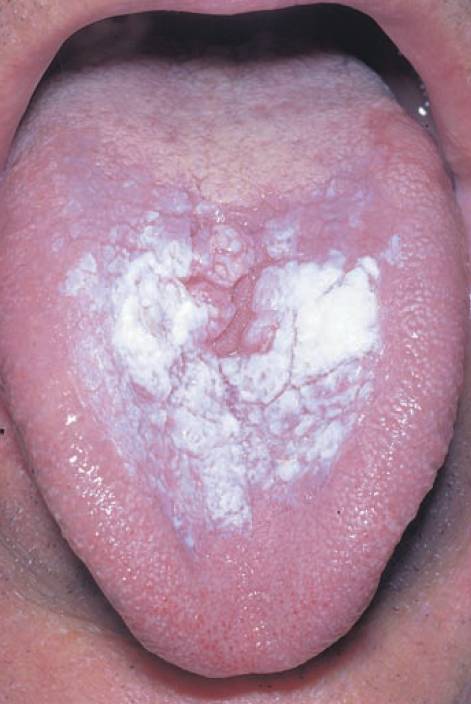
This post is an answer to the Case – White Discoloration of the Tongue
Where else may this condition be found?
Anywhere within the oral cavity, but it may affect other mucosal squamous epithelia – the larynx, vulva and lower anal canal.
What does this condition look like under the microscope?
There is hyperkeratosis – increased thickness of the prickle cell layer of the epithelium and retention of the nuclei in the keratinized layer.
What mnemonic covers its aetiological factors?
Although this condition may occur without obvious cause, remember the S’s!
- Smoking (as probably in this case): Pipes even more than cigarettes.
- Syphilis: Always carry out serological tests for syphilis in these patients (negative in this case).
- Septic teeth.
- Spirits.
- Spices: It is especially common in the Indian subcontinent and it is estimated that some 20% of betel nut users over the age of 60 have this condition.
What is the importance of this condition?
It is often premalignant. Suspect it if there is local thickening, pain, ulceration, bleeding or local erythema.
Which patients are at particular risk of malignant change?
The danger increases with the age of the lesion and is in the region of 4–5% at 20 years. The risk is greater in patients over the age of 70 (about 7%) than for patients under 50 (about 1%).
How is this condition managed ?
- Remove any underlying cause. For example, as in this patient, by stopping smoking, having warned him of his risk of developing a very unpleasant cancer.
- Biopsy any suspicious area for malignancy.
- Surgical excision, with skin graft if necessary. In this patient laser excision was performed