This post is an answer to the ECG Case 210
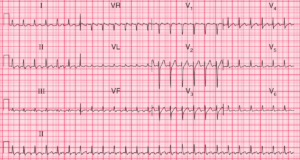
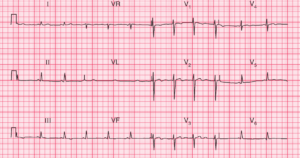
- Rate: 88bpm
- Rhythm:
- Regular sinus rhythm
- Single PVC
- Axis:
- Normal (~20 deg)
- Intervals:
- PR – Prolonged (~240ms)
- QRS – Normal (100ms)
- QT – 400ms (QTc Bazette ~ 480 ms)
- Segments:
- ST elevation with coved morphology in leads V1 (2mm) and V2 (~4mm)
- ST elevation with concave morphology in leads I (<1mm) and V3 (~2mm)
- ST depression in V4, V5
- Additional:
- T wave inversion leads aVR, aVL, V1-3
- Compensatory pause post PVC of ~1.2s
- Partial RBBB
- rsR’ pattern V2
- Note PVC is closely coupled near preceding T wave peak
Interpretation
- Brugada Syndrome
- History of syncope
- Type 1 Pattern
- 1st degree AV block
What happened next?
What happened next in this case really highlights why anyone looking at ECG’s needs to be able to recognize this particular ECG pattern.
Shortly after the patient arrived in the Emergency Department he had two episodes of VF arrest both reverted following asynchronous DC cardioversion. He was transferred to a tertiary center for further investigation and management, including:
- Angiogram – multi-vessel irregularities
- ECHO – normal, ejection fraction of 65%
- Cardiac MRI – no RV or outflow tract dysplasia, no LV scarring or lesion.
He then underwent Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD) insertion and was discharged from hospital within the week.
What is Brugada Syndrome ?
It’s an inherited sodium channelopathy, associated with sudden death and syncope due to polymorphic VT and, as in our case, VF. Three types of ECG pattern are describe in Brugada, although only type 1 is considered diagnostic, as shown in our ECG.
Type 1 ECG pattern:
- Cove-shaped ST elevation of at least 2mm followed by a negative T wave in one or more of leads V1-3
In conjuction with these ECG features you need, at least, one of the following:
- Document VF / polymorphic VT
- Family history of sudden cardiac death at <45 years
- Type 1 pattern ECG i n family members
- Inducibility of VT with programmed stimulation
- Syncope
- Nocturnal agonal respiration
- Attributed to self-terminating VF/polymorphic VT
READ MORE: Pearls in Syncope ECG Interpretation
SIMILAR CASES:

![Read more about the article Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH): How to Recognize it on ECG [With Examples]](https://manualofmedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Major-ECG-findings-induced-by-left-ventricular-hypertrophy-LVH-257x300.png)