This post is an answer to the ECG Case 215
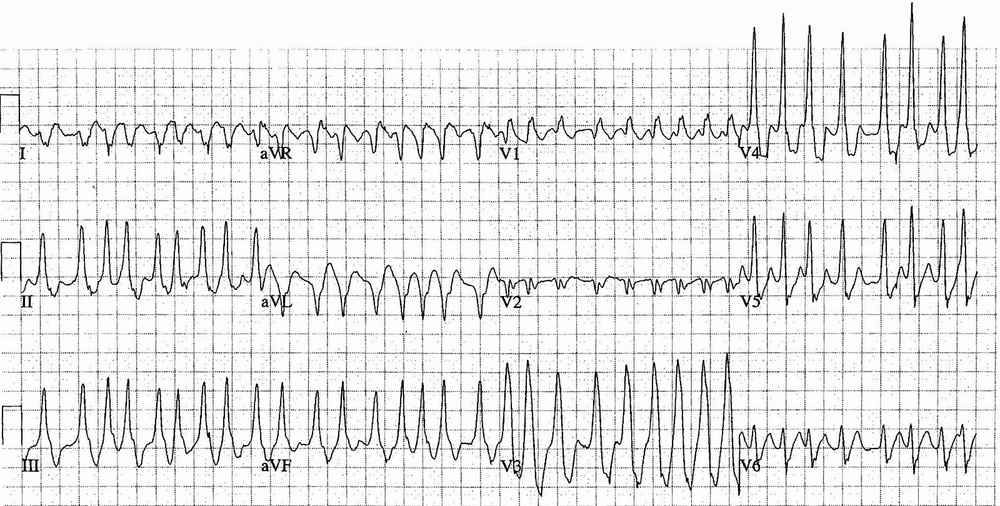
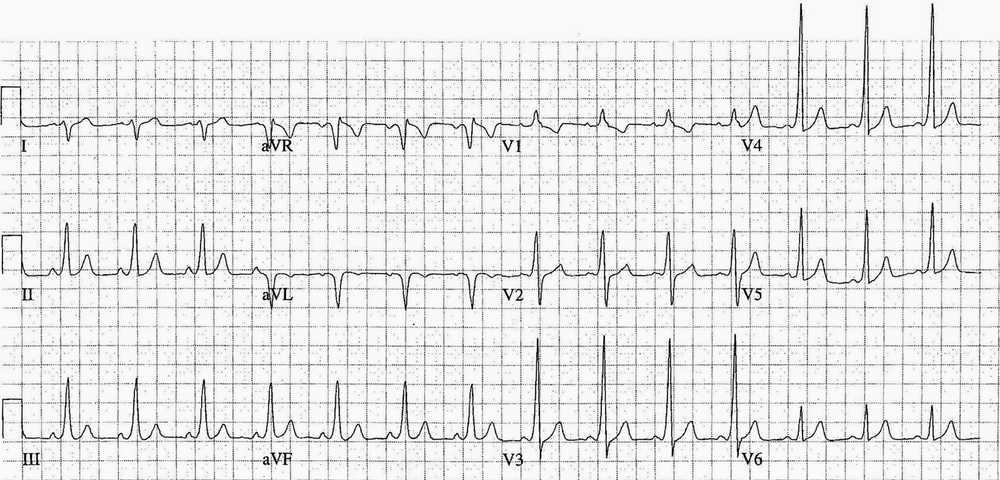
- Rate:
- Mean ventricular rate ~205 bpm
- Variable rate between 140 – 300 bpm
- The very high rates are due to conduction via an accessory pathway with a short effective refractory period
- Rhythm: Irregular
- Axis: Right axis deviation (105 deg)
- Intervals: QRS – Prolonged (160ms)
- Additional: Variable QRS Morphology
Interpretation
Pre-excited Atrial Fibrillation (AF) a.k.a AF with Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW)
Why is recognizing this rhythm important ?
The reason for this is reasonably simple, this is a clinical situation in which significant harm to the patient can occur if the ECG features are not recognized and acted on appropriately.
The concern with pre-excited AF is the ability for the accessory pathway to conduct at much higher rates than the AV node with the potential for degeneration into ventricular fibrillation. It is for this reason that any drugs which block the AV node are ABSOLUTELY CONTRAINDICATED in this scenario including adenosine, calcium-channel blockers, beta-blockers and digoxin.
If the AV node is blocked then there is increased conduction via the accessory pathway which may precipitate ventricular fibrillation. Put simply if you give the patient AV nodal blocking drugs you might kill them.
The safest and easiest method to restore sinus rhythm is synchronized cardioversion. Chemical cardioversion is a possible alternative in stable patients with iv procainamide being the commonly used agent.
What happened next this case ?
The patient underwent synchronised DC cardioversion under sedation and the post cardioversion ECG is below.
READ MORE: Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome
SIMILAR CASES: