This post is an answer to the Case – ECG Case 218
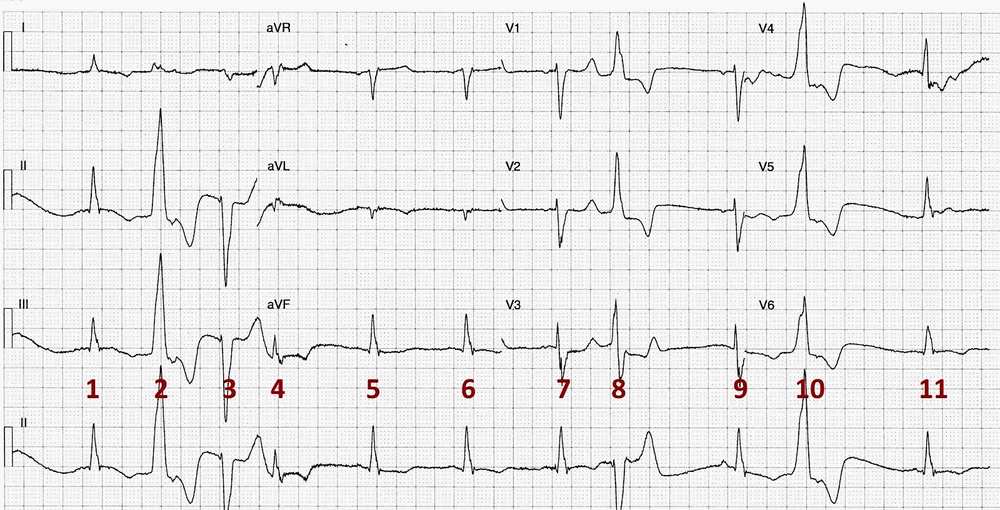
- Rate: Mean ventricular rate ~66 bpm
- Rhythm:
- Sinus rhythm
- Complexes # 1, 5, 6, 7, 9, 11
- P waves difficult to see but best appreciated in leads V1 & V2
- Ventricular Ectopics
- Complexes # 2, 3, 8, 10
- Premature Junctional Complex
- Complex #4
- Sinus rhythm
- Axis: Normal
- Intervals for Sinus Complexes:
- PR – Normal (~130ms)
- QRS – Prolonged (140ms)
- QT – 490ms (QTc Bazette ~ 500 ms) – Prolonged
- Segments:
- Discordant ST / T wave changes with ventricular ectopic complexes
- Additional:
- T wave inversion sinus complexes in leads I, II, II, aVL, V6
- Ventricular ectopics occur close to T wave especially in complexes # 2 & 10
Interpretation
- Life-threatening electrolyte abnormalities
- ECG manifestations consistent with hypomagnesaemia and hypocalcaemia
- QT Prolongation
- QRS Prolongation
- Multiple ectopic complexes
- Risk of Torsades de Pointes
What happened next ?
Biochemistry Results on admission:
- Creatinine 421 umol/L [70-150]
- Patient’s baseline creatinine ~300 umol/L
- Mg 0.17 mmol/L [0.65-1.10]
- Note K was normal
- Cor Cal 1.35 mmol/L [2.15-2.55]
- Ionised Ca 0.66 mmol/L [1.12 – 1.30]
- Phos 2.0 mmol/L [0.7-1.5]
- Alb 31 g/L [34-45]
The patient was admitted to the Critical Care Unit for cardiac monitoring and electrolyte replacement. Further biochemistry revealed an elevated Parathyroid Hormone 20.9 pmol/L [1.5 – 8.0], and mild vitamin D deficiency, consistent with secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic renal disease. With rehydration and electrolyte replacement the patient’s clinical condition improved and he was discharged.
Biochemistry on discharge showed:
- Creatinine 270 umol/L [70-150]
- Mg 0.76 mmol/L [0.65-1.10]
- Cor Cal 2.08 mmol/L [2.15-2.55]
SIMILAR CASE: Hyperkalemia and Hypocalcemia on ECG