ECG Interpretation
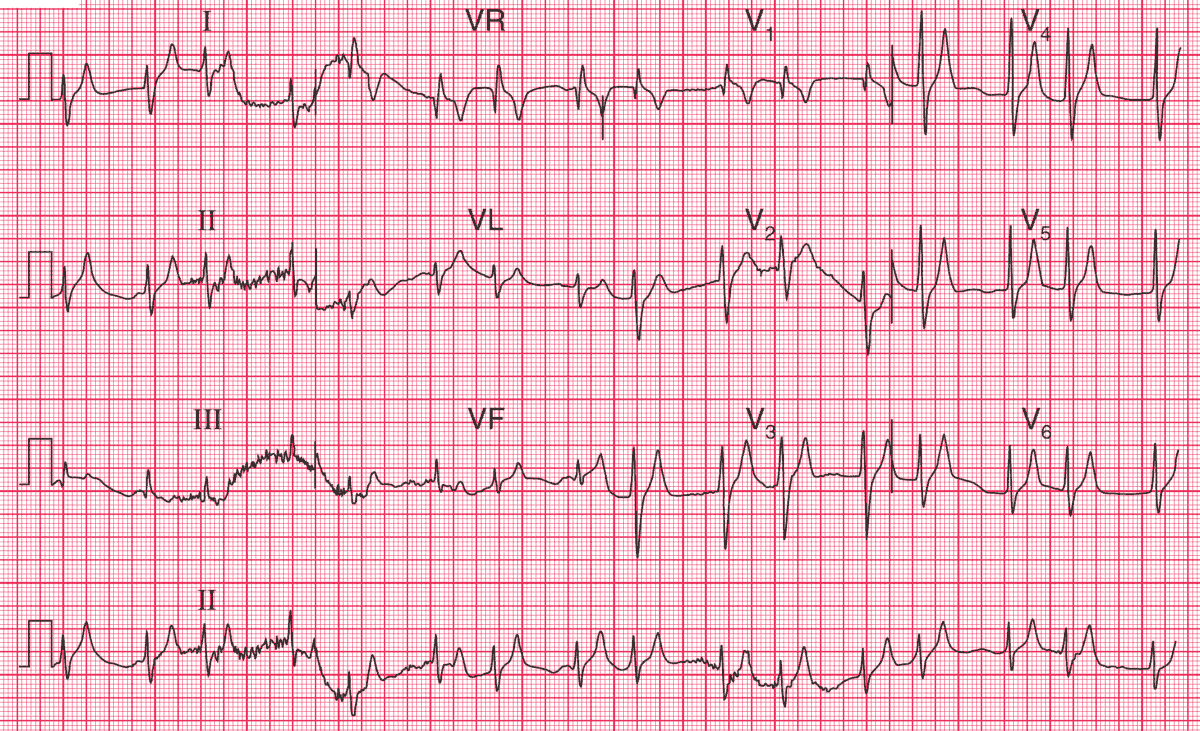
This is not a technically good record, and exhibits considerable artefacts. However, the ECG shows:
- The rhythm is probably sinus, with coupled junctional extrasystoles
- P waves difficult to identify, but there are probably flattened P waves before the first of each pair of QRS complexes, best seen in lead aVR
- Probably normal PR interval
- Normal axis
- Narrow QRS complexes, so this is a supraventricular rhythm
- QRS complexes apparently in pairs, which are identical
- QRS complex duration at the upper limit of normal (120 ms)
- ST segment not easy to identify
- T waves sharply peaked in all leads
Clinical Interpretation
These changes are characteristic of hyperkalaemia, which of course is likely to be present in diabetic ketoacidosis.
READ MORE about Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm
What to do ?
This ECG should alert you to check the serum potassium level immediately: in this patient it was found to be 7.1 mmol/l. It settled rapidly with treatment of the diabetes.
- READ MORE: ECG Interpretation – All you need to know
- Similar Cases: Hyperkalemia and Hypocalcemia on ECG