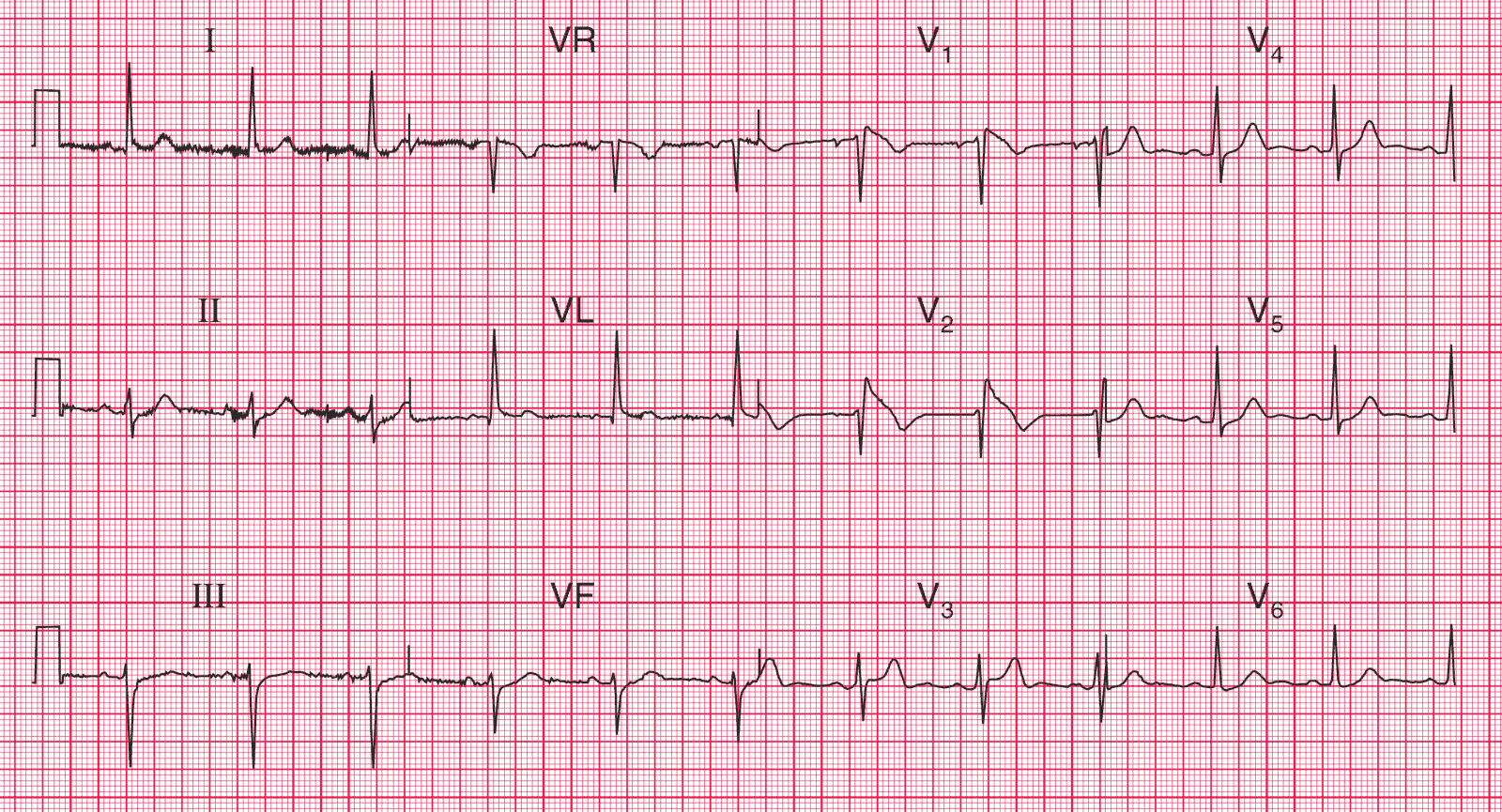
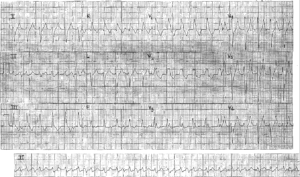
ECG Interpretation
- Sinus rhythm, rate 70/min
- Normal PR interval and QRS complex duration
- Normal axis
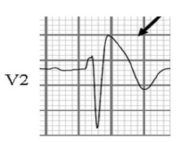
- QRS complexes in leads V1–V2 show an RSR1 pattern
- ST segments elevated, and downward-sloping, in leads V1–V2
Clinical Interpretation
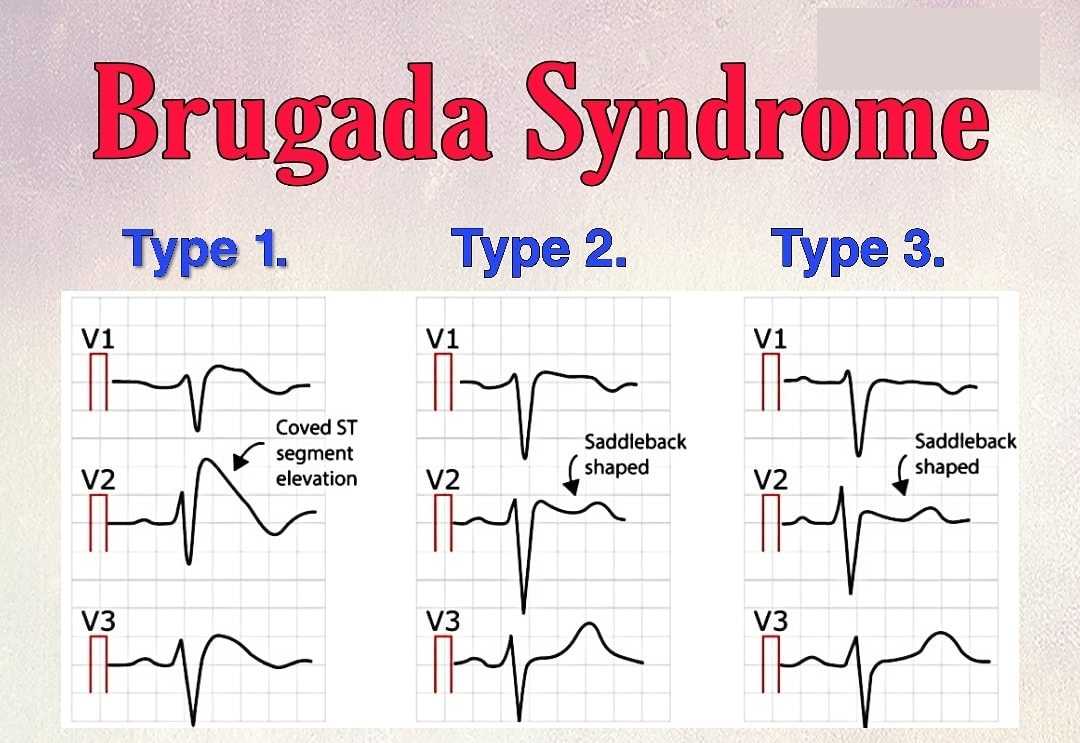
This is not a normal ECG. The appearances in leads V1–V2 are characteristic of the Brugada syndrome.
What to do ?
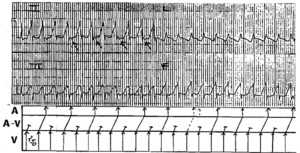
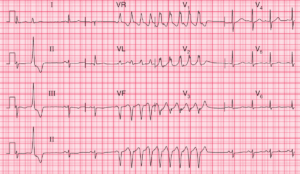
The Brugada syndrome involves a genetic abnormality that alters sodium transport in the myocardium, and predisposes to ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation. This patient’s collapse may well have been due to an arrhythmia.
The syndrome is often familial. The ECG changes are not constant, and on the day after admission this patient’s ECG was perfectly normal.
The ECG changes can be induced, and ventricular tachycardia caused, by antiarrhythmic drugs. The only treatment is an implanted defibrillator.