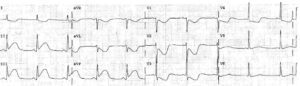
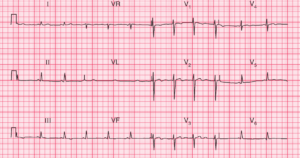
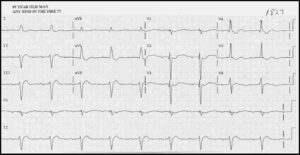
ECG Interpretation
- Atrial flutter with 2:1 block (best seen in leads II, III, VF);
- P waves at a rate of 300/min;
- QRS at a rate of 150/min;
- Normal axis;
- Normal QRS complexes;
- The T waves are difficult to identify because of the flutter waves;
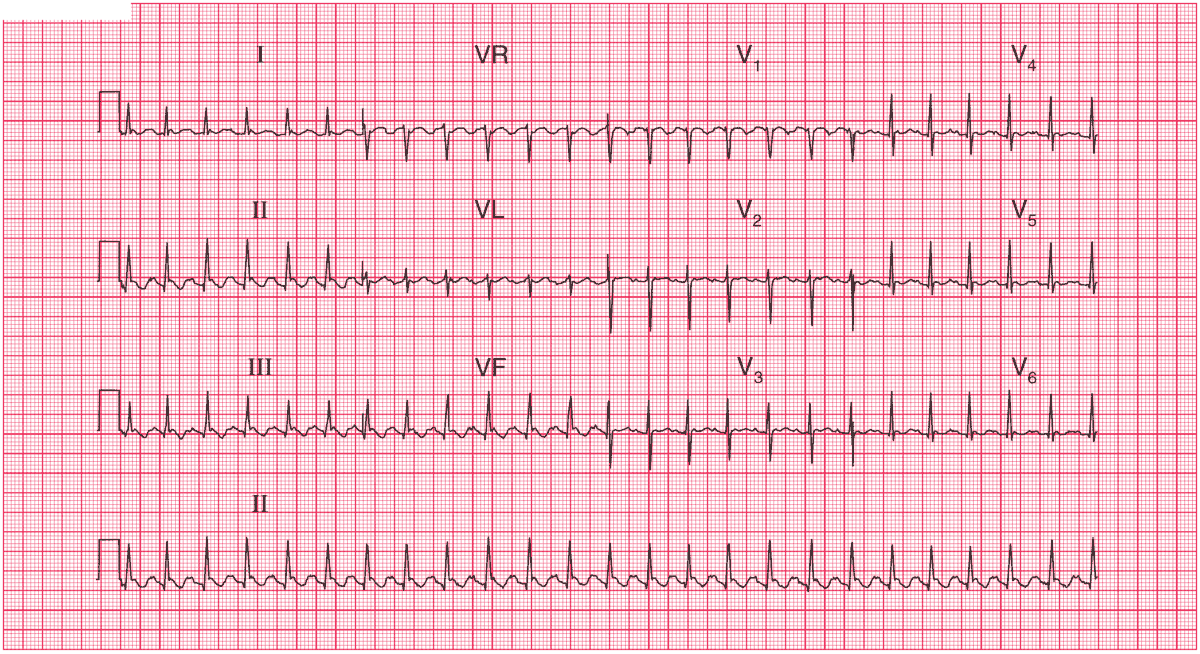
Clinical interpretation
The sudden onset of atrial flutter presumably explains the heart failure. There is nothing on the ECG to suggest a cause for the arrhythmia.
What to do ?
When an arrhythmia causes severe heart failure, immediate treatment is more important than establishing the underlying diagnosis.
Carotid sinus pressure and adenosine may increase the degree of block, but are unlikely to convert the heart to sinus rhythm. It is worth trying intravenous flecainide, but a patient with severely compromised circulation is best promptly treated with DC cardioversion.
In the long term, ablation therapy to prevent further episodes of atrial flutter may be needed.
- READ ALSO:
- MORE Similar ECG Cases