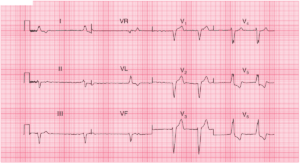
Small QRS complexes indicate that relatively little of the voltage generated by ventricular depolarization is reaching the ECG electrodes.
Diagnostic criteria
- The amplitudes of all the QRS complexes in the limb leads are < 5 mm
- The amplitudes of all the QRS complexes in the precordial leads are < 10 mm
Causes
Small QRS complexes may simply reflect a variant of normal. However, always check for:
- Incorrect ECG calibration (should be 1 mV = 10 mm).
For easy memorizing of the causes you can use the mnemonic FFAIL:
- Fluid: Pericardial effusion; Pleural effusion
- Fat: Obesity
- Air: Emphysema; Pneumothorax
- Infiltrative / Connective Tissue Disorders
- Myxoedema
- Infiltrative myocardial diseases — i.e. restrictive cardiomyopathy due to amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, haemochromatosis
- Constrictive pericarditis
- Scleroderma
- Loss of viable myocardium:
- Previous massive MI
- End-stage dilated cardiomyopathy
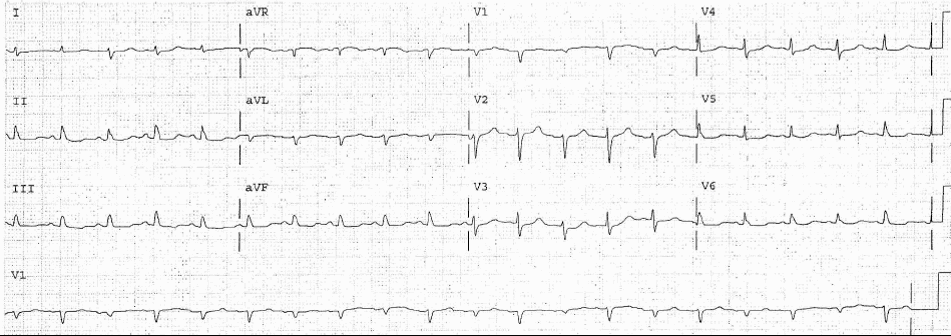
ECG Example
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Low QRS Voltage
- Alternating QRS Amplitude (Electrical Alternans)
This patient had Pericardial Effusion / Tamponade

![Read more about the article Hypokalemia ECG Changes [With Examples]](https://manualofmedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Hyperkalemia-and-Hypokalemia-ECG-Changes-2-300x127.jpg)