Understanding Acute Kidney Failure: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
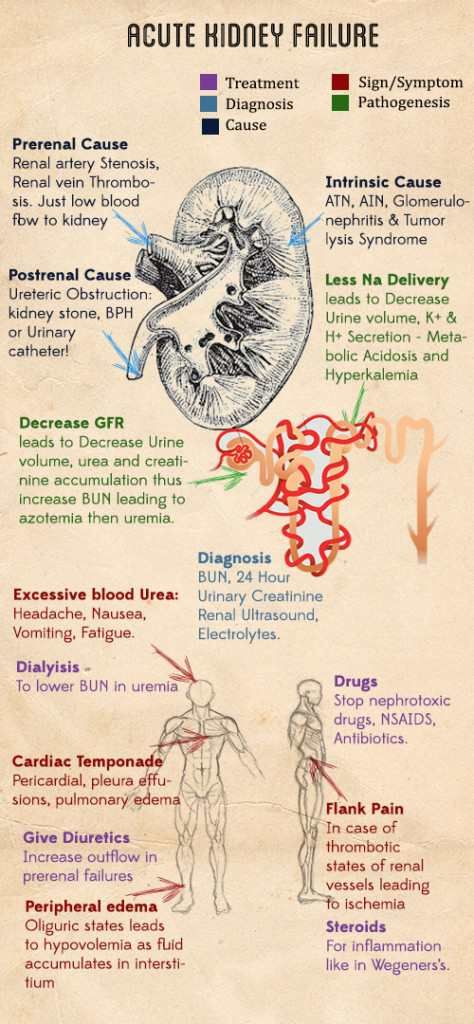
Acute kidney failure is a rapid decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) sufficient to cause uremia. Oliguria (below 15 mL per hour) is often a feature, although nonoliguric renal failure can also occur, particularly in...