This post is an answer to the Case – Optic Neuritis and Episodes of Sensory and Motor Symptoms
What does the MRI show?
Ovoid high signal periventricular lesions perpendicular to the ventricular wall involving the corpus callosum.
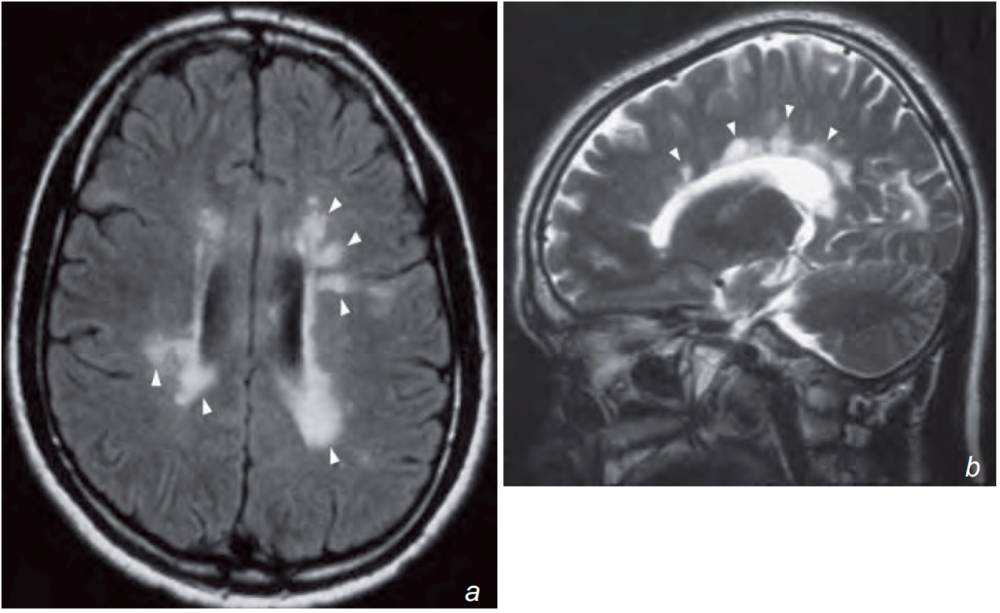
(b) sagittal T2-weighted images of the brain shows multiple ovoid periventricular demyelination plaques of high signal (arrowheads) aligned almost perpendicular to the ventricular wall in a patient with multiple sclerosis (MS).
What is the most likely diagnosis?
In view of the patient’s history (optic neuritis and multiple episodes of remitting and relapsing sensory and motor symptoms) and high signal periventricular lesions on MR, the most likely diagnosis is multiple sclerosis.
The lesions in the corpus callosum represent areas of demyelination and similar lesions/plaques may also be found in the optic nerves and the spinal cord.
Discussion
Multiple sclerosis is autoimmune demyelinating disease with a typical history of multiple focal neurological deficits with a remitting and relapsing course. Symptoms depend on anatomical location of lesions but visual loss, gait and sensory disturbances are common.
MRI is the imaging investigation of choice for multiple sclerosis:
- Plaques are usually multiple and may be found anywhere in the CNS
- On T1W scans inactive plaques show low signal intensity and do not enhance following the injection of gadolinium. The enhancement in active plaques is variable and may be homogeneous, heterogeneous or ring-like
- Plaques show high signal on FLAIR and T2W images and typically appear as oblong, elliptical lesions at the callososeptal interface and subependymal periventricular white matter extending into the deep white matter (Dawson’s fingers).
Ischaemic/inflammatory change and other causes of demyelination also appear as focal or multiple areas of high signal on FLAIR and T2W scans, in the periventricular region. The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis therefore depends on a combination of clinical, laboratory and imaging findings.
Although MR can demonstrate plaques in multiple sclerosis the diagnosis depends on a combination of clinical, laboratory and imaging findings. MR is also used for monitoring treatment response.