This post is an answer to the Case – Painful and Tender Lesion on Neck
What is this condition called?
Cellulitis.
What is the meaning of this term?
A spreading infection of cellular tissues – in this case the superficial fascia of the neck and the overlying skin. It may involve other cellular tissues, for example orbital cellulitis, which affects the connective tissues of the eye socket.
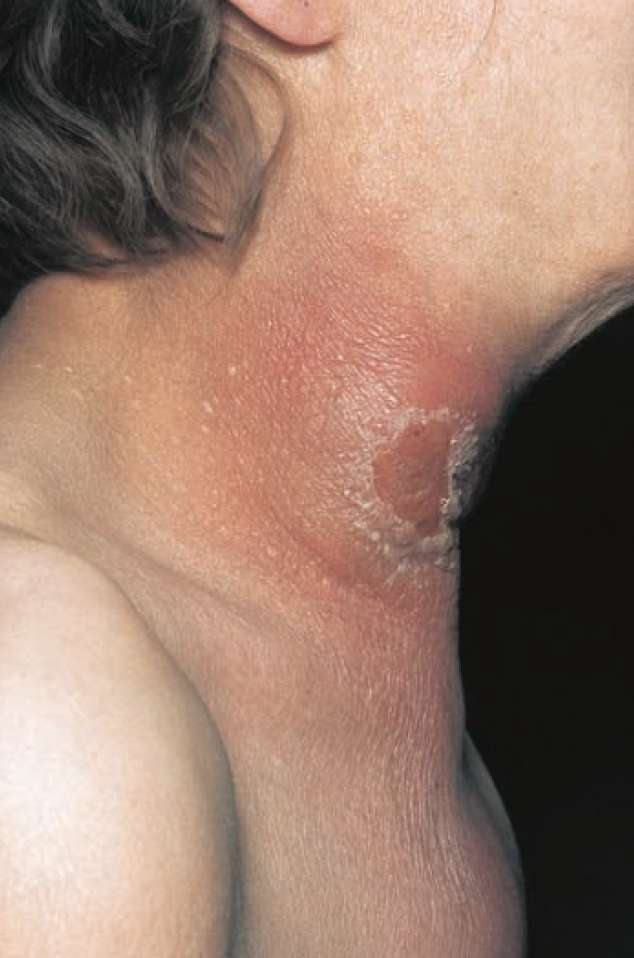
What are the characteristic clinical features of cellulitis?
- Those of any acute superficial infection – classically ‘calor, dolor, rubor, turgor’, that is heat, pain, redness and swelling. The heat and redness result from vasodilatation, the pain from the stimulation of the pain receptors in the skin and superficial tissues, and the swelling results from tissue oedema. There may be blistering of the overlying skin and occasionally skin necrosis (gangrene).
- The cellulitis may progress to the formation of an abscess (defined as a local collection of pus). Associated features may be lymphangitis (inflammation involving the draining lymphatic channels), which manifests as visible red streaks in the skin along the course of the lymphatics, and lymphadenitis where the draining lymph nodes become swollen and tender.
- Systemic features may often accompany a severe cellulitis. There is usually pyrexia, the patient feels ill and may have rigors.
How is this condition treated?
- If possible, the part is put to rest. A septic hand, for example, is splinted and elevated in a sling. In this case, a cervical collar would make the patient much more comfortable.
- The area is swabbed and blood cultures taken. Antibiotic therapy is then commenced. The initial choice of antibiotic would be intravenous benzyl penicillin to cover the group A (β-haemolytic) streptococci (e.g. Streptococcus pyogenes) and flucloxacillin to cover Staphylococcus aureus (most community-acquired staphylococci are flucloxacillin-sensitive). Erythromycin is the antibiotic of choice in patients who are allergic to penicillins. Metronidazole is added if there is ischaemic tissue or the subject is diabetic to cover anaerobes.
- If pus formation occurs, the abscess is drained
SIMILAR CASE: Cellulitis after Treatment for Breast Cancer