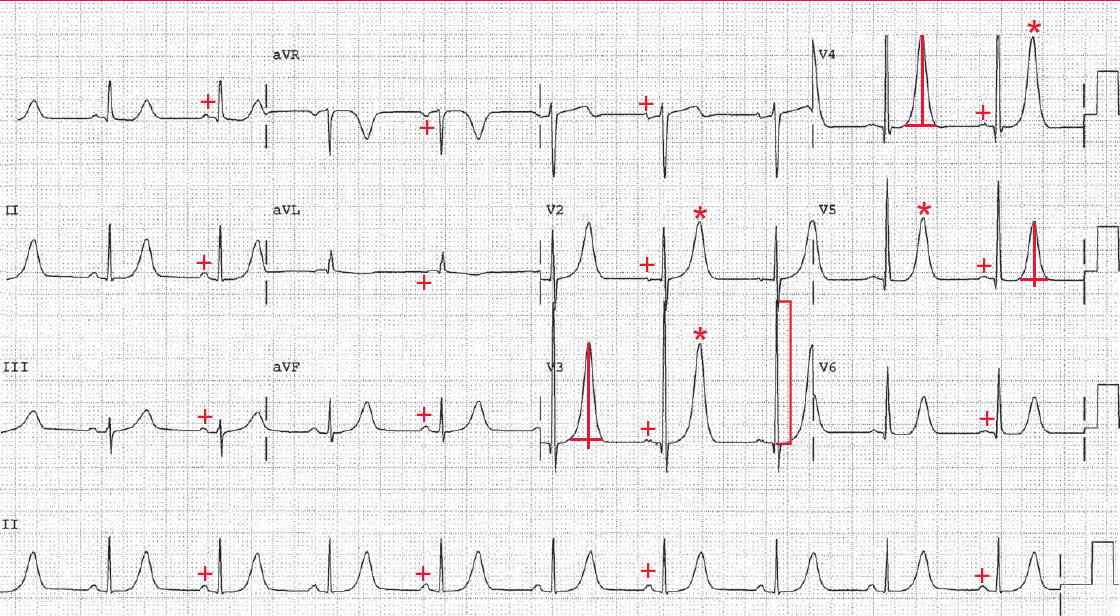
There is a regular rhythm at a rate of 56 bpm. There is P wave (+) before each QRS complex and the PR interval is stable (0.16 sec). The P wave is positive in leads I, II, aVF, and V4–V6. Hence this is a sinus bradycardia.
The QRS complex duration is normal (0.08 sec). The R wave amplitude in lead V3 is 33 mm or boxes ( ] ), meeting one of the criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy (ie, ≥ 25 mm in any precordial lead).
The T waves are tall, peak and symmetric (*), especially prominent in leads V3–V5. The T wave morphology is seen with hyperkalemia. The normal T wave is asymmetric, regardless of amplitude. The upstroke of the T wave is slower, while the downstroke of the T wave is faster.
T waves that are tall, peaked, and symmetric (upstroke and downstroke equal) are seen with hyperkalemia and with acute MI, but in the case of acute MI the T waves (hyperacute T waves) are wider.
- READ MORE: ECG Interpretation – All you need to know
- SIMILAR CASES: