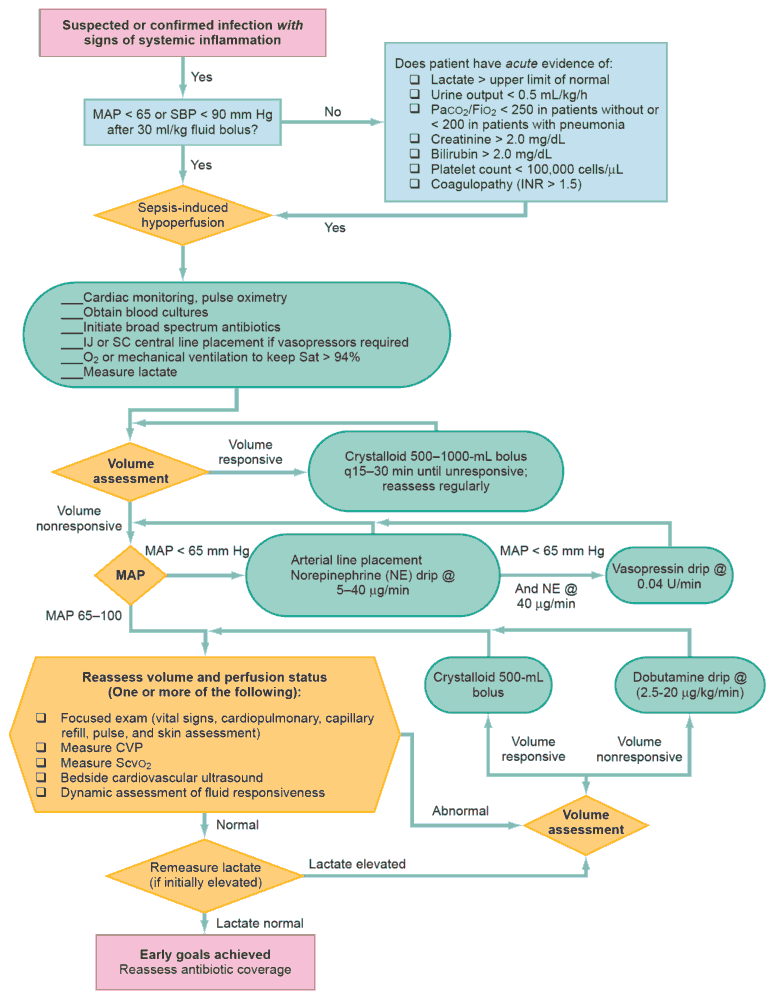
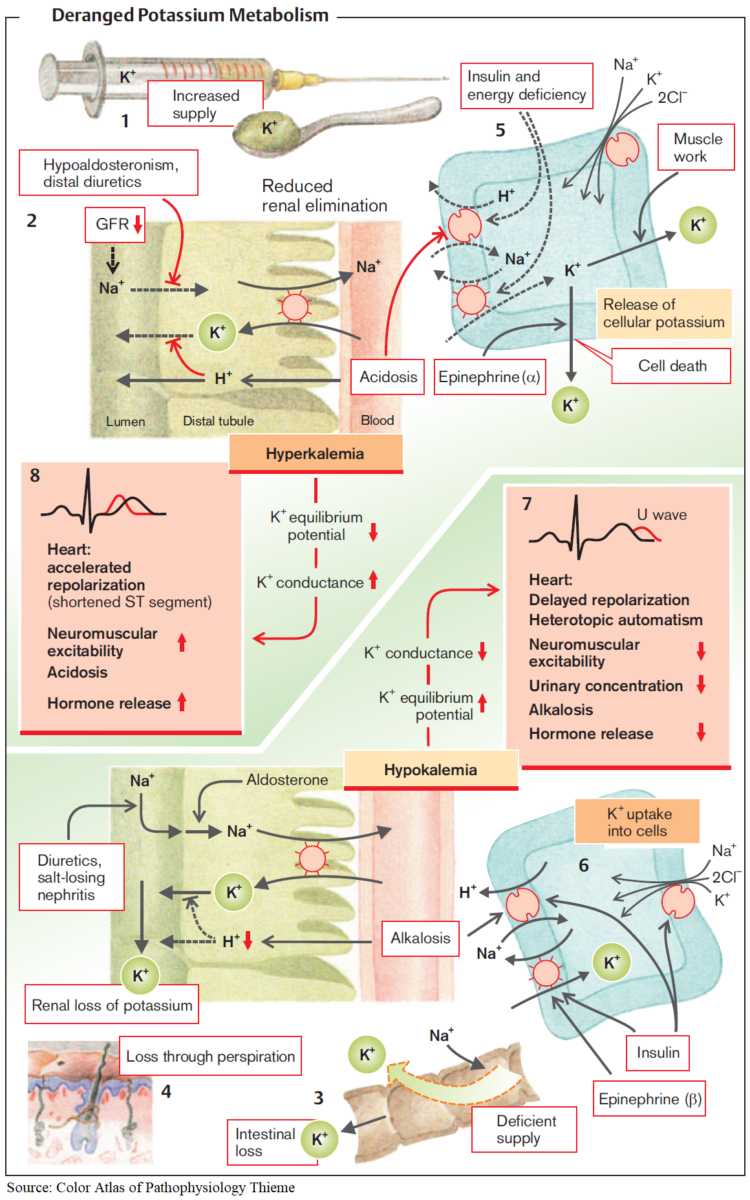
Resistant hypertension is a multifaceted condition that complicates standard hypertension management. Its complexity stems from various overlapping causes and population-level disparities...