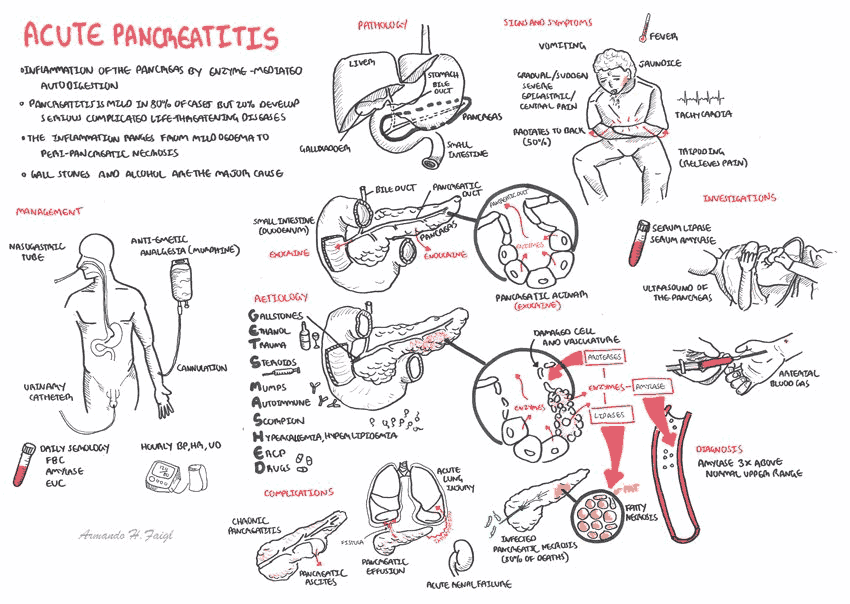
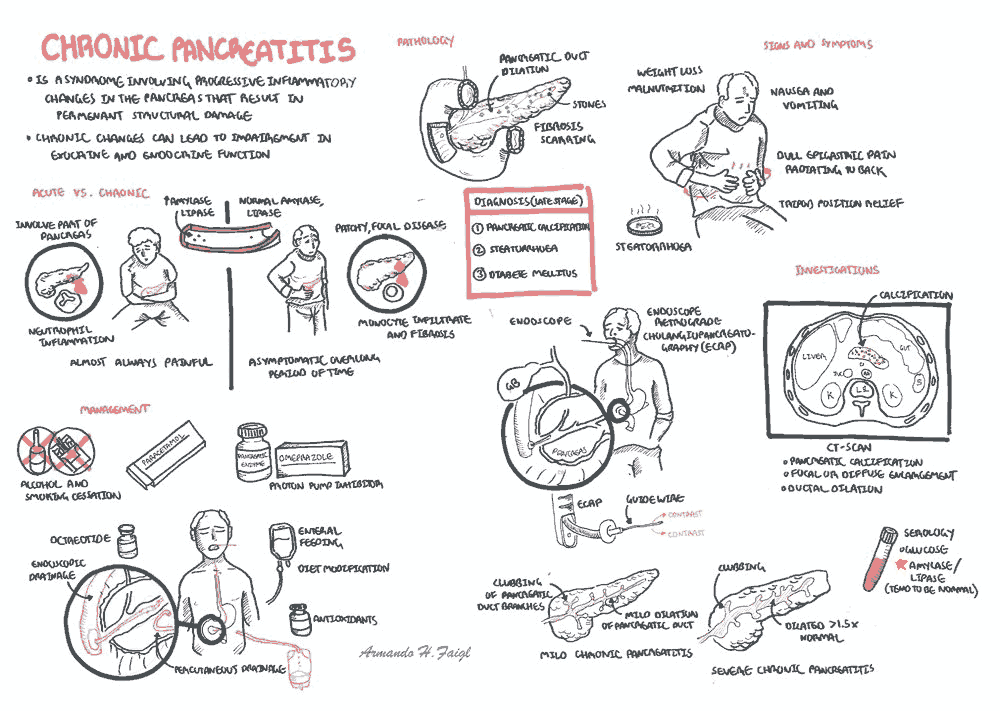
Acute Pancreatitis: Approach, Evaluation and Management
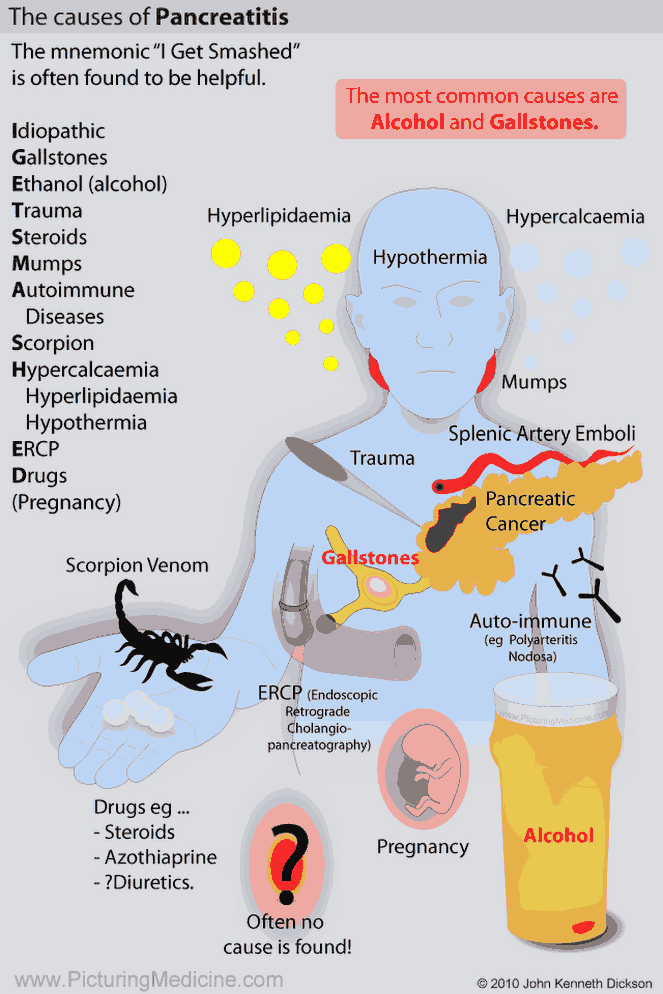
The causes of pancreatitis can be recalled from the mnemonic GET SMASH'D: gallstones, ethanol, trauma, steroids, mumps, autoimmune diseases, scorpion stings, hypertriglyceridemia, and drugs (e.g., azathioprine or diuretics).

![Read more about the article Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH): How to Recognize it on ECG [With Examples]](https://manualofmedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Major-ECG-findings-induced-by-left-ventricular-hypertrophy-LVH.png)
![Read more about the article Atrial Flutter: ECG Interpretation [With Examples]](https://manualofmedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Atrial-Flutter-with-4-1-AV-Block.png)