This post is an answer to the ECG Case 226
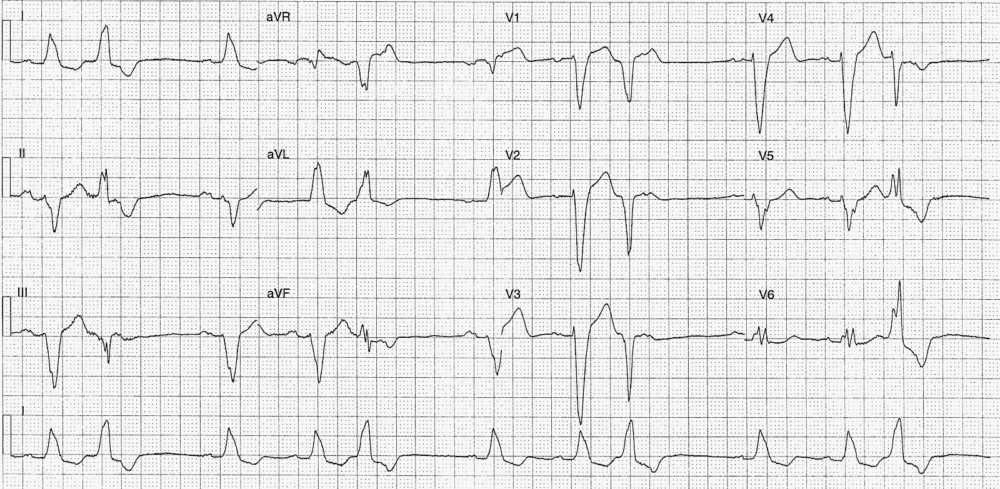
- Rate:
- Mean ventricular rate ~66 bpm
- Atrial activity rate ~68 bpm
- Rhythm:
- Regular atrial activity
- Sinus rhythm
- Regular unifocal PVC’s
- Pattern – P-QRS, P-QRS, PVC
- Full compensatory associated with PVCs
- Axis:
- Sinus complexes – LAD
- PVCs – Normal
- Intervals – Sinus Complexes:
- PR – Prolonged (~210ms)
- QRS – Prolonged (180ms)
- QT – 440ms
- Interval – PVCs:
- QRS – Prolonged (160ms)
- QT – 400ms
- Segments:
- Sinus complexes – Discordant ST segment & T wave changes
- ST Elevation leads in III, aVF, aVR, V1-4
- ST Depression in leads I, aVL, V6
- T wave inversion in leads I, II, aVL
- Sinus complexes – Discordant ST segment & T wave changes
- Additional:
- LBBB Morphology – sinus complexes
- P waves broad (120ms) and notched in lead II
- Intra-atrial block
Interpretation
- PVCs in Trigeminy
- LBBB
- 1st Degree AV Block
What happened next ?
This patient presented with severe cardiac failure and an out-of-hospital collapse. The ECG features of LBBB and 1st degree AV block were longstanding with no acute change in the LBBB morphology.
The patient had a normal potassium but was profoundly acidotic, ABG below :
- pH 6.9
- pCO2 90 [mmHg]
- PO2 96 [mmHg]
- HCO3 18 [mmol/L]
- Lactate 11 [mmol/L]
- Anion Gap 17 [mmol/L]
Previous ECHO, over 12 month prior, had shown the following:
- Dilated LV with inferolateral akinesis
- Severe LV impairment
- Severe mitral regurgitation
- Severely dilated left atrium
- Severe pulmonary hypertension
Last angiogram, over 12 month prior, showed:
- LAD – 70% proximal stenosis
- RCA – 30% proximal stenosis, 50% distal stenosis
Given associated extensive comorbidities and previous unsuitability for invasive treatment management focused on symptomatic relief and comfort measures only.
READ MORE: