This post is an answer to the ECG Case 251
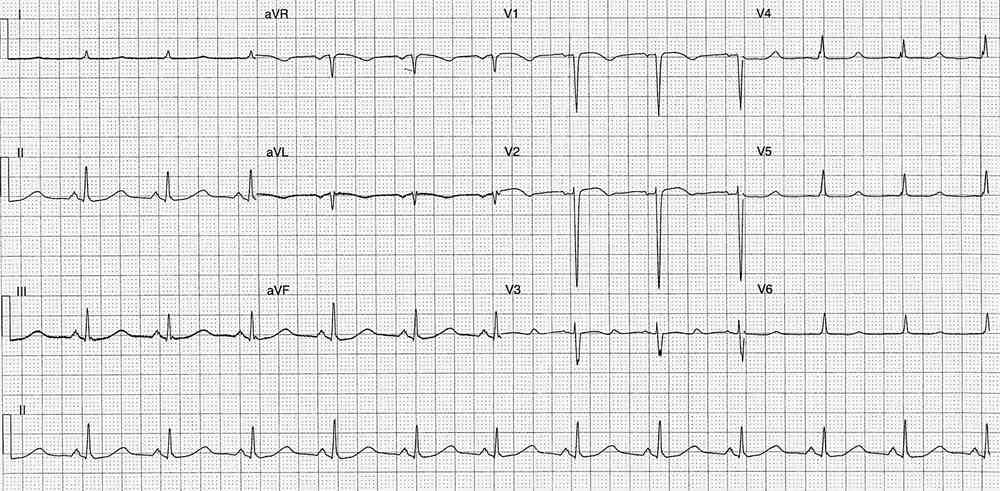
- Rate: ~115 bpm
- Rhythm: Regular Sinus rhythm
- Axis: Marked LAD / Extreme axis
- Intervals:
- PR – Normal (~180ms)
- QRS – Prolonged (120-130ms)
- QT – 360ms
- QTc – 500 ms (Bazette’s)
- Segments:
- ST Elevation in leads V1-3
- ST Depression in lead V6
- Additional:
- Terminal R wave in lead aVR > 3mm and R/S ratio > 0.7
- Prominent T waves in leads V1-4
Interpretation
- Broad Complex Tachycardia
- QTc Prolongation
- Terminal R wave aVR
In the setting of suspected or known overdose there are several agents that could cause this ECG picture. As a single agent the most likely culprit is a sodium channel blocking agent given the QRS prolongation and findings in lead aVR.
Many of the sodium channel blocking drugs can also cause QT prolongation, although multiple non-sodium channel blocking drugs can also cause QT prolongation.
The prominent T waves could be secondary to drug effects, acid-based disturbance but I’d also want an urgent potassium on this patient.
What happened next ?
We’ve got a patient after a suspect overdose of unknown agents, ECG features consistent with sodium channel toxicity +/- other ingestants and the patient has a significantly reduced conscious level.
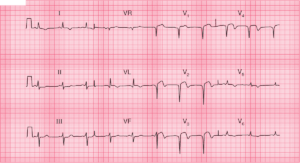
The patient received sodium bicarbonate bolus and was promptly intubated. Post intubation they were hyperventilated to a pH of 7.5 and given nasogastric charcoal. The following ECG is below.
- Minor ST elevation in leads V1 & V2
- Significantly reduced ST elevation and QRS voltage when compared with 1st ECG
- Resolution of terminal R wave in lead aVR
- Resolution of features of sodium channel toxicity
- QRS Narrowed
- Terminal R wave resolved
- Persistent QT Prolongation
The persistent QT prolongation in this case may be multi-factorial and could be caused by one or a combination of:
- Hyperventilation / Respiratory Alkalosis
- Drug toxicity either additional agents to sodium channel blocker or from single agent
READ MORE: Know When to Administer Sodium Bicarbonate in the Critically ill Poisoned Patient