This post is an answer to the ECG Case 273
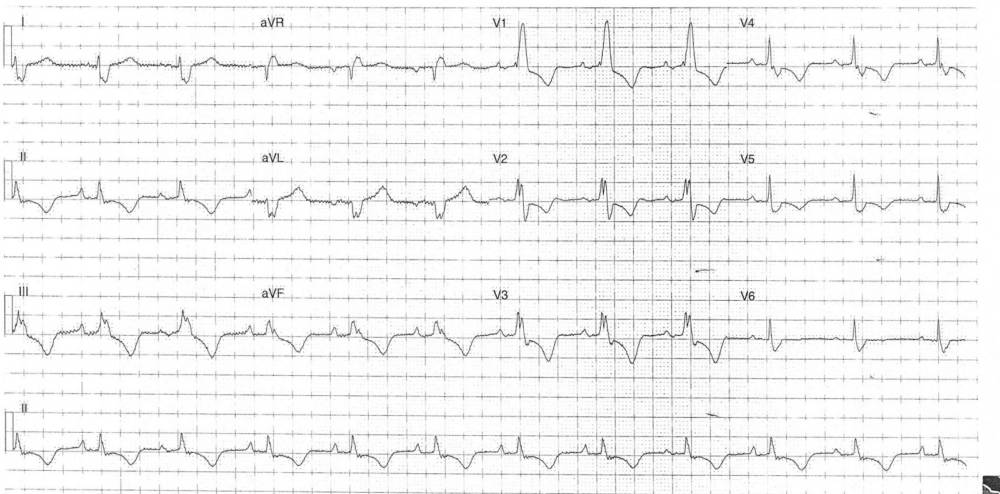
- Rate: 72 bpm
- Rhythm: Regular Sinus Rhythm
- Axis: Right axis deviation (~125 deg)
- Intervals:
- PR – Normal (~200ms)
- QRS – Prolonged (140ms)
- QT – 440ms (QTc Bazette 380-400 ms)
- Segments:
- ST Depression in leads II, III, aVF, V1-4
- Additional:
- T wave inversion in leads II, III, aVF, V1-5
- Peaked P wave in lead II
- RBBB Morphology
- R/S ratio in lead I <0.5
Interpretation
In isolation there are several broad differentials for these ECG features including:
- Acute RV strain e.g. PE
- Chronic RV strain with resultant RV hypertrophy
- Ischemia
- Raised ICP
- Myocarditis
- Cardiomyopathy
This patient had already had extensive investigation by his primary care physician and his recent ECG’s were identical to the one above. He had also had a recent ultrasound.
What did the ultrasound show ?
- Concentric LVH
- Normal LV size and systolic function
- Severely dilated right ventricle
- Moderation RV systolic impairment
- Dilated right atrium
The patient was admitted under the General Physicians for medical management of his right heart failure which was secondary to chronic pulmonary disease.
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH)
The diagnosis of RVH with RBBB is a difficult one but our ECG above has many features which suggest RVH in the setting of RBBB:
- Right axis deviation + RBBB
- R/S Ratio in lead I <0.5
Other features that suggest RVH in RBBB are:
- R’ wave height >15mm
- Right Atrial Enlargement – our ECG is suggestive but doesn’t quite met the voltage criteria
SIMILAR CASES: