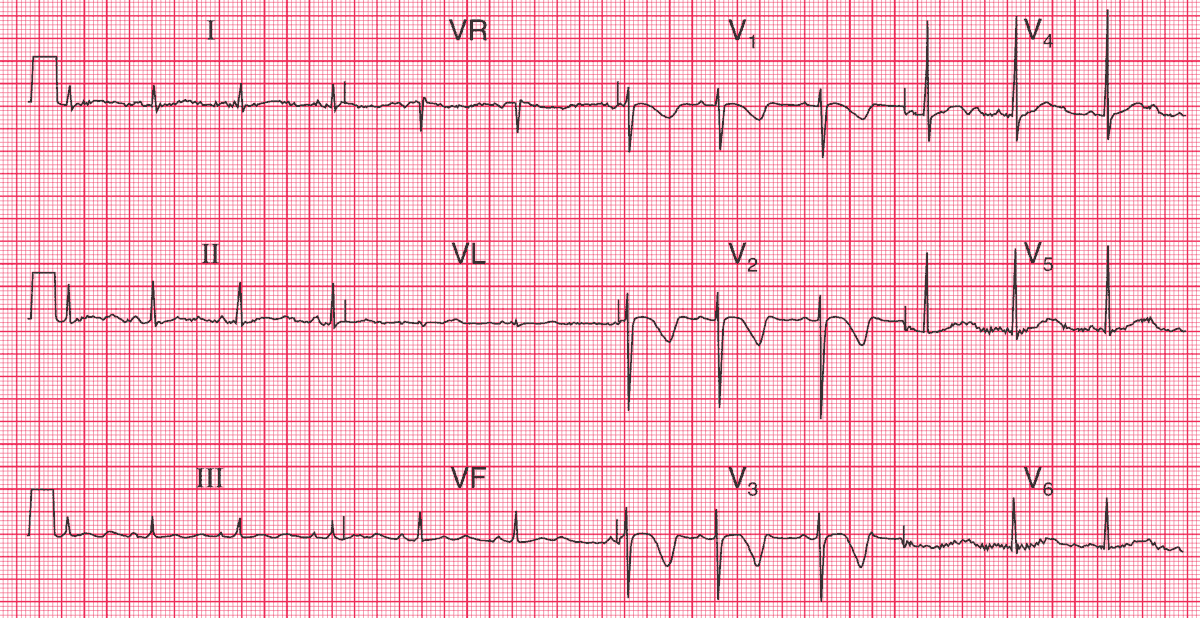
ECG Interpretation
- Sinus rhythm, rate 75/min
- Normal PR interval and QRS complex duration
- Normal axis
- Normal QRS complexes
- Inverted T waves in leads V1–V3
- Long QT interval (520 ms)
Clinical Interpretation
A collapse during exercise raises the possibility of aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, or an exercise-induced arrhythmia. This ECG does not show the pattern of left ventricular hypertrophy, so aortic stenosis is unlikely.
Anterior T wave inversion is characteristic of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, but this does not normally cause a prolonged QT interval. Exercise-induced arrhythmias are typical of the familial long QT syndrome, and this boy’s sister had died suddenly.
READ MORE about Pearls in Syncope ECG Interpretation
What to do ?
Initial treatment is with a beta-blocker, but an ICD (implantable cardioverter defibrillator) must be considered.

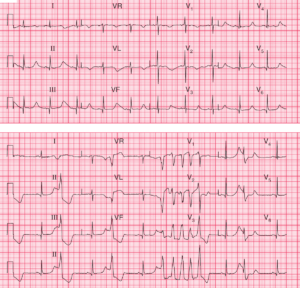
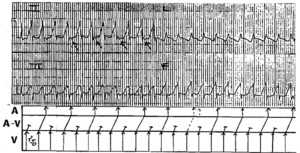
![Read more about the article Conduction Blocks at the AV Node (AV Blocks) [With Examples]](https://manualofmedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Excerpt-AV-Blocks-300x243.jpg)