This post is an answer to the Case – Headache and Unsteady Gait
What is seen on the non-contrast CT and contrast enhanced T1W MR image ?
- On CT there is a well-defined densely calcified right posterior cranial fossa mass.
- On contrast enhanced MR there is a large well defined enhancing mass which on the coronal image is inseparable from the right tentorium cerebelli and appears extra-axial in origin.
- No evidence of peritumoural oedema.
- Slight mass effect on the 4th ventricle.
- No proximal ventricular dilatation.
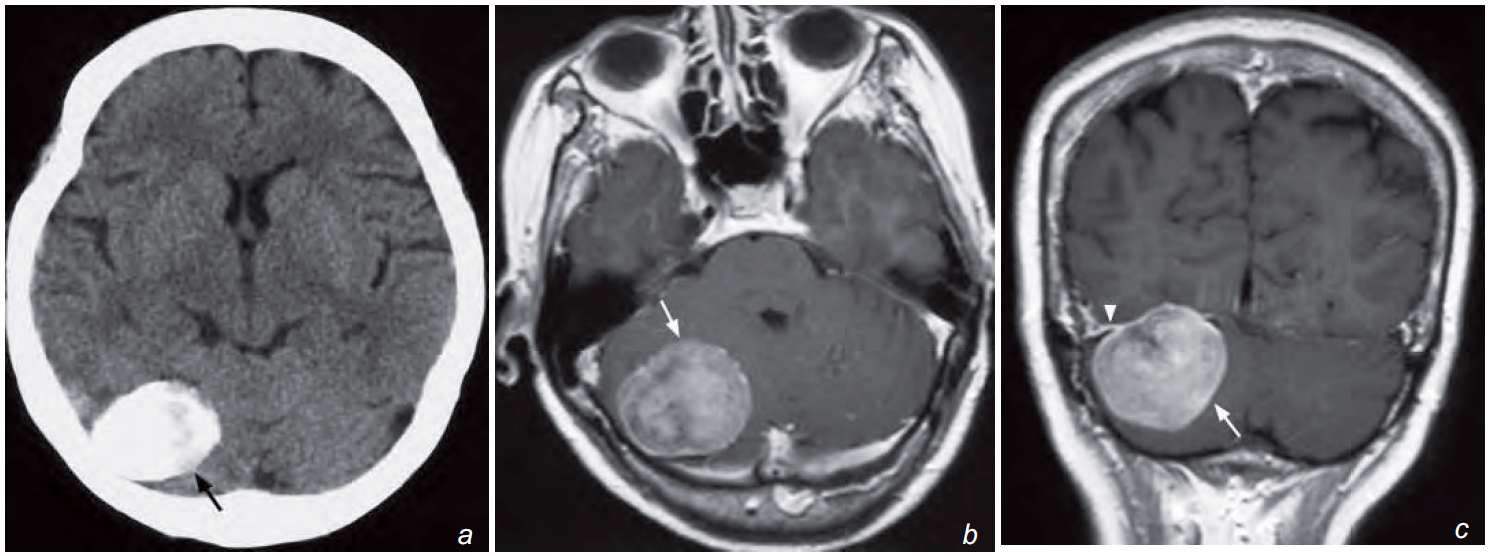
(b, c) Post-gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted axial (b) and coronal (c) MRI images show a homogeneously enhancing tumour (arrow) in the right posterior fossa inseparable from the right tentorium cerebelli with dural enhancement (arrowhead). There is no peritumoural oedema and mild mass effect is seen on the 4V. The diagnosis is a meningioma.
What is the diagnosis ?
Non-contrast axial CT (a) showing a densely calcified mass (arrow) in the posterior fossa on the right. It does not show peritumoural oedema.
Post-gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted axial (b) and coronal (c) MRI images show a homogeneously enhancing tumour (arrow) in the right posterior fossa inseparable from the right tentorium cerebelli with dural enhancement (arrowhead). There is no peritumoural oedema and mild mass effect is seen on the 4V.
In view of its extra-axial location, dense calcification, close relationship to the tentorium cerebelli and enhancement of the adjacent dura, the diagnosis is a meningioma.
Discussion
Meningioma is the most common extra-axial intracranial tumour with a predilection for elderly females.
Location: majority are supratentorial–cerebral convexity, parasagittal, sphenoid ridge; infratentorial–cerebellar convexity, tentorium cerebelli, cerebellopontine angle.
CT appearances: well-defined, may be calcified hyperdense mass with wide attachment to adjacent dura and intense homogeneous enhancement; hyperostosis of adjacent skull may be seen.
MRI appearances: hypointense/ isointense on T1-weighted images and isointense/hyperintense on T2- weighted images with intense contrast enhancement.
Meningiomas are almost always supplied by the external carotid artery and may be complicated by local invasion into the venous sinuses.
Simple meningiomas do not demonstrate significant peritumoural oedema in contrast to other aggressive lesions.
Meningiomas show intense homogeneous enhancement unlike some of the other tumours such as glioma and lymphoma.