This post is an answer to the Case – IV drug Addict with Headache and Fever
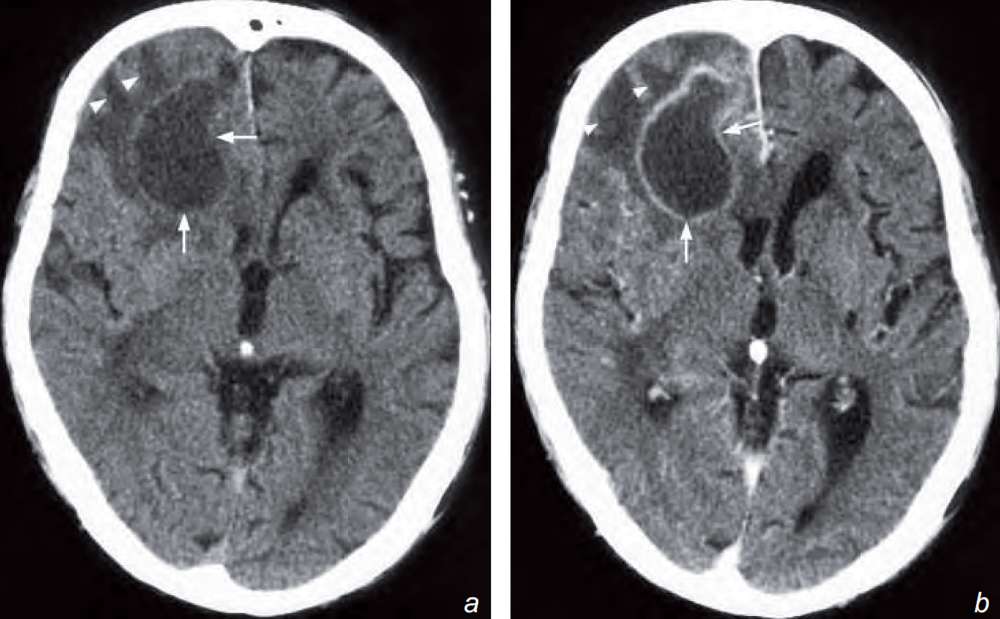
What is shown on the CT ?
- There is a large ring-enhancing lesion in the right frontal lobe.
- Perilesional white matter oedema.
- Mild mass effect on the frontal/anterior horns with slight midline shift to the left.
What is the diagnosis ?
Non-contrast (a) and contrast enhanced (b) axial CT scans show an area of low attenuation in the right frontal lobe with rim enhancement (arrows) and perifocal white matter oedema (arrowheads). Note the mass effect on the ipsilateral frontal/anterior horn. The diagnosis is a brain abscess (in view of clinical signs of symptoms).
Discussion
The common differential diagnoses for a solitary ring-enhancing lesion in the brain include:
- Brain abscess
- Neoplasm: brain metastasis, glioma
However, in view of the high fever, a history of intravenous drug abuse and raised white cell count, the most likely diagnosis in this case is a brain abscess.
Brain abscess is focal infection of the brain parenchyma and may be a result of haematogenous dissemination of infection. Associated predisposing factors include endocarditis, IV drug abuse, pulmonary infection, right-toleft cardiac shunt or pulmonary AVM.
It may also result from direct contagious spread from adjacent source of sepsis, e.g. from paranasal sinusitis and otomastoiditis or due to penetrating trauma with direct inoculation.
Imaging findings on CT:
- Initial changes are of cerebritis which appears as an ill-defi ned intra-axial lesion of decreased attenuation with variable amount of oedema and mass effect. There is typically no contrast enhancement in the early stage cerebritis
- Contrast enhancement gradually develops with eventual formation of a ring-enhancing lesion which typically shows:
- Thin, smooth enhancing rim
- Eccentric wall thickness which is thicker on the outer grey matter side presumably due to better blood supply and thinner on the inner white matter side – this gives rise to the potential complication of abscess rupture into the ventricles causing ventriculitis
- Formation of adjacent daughter abscesses
- Evaluate if there is any evidence of associated meningitis such as intense meningeal enhancement following injection of contrast and hydrocephalus
- Perilesional oedema and contrast enhancement of brain abscess may be suppressed by steroid therapy.