ECG Interpretation
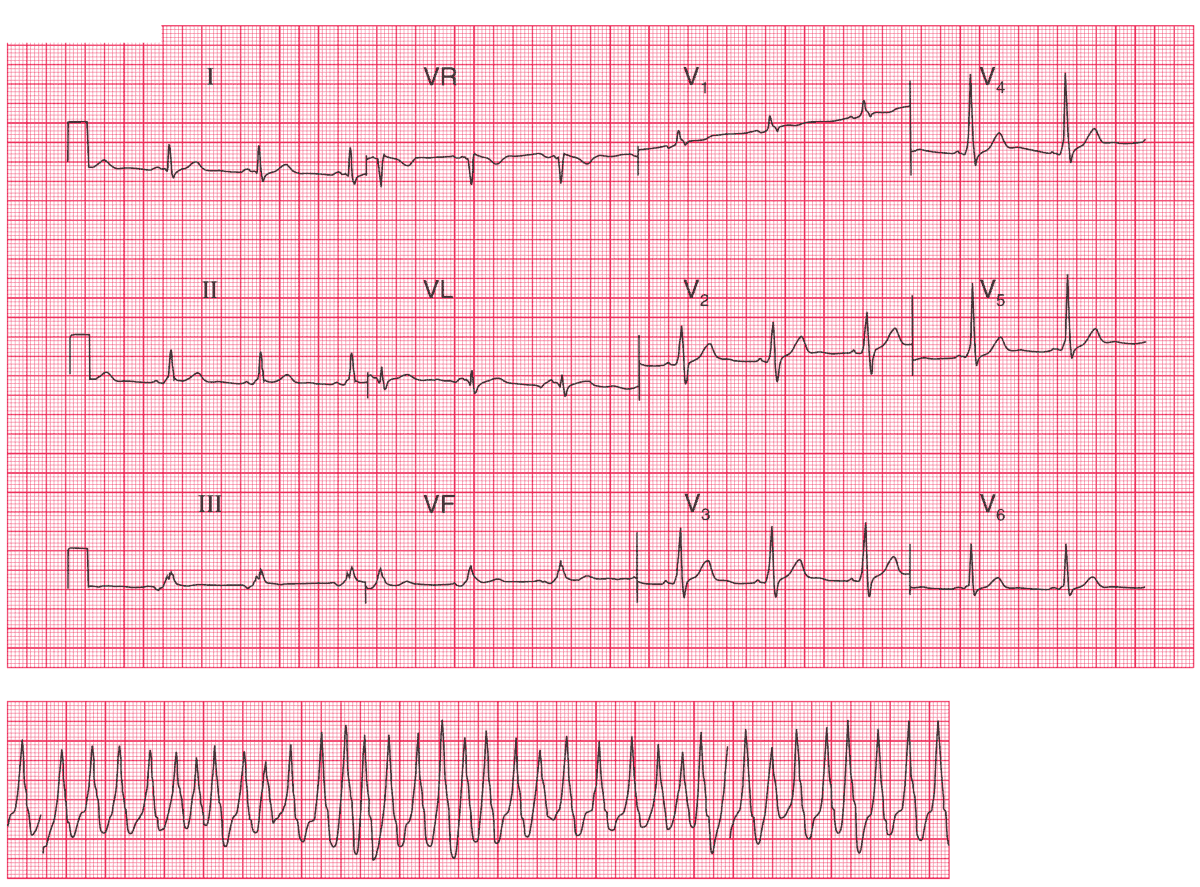
The upper ECG shows:
- Sinus rhythm, rate 64/min
- Short PR interval, best seen in leads V4–V5
- Normal axis
- Dominant R waves in lead V1
- Slurred upstroke (delta wave) in the QRS complexes
The lower ECG (rhythm strip) shows:
- A broad complex tachycardia
- Rate about 230/min
- The rhythm is irregular
- There is a slurred upstroke in some of the beats, suggesting pre-excitation
Clinical Interpretation
This is the Wolff–Parkinson–White (WPW) syndrome, involving a short PR interval and a widened QRS complex. This pattern, with a dominant R wave in lead V1 and where there is a left-sided accessory pathway, is called ‘type A’. It can easily be mistaken for right ventricular hypertrophy.
The patient’s palpitations are due to atrial fibrillation; an irregular broad complex tachycardia is characteristic of atrial fibrillation in the WPW syndrome.
What to do ?
Atrial fibrillation in association with the WPW syndrome is extremely dangerous. The patient needs an immediate electrophysiological study with a view to ablation of the accessory pathway.
- READ MORE:
- Similar Cases:
- ECG Case 80: Atrial Fibrillation and WPW Syndrome
- ECG Case 71: Atrial fibrillation with RVR, LAFB and Acute Anterolateral STEMI
- ECG Case 66: Atrial Fibrillation with an Uncontrolled Ventricular Rate
- ECG Case 59: Atrial Fibrillation with Rapid Ventricular Response (RVR) and Diffuse Subendocardial Ischemia