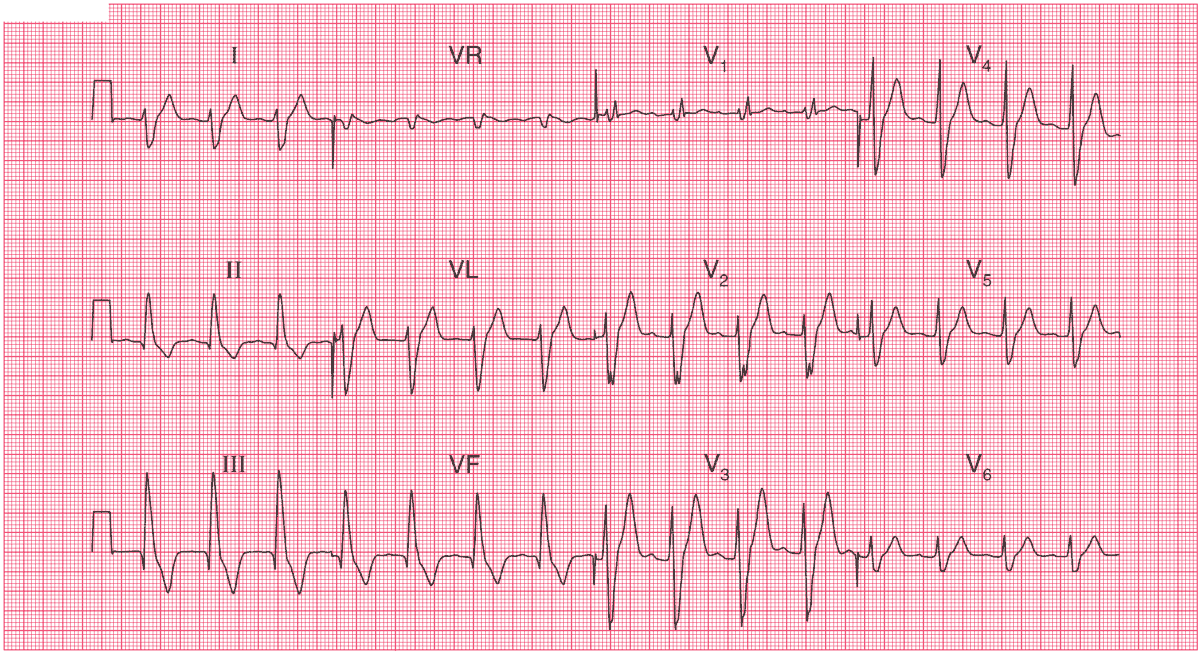
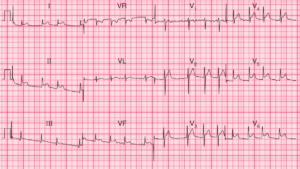
ECG Interpretation
- Sinus Tachycardia at a rate of 90/min
- Right axis deviation
- Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- Left Posterior Fascicular Block (LPFB)
- First Degree AV Block (PR interval > 200ms (five small squares))
Clinical Interpretation
The right axis deviation suggests Left Posterior Fascicular Block (LPFB), and, combined with RBBB, this suggests bifascicular block. The patient is therefore at risk of complete (third degree) block, which could cause a Stokes–Adams attack.
What to do next?
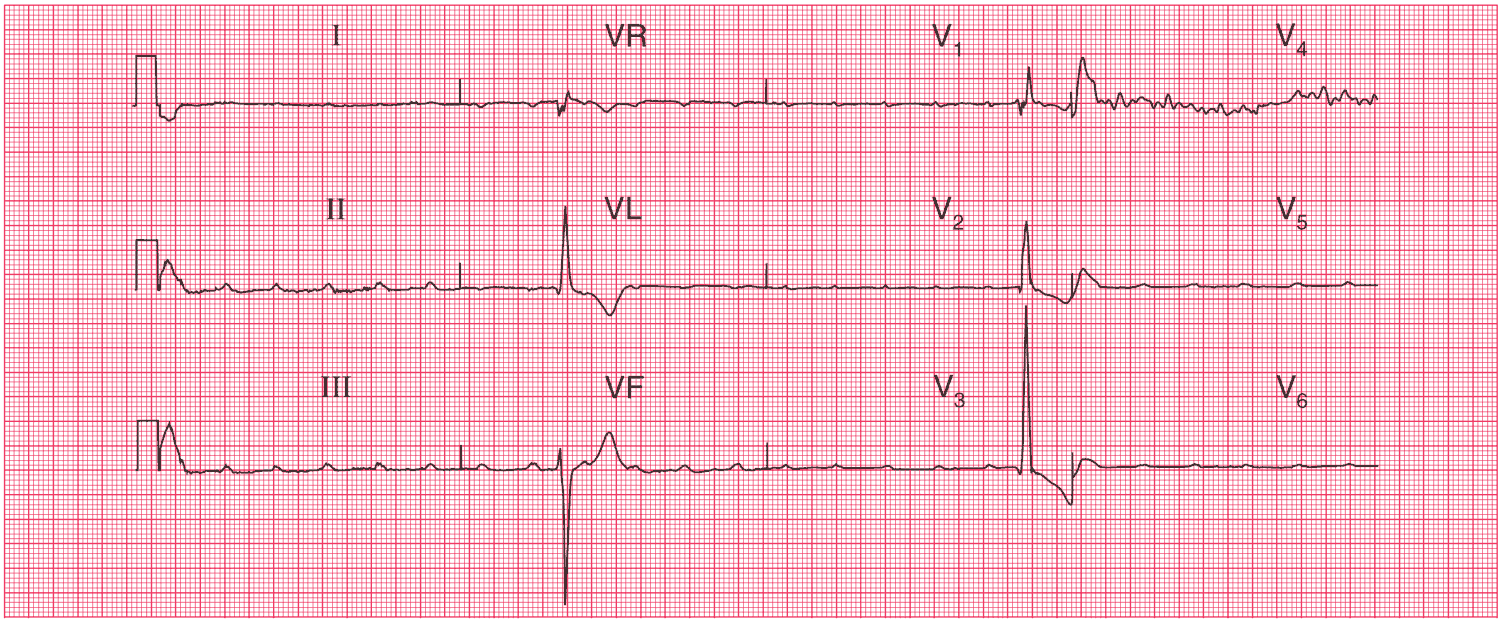
This woman was admitted to hospital and monitored, and had a severe attack of dizziness and fainting. During this attack, another ECG was recorded (see below). This ECG shows complete heart block with a ventricular rate of about 15/min. The patient was immediately given a permanent pacemaker.
READ MORE about: Conduction Blocks at the AV Node (AV Blocks)