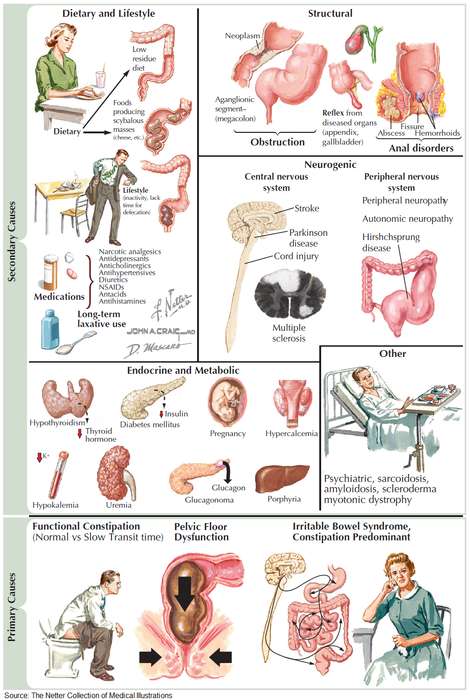
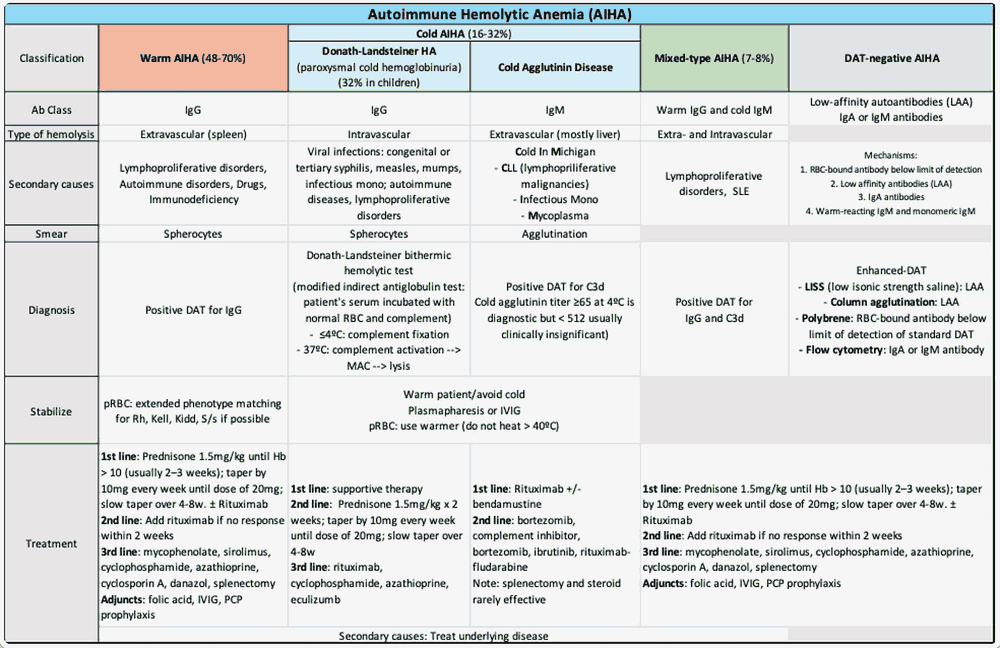
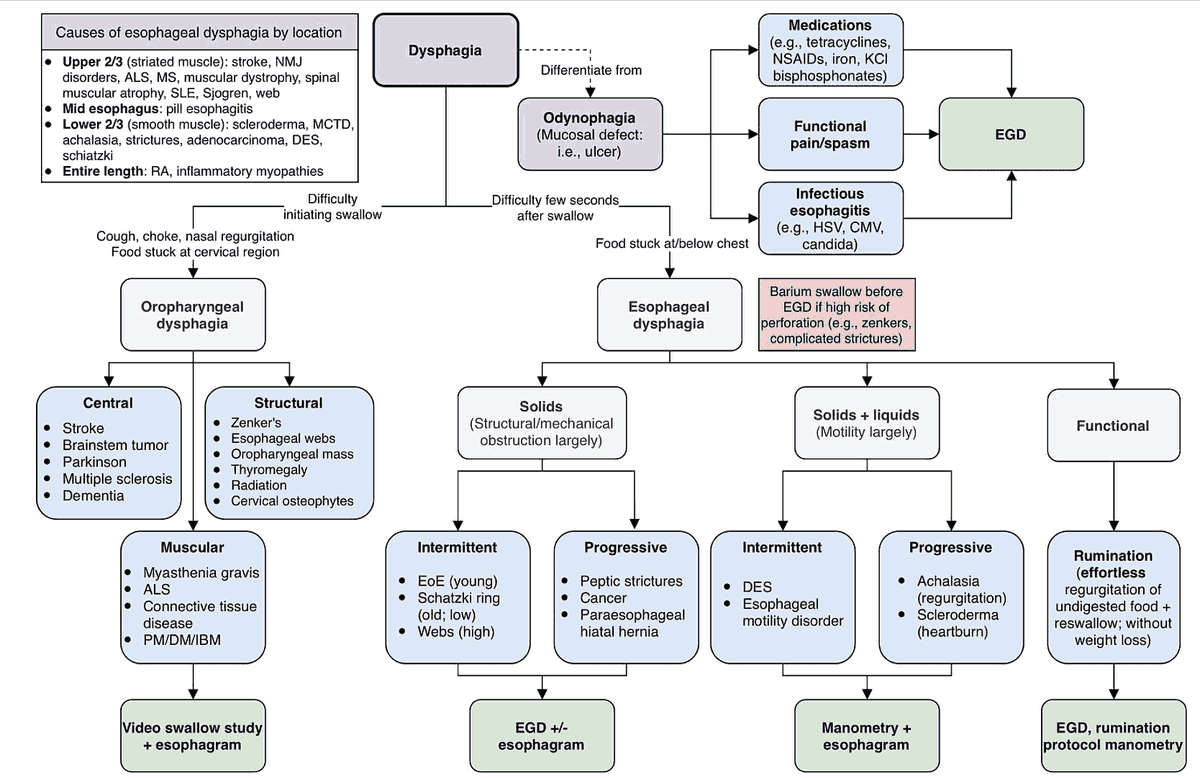
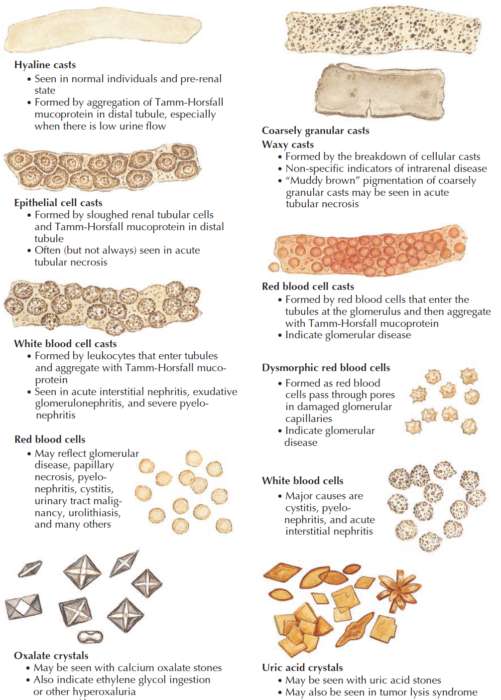
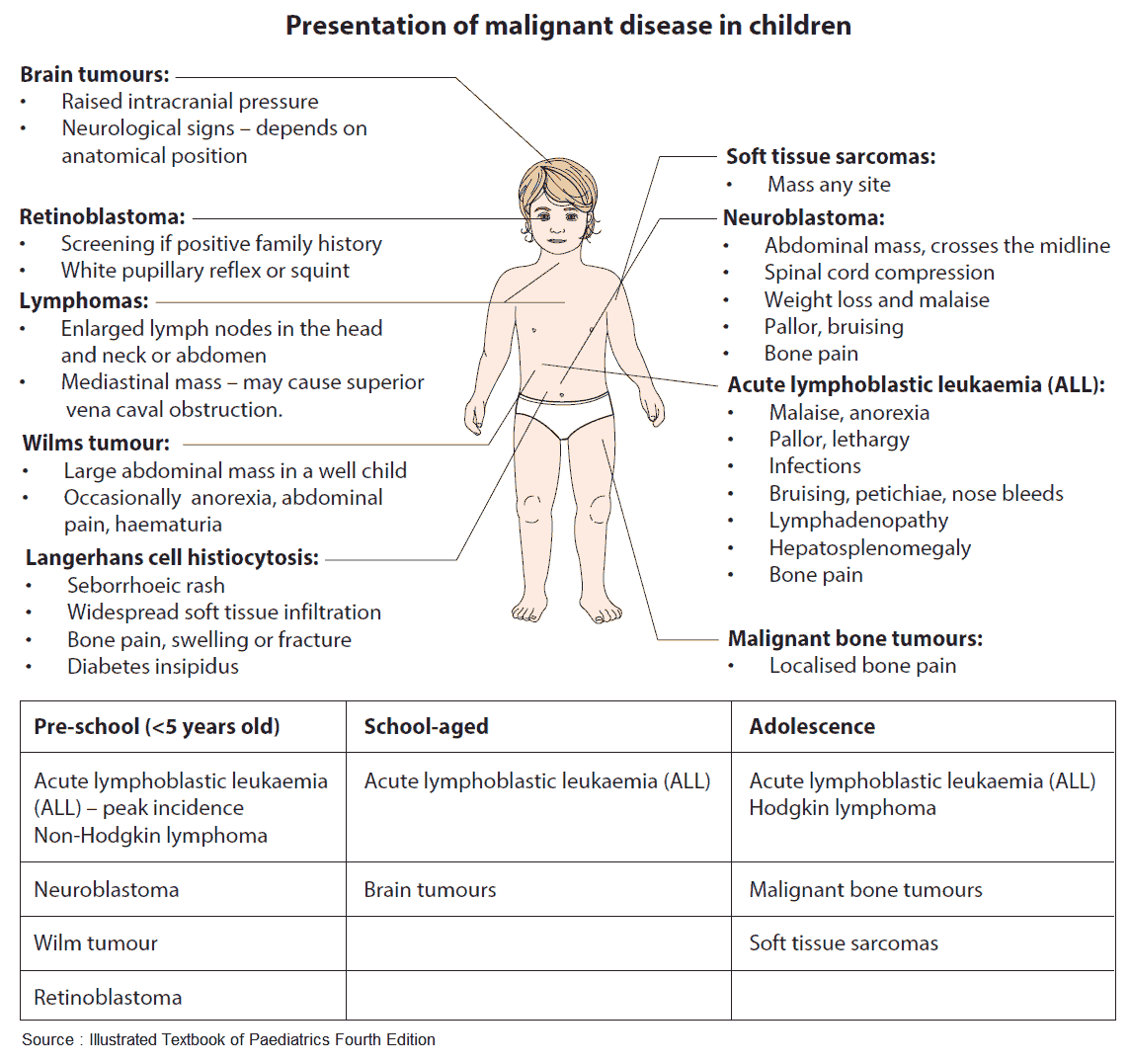
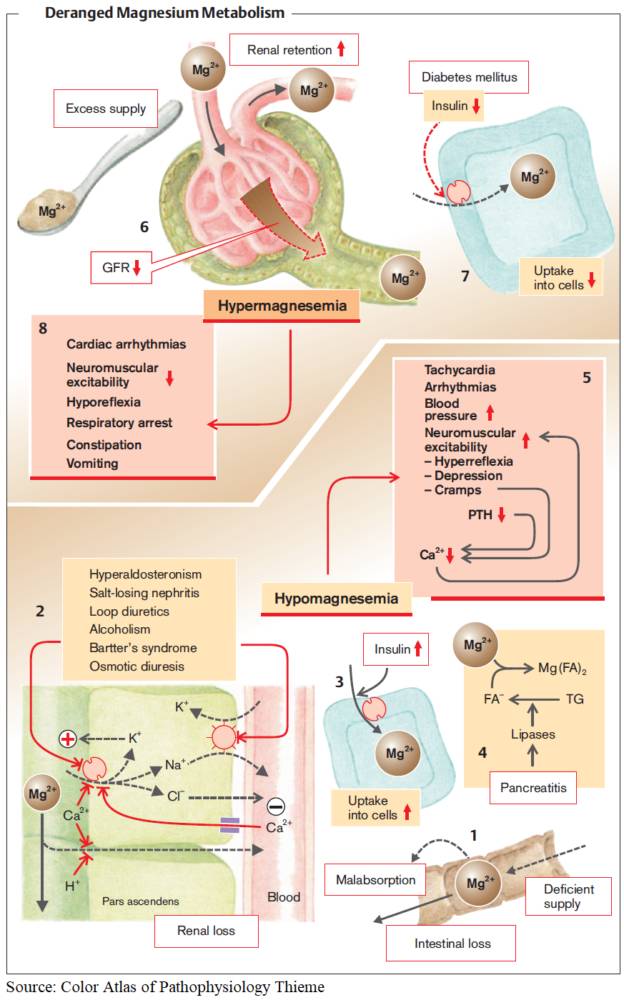
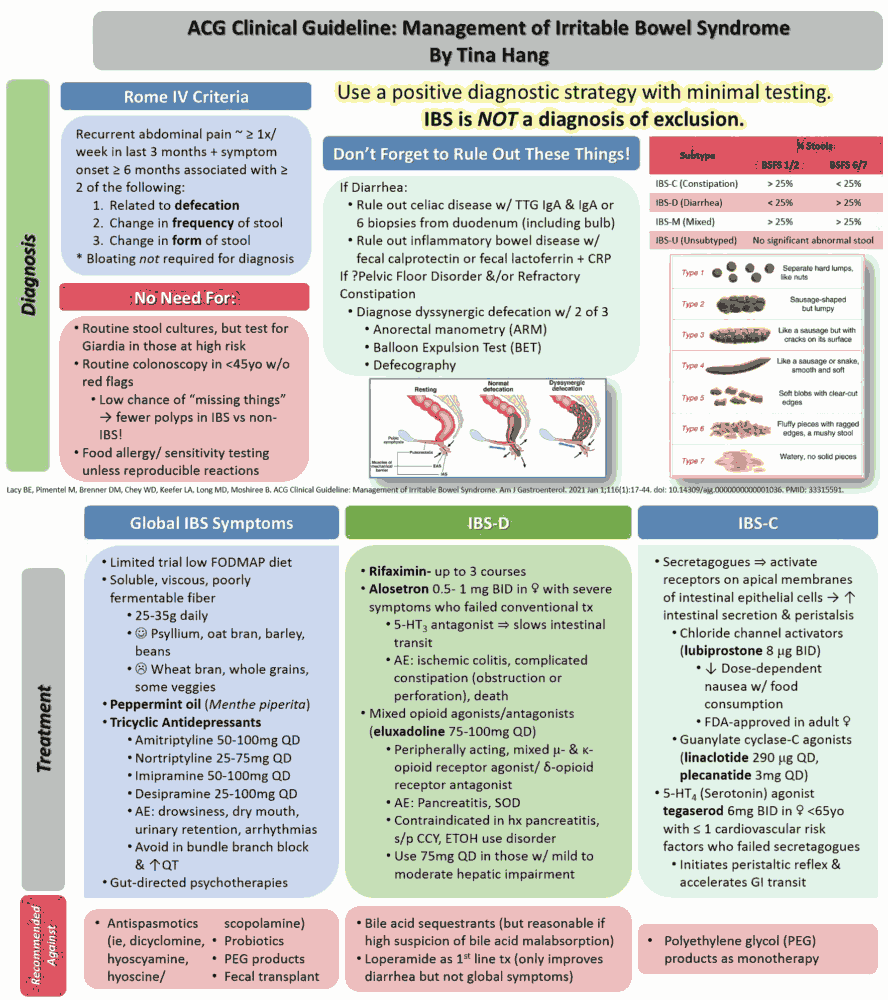
Gut on Pause: Clinical Insights Into Constipation
In everyday clinical practice constipation can be defined as less than two bowel actions per week, usually passing hard stool, and associated with straining. However, when applying this definition it must be kept in mind...