This article is an answer to the ECG Case 186
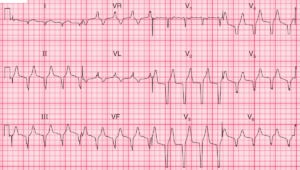
- Rate: 102/min
- Rhythm: Sinus
- Axis: LAD (-30 to -60)
- Intervals:
- PR – Prolonged (200 – 240ms)
- QRS – Normal (80ms)
- QT – 440ms (QTc Bazette 310ms)
- Segments:
- ST Elevation aVR (3-4 mm) V1 (3mm) V2 (2mm)
- ST Depression I, II, aVF, aVL, V4-6
- Additional:
- Notched P wave in lead II, possible biphasic P wave in V1
- Poor R wave progression
Interpretation
- Most marked abnormality is ST elevation in aVR, V1-2, with ST Depression I, II, aVF, aVL, V4-6
- Also 1st Degree AV block and possible left atrialenlargement (P mitrale)
- This pattern is most consistent with a LMCA occlusion (STE aVR >/= V1)
- LMCA occlusion associated with a high mortality (aVR STE>1.5mm up to 70% mortality)
- Could also be proximal LAD lesion or severe 3-vessel disease (3VD)
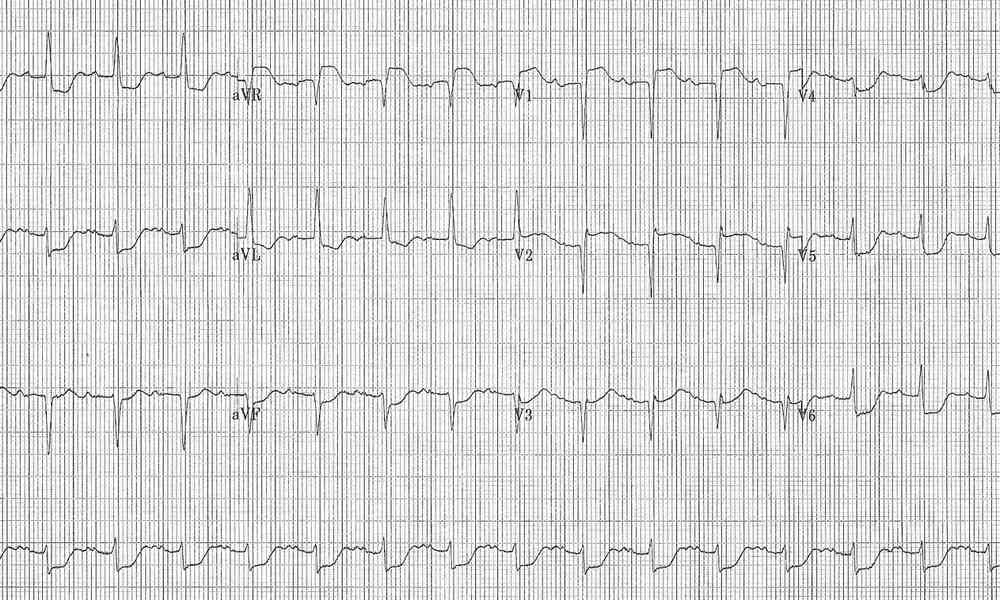
Management
- Urgent liaison with cardiology is required
- Need to discuss reperfusion therapy based on available resources / local policies
- Consideration of likelihood of requiring CABG is needed as this may affect initial drug therapy, particularly clopidogrel or prasugrel due to increased incidence of post operative bleeding
What happened next ?
- Patient was reviewed and admitted by cardiology team
- Planned for urgent angiography
- Patient declined intervention
- Re-presented with APO and cardiogenic shock
SIMILAR CASES: