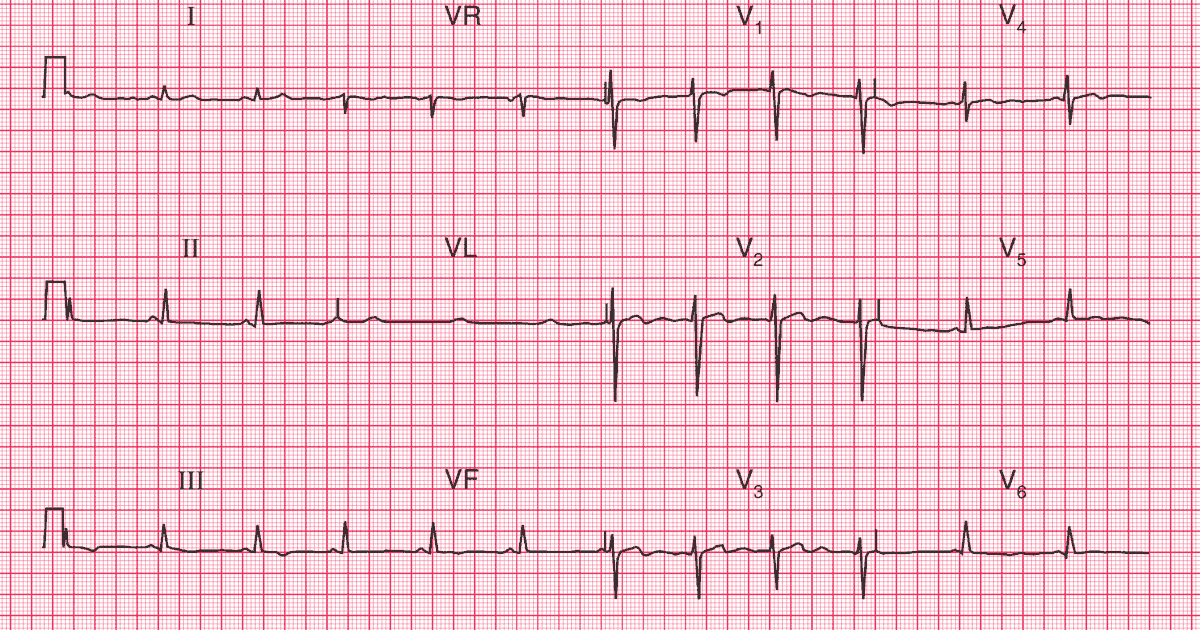
ECG Interpretation
- Sinus rhythm, rate 71/min
- Normal axis
- Normal QRS complexes
- Inverted T waves in leads III, VF; biphasic T waves in lead V4; flattened T waves in leads V5–V6
- U waves in leads V2–V3 (normal)
Clinical interpretation
These T wave changes, particularly those in the inferior leads, could well be caused by ischaemia. The flattened T waves in the lateral leads can only be described as ‘nonspecific’.
What to do ?
When confronted with an ECG showing this sort of ‘nonspecific’ abnormality, action depends primarily on the clinical diagnosis.
If the patient is asymptomatic it is fair to report the ECG as showing ‘nonspecific changes’; if the patient has symptoms at all – as in this case – it is probably worth proceeding to an exercise test.
In this patient, the exercise test was perfectly normal, and his symptoms cleared without any intervention. A repeat ECG, recorded purely out of interest a month later, showed similar changes.
READ MORE about ECG Interpretation: All you need to know