This post is an answer to the Case – 1-year-old Baby With Decreased Conscious Level and Vomiting
Interpretation
- Acute right frontal subdural and interhemispheric haematoma – due to shearing force from shaking the baby resulting in rupture of small vessels crossing subdural spaces
- Non-depressed fracture of left parietal bone with no associated intracranial or scalp haematoma
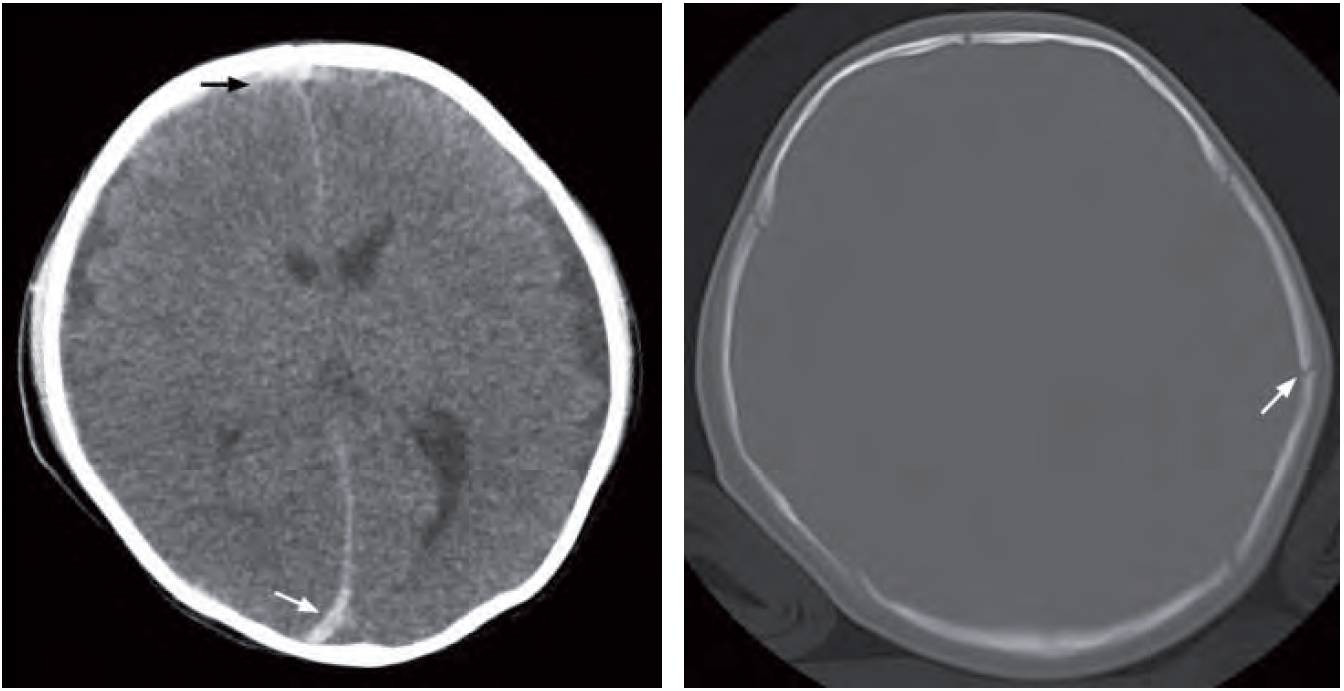
Right image: Bone window of CT brain shows a non-depressed fracture in the left parietal bone (arrow). This is an old fracture as there is no associated intracranial or scalp haematoma.
Diagnosis
Non-accidental injury (from shaking the baby) resulting in acute right frontal subdural haemorrhage and interhemispheric subdural haemorrhage along the posterior aspect of falx.
Key Points
- Diagnosis of nonaccidental injury relies on a high index of clinical suspicion (atypical history) and physical examination findings.
- Interhemispheric, subdural haemorrhage is a specific finding on CT brain.
- Metaphyseal fractures and posterior rib fractures are more likely of non-accidental origin.