This post is an answer to the ECG Case 264
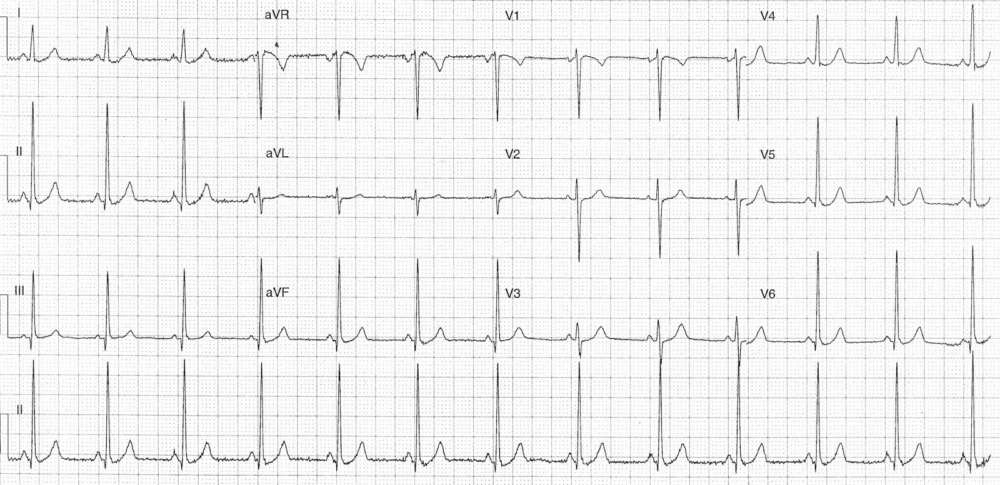
- Rate: 78 bpm
- Rhythm: Regular
- Axis: Normal
- Intervals:
- PR – Short (~200ms)
- QRS – Normal (80ms)
- QT – 320ms (QTc Bazette 365ms)
- Segments:
- Subtle ST depression leads I, V4-6
- Additional:
- Voltage criteria LVH: S wave V1 + R wave V6 =~38mm
Interpretation
- Short PR Interval
- Could this be Lown-Ganong-Levine ?
- Voltage criteria for LVH
What happened ?
The patient was admitted for investigation under joint care of cardiologists and obstetricians. Investigation for PE was normal.
Echo showed:
- Normal left ventricular size with normal wall thickness and normal systolic function.
- Possible mild dilatation of the right ventricle
- May be physiological due to stage of pregnancy.
- Normal right ventricular systolic function.
- Normal atrial size
- No significant valvular abnormality
In-patient telemetry revealed no arrhythmia despite the patient complaining of palpitations. The patient was discharge with on-going obstetric follow-up.
Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL)
LGL is often grouped with WPW as part of the pre-excitation syndromes the major ECG difference is that LGL has only pr shortening without the QRS changes associated with WPW.
The advent of EP studies has resulted in a greater understanding of cardiac conduction and it’s role in arrhythmogenesis with the existence of LGL as a clinical entity disputed. It is likely the short PR reflects an extreme of the normal variation and may not play any role in arrhythmogenesis.
READ ALSO: Pearls in Syncope ECG Interpretation
SIMILAR CASE: ECG Case 101: Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL) syndrome