ECG Interpretation
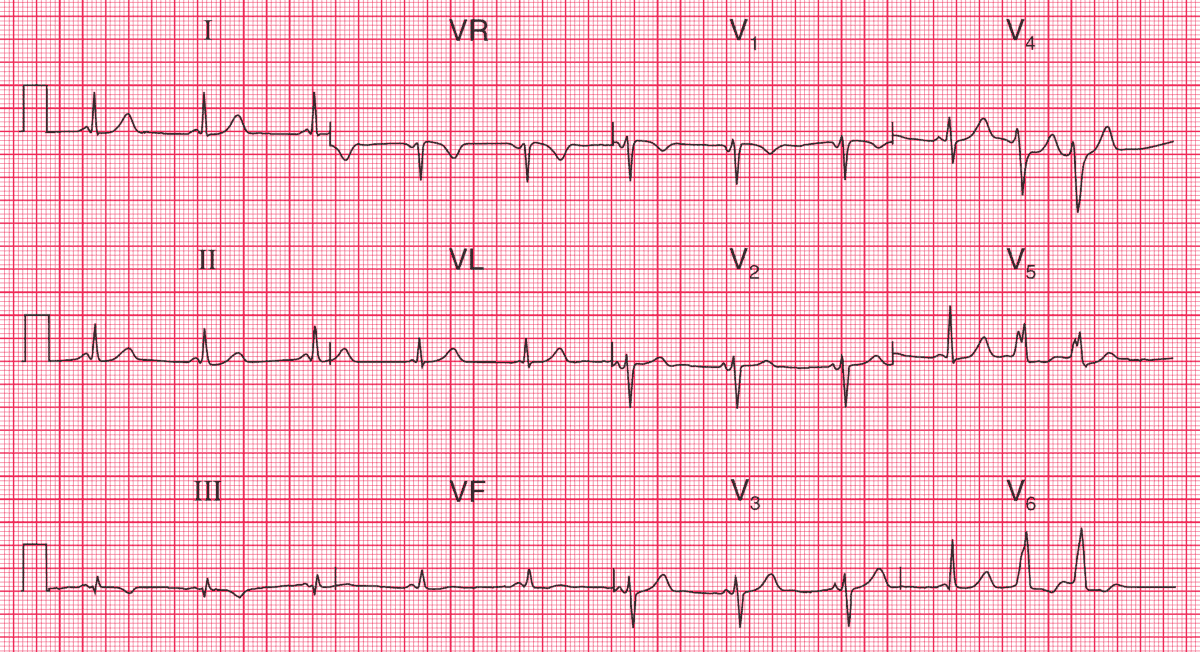
- Sinus rhythm, rate 64/min, with ventricular extrasystoles
- Very short PR interval
- Normal axis
- Normal QRS complexes and T waves, apart from a small Q wave and an inverted T wave in lead III
Clinical Interpretation
This is the Lown–Ganong–Levine (LGL) syndrome. Unlike the Wolff–Parkinson– White (WPW) syndrome, in which there is an accessory pathway separate from the atrioventricular node and His bundle, in the LGL syndrome there is a bypass close to the atrioventricular node, connecting the left atrium and the His bundle.
In the WPW syndrome the QRS complex shows an early delta wave, but in the LGL syndrome the QRS complex is normal.
What to do ?
Ambulatory ECG recording may confirm the diagnosis if attacks are frequent enough. Infrequent and short-lived attacks such as this patient describes are not dangerous, but she should be taught vagal-stimulating procedures such as Valsalva’s manoeuvre and carotid sinus pressure.
An electrophysiological study and ablation of the abnormal tract may be necessary. The ventricular extrasystoles are not important, but she should be advised not to smoke, and to avoid alcohol and caffeine.
READ MORE: ECG Interpretation – All you need to know