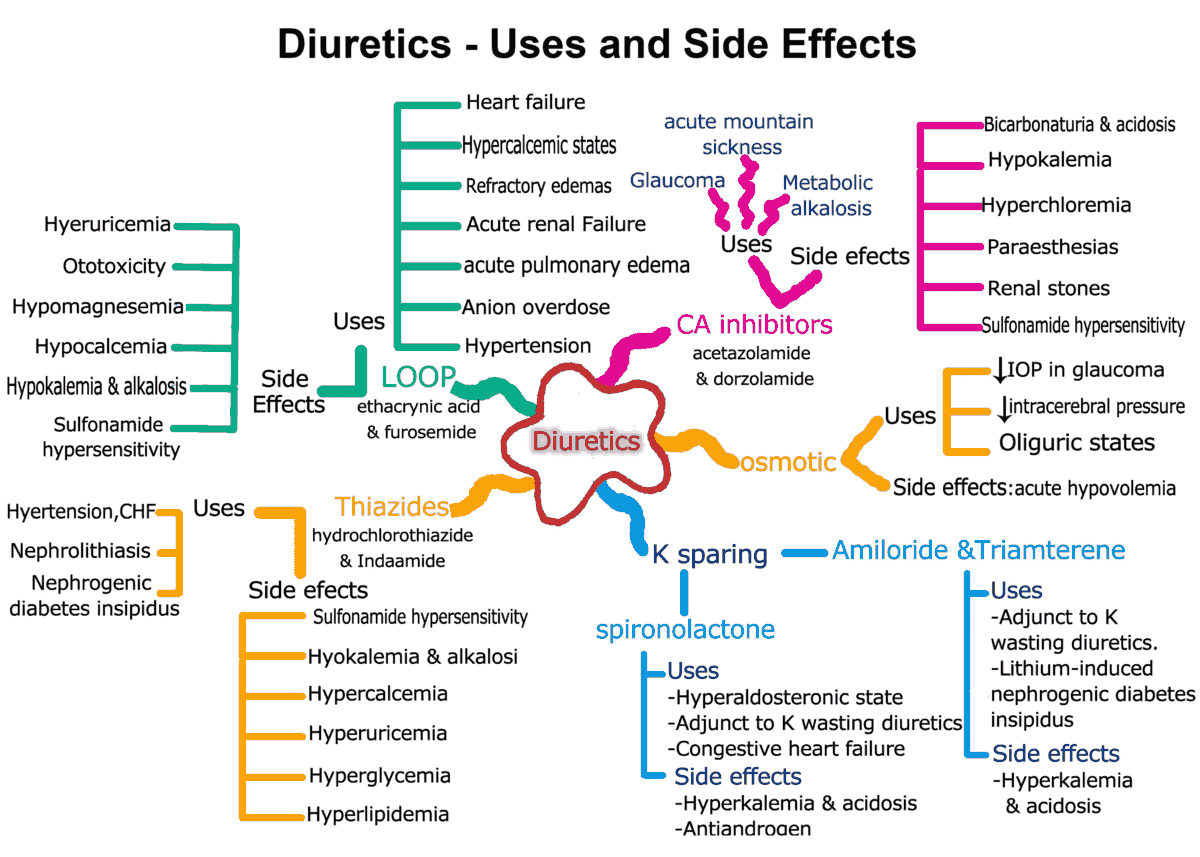
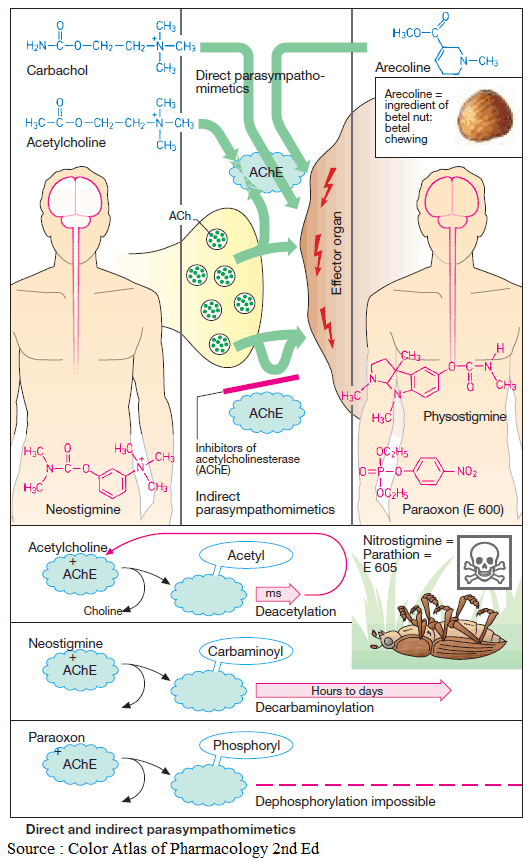
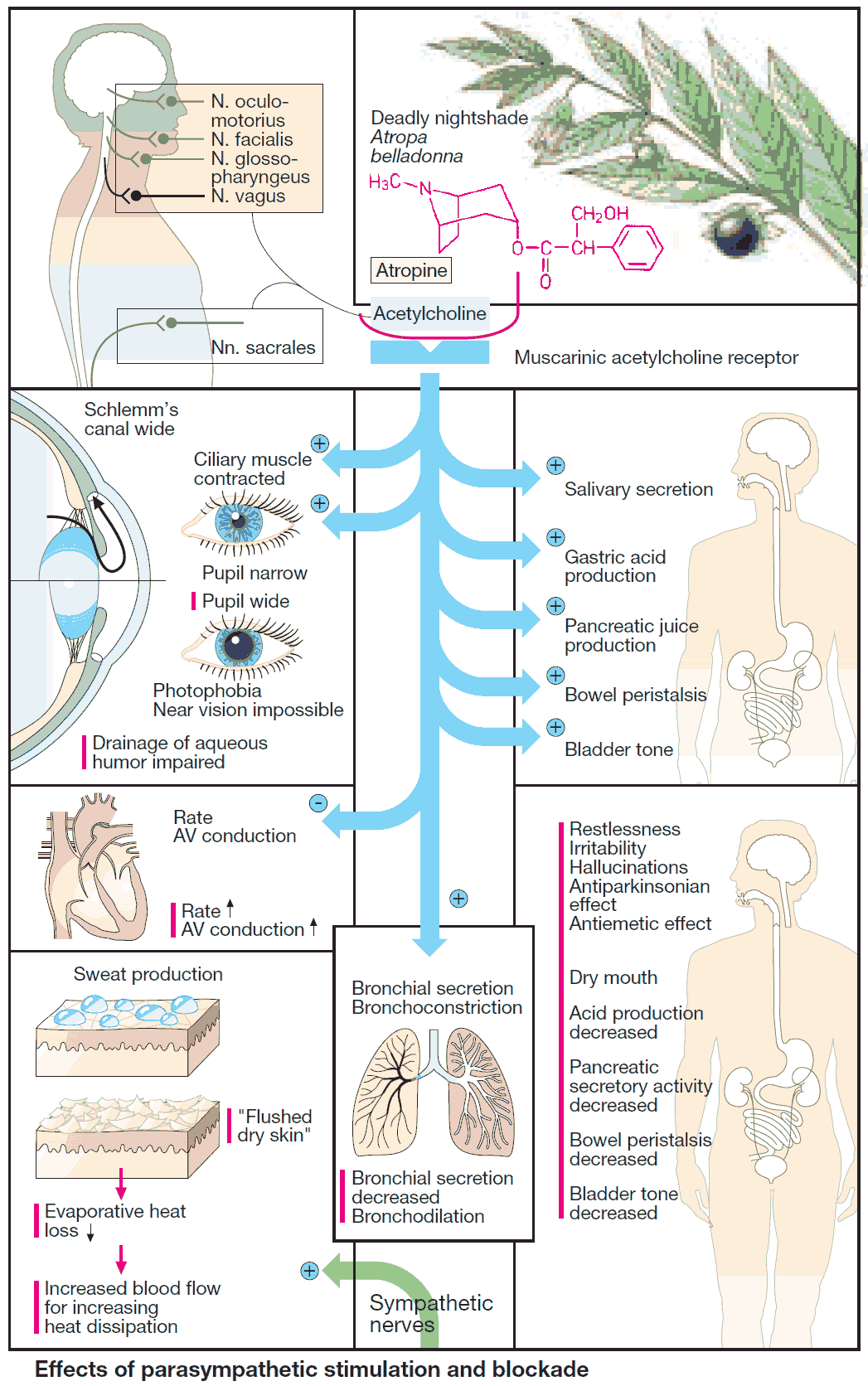
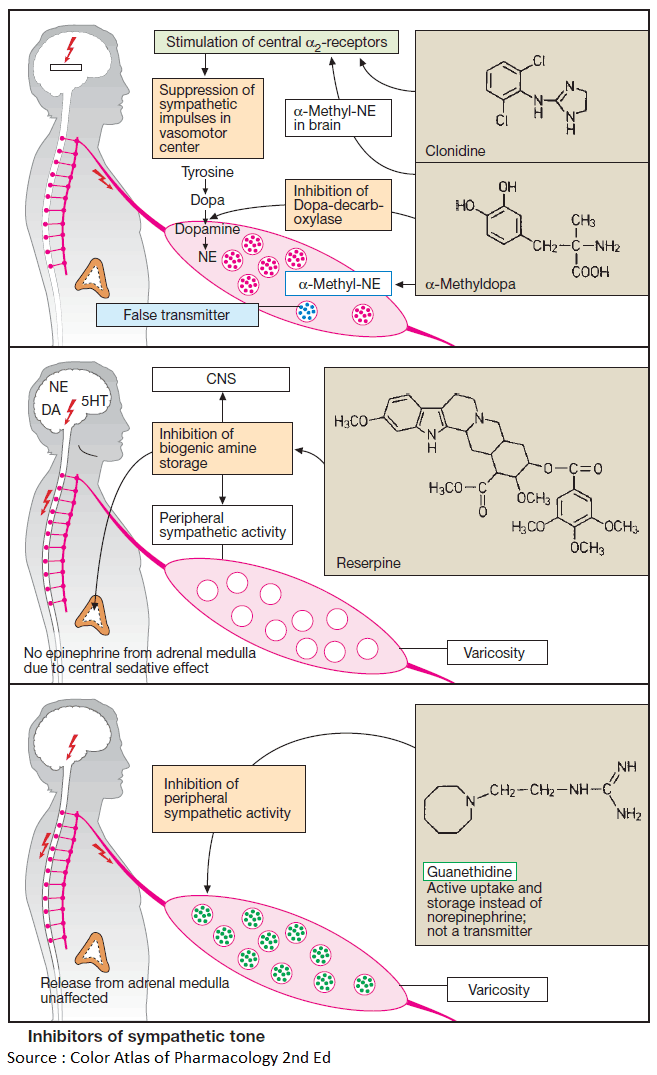
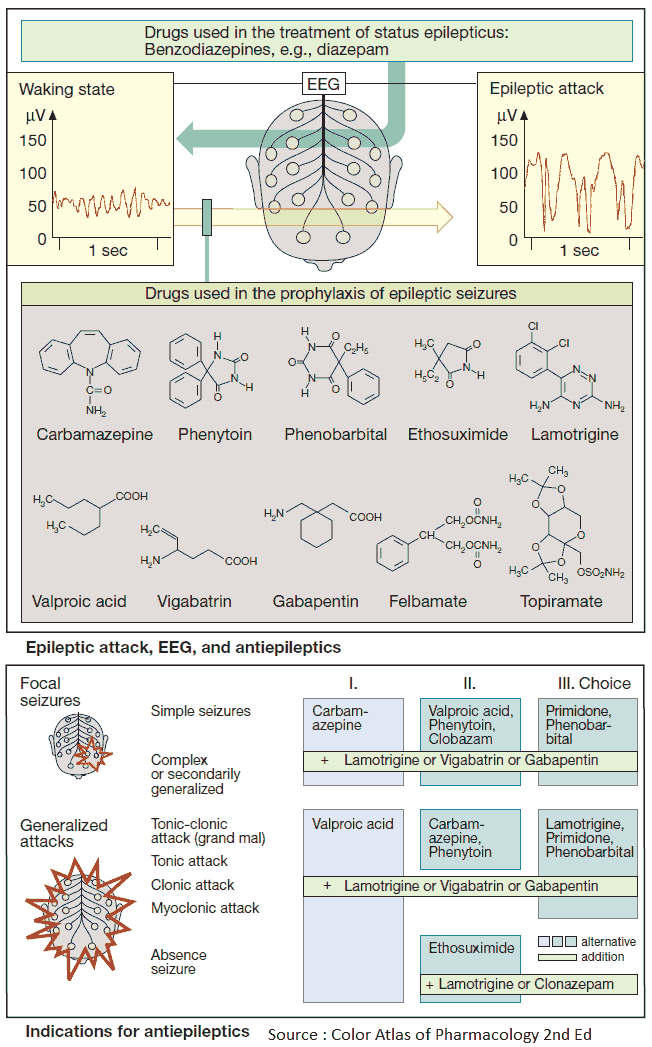
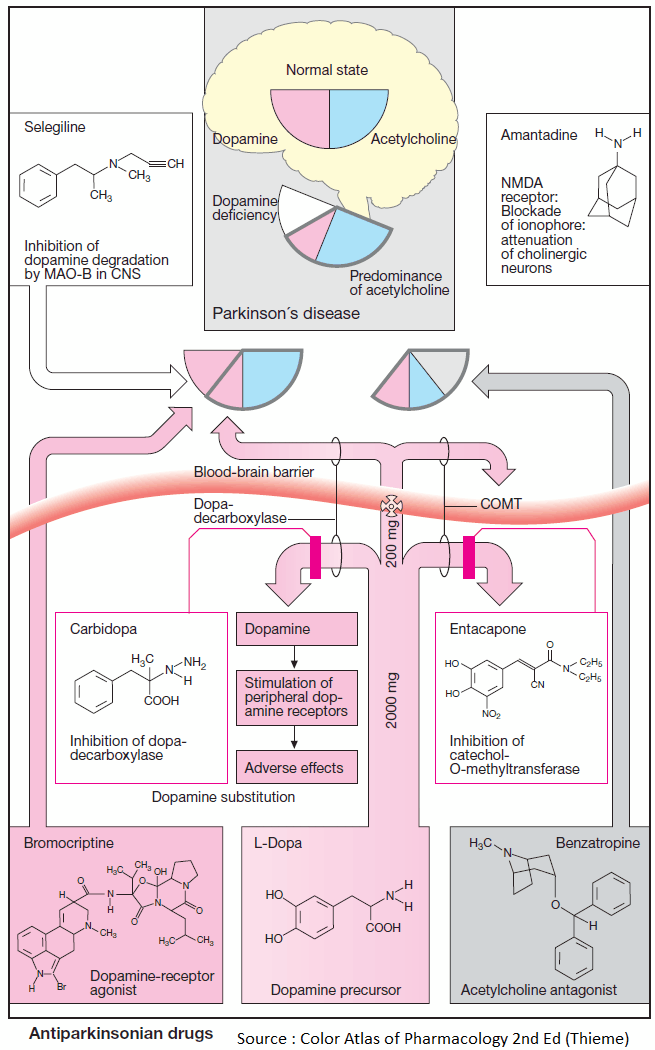
Diuretics – An Overview
Diuretics (saluretics) elicit increased production of urine (diuresis). In the strict sense, the term is applied to drugs with a direct renal action. The predominant action of such agents is to augment urine excretion by inhibiting the reabsorption of NaCl and water.