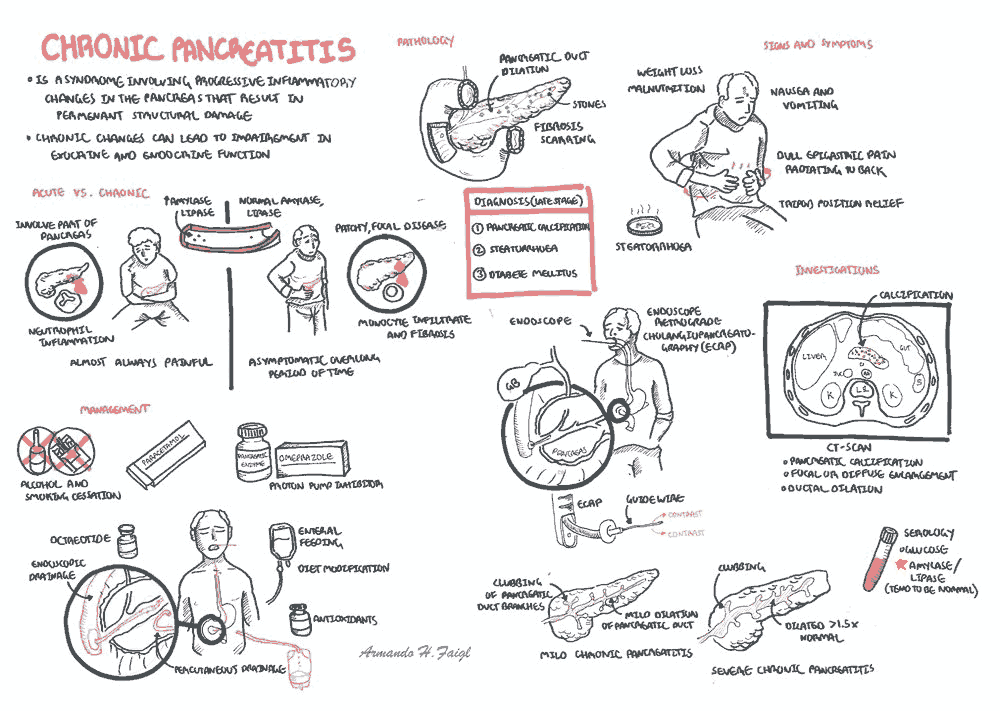
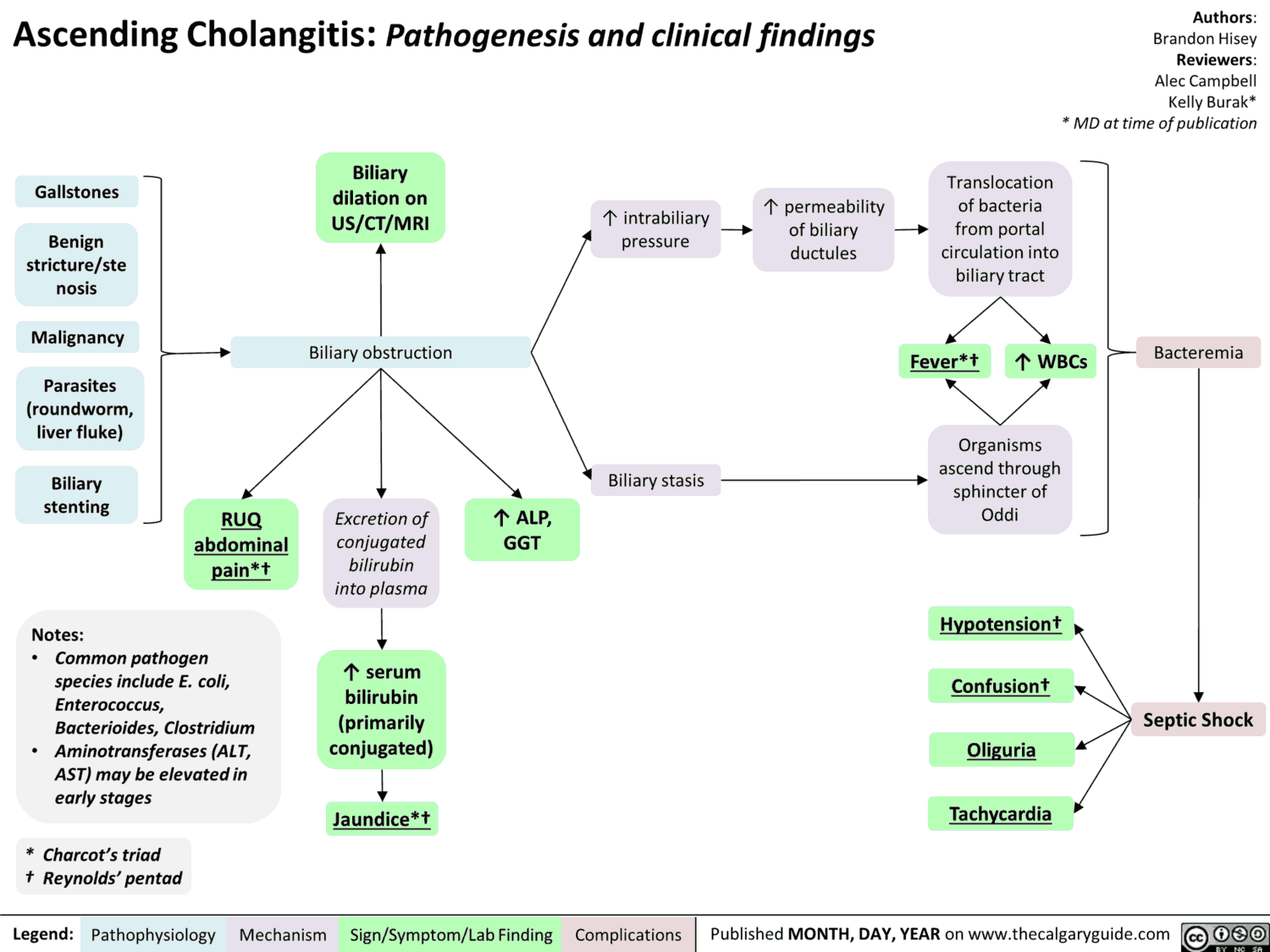
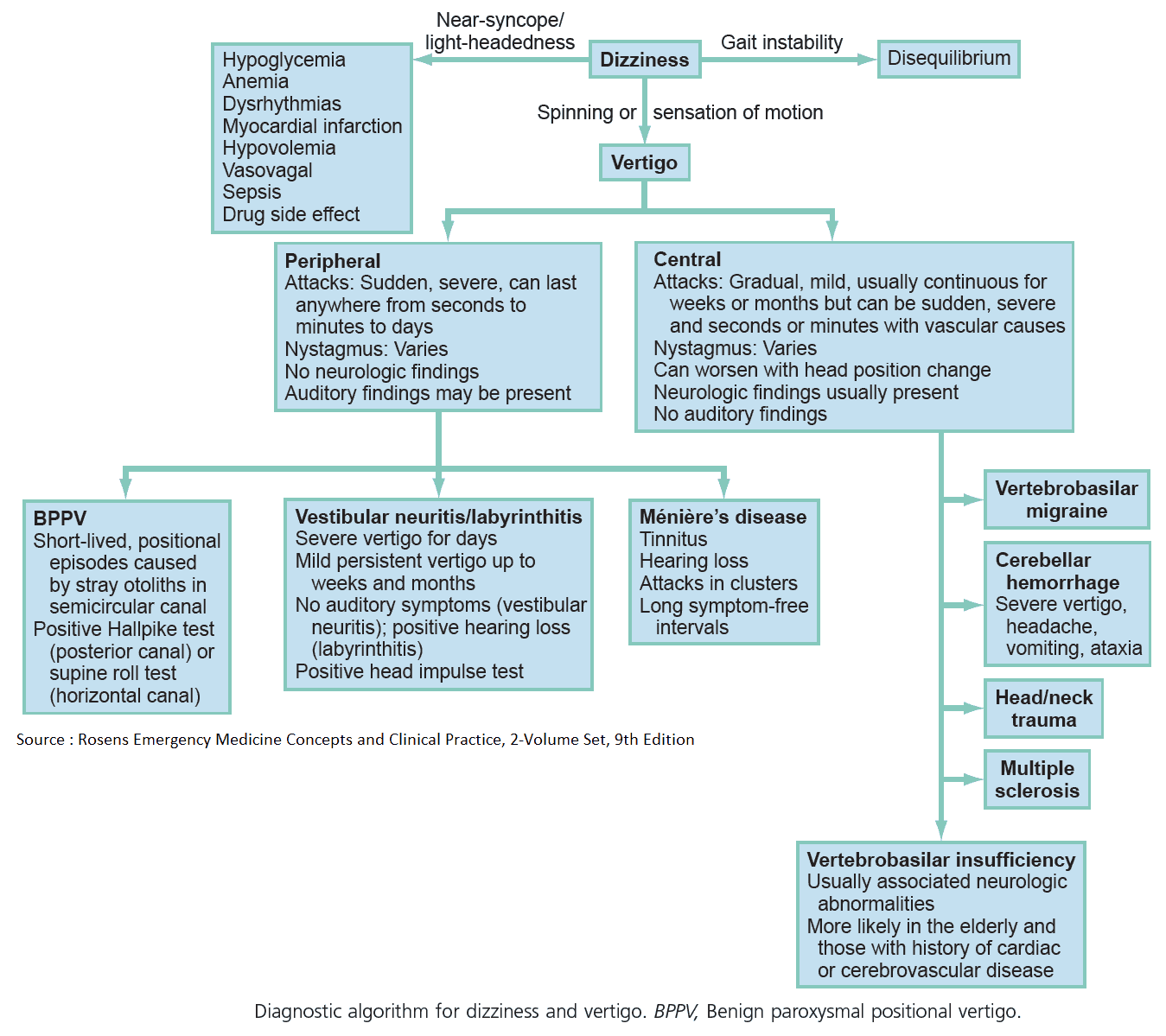
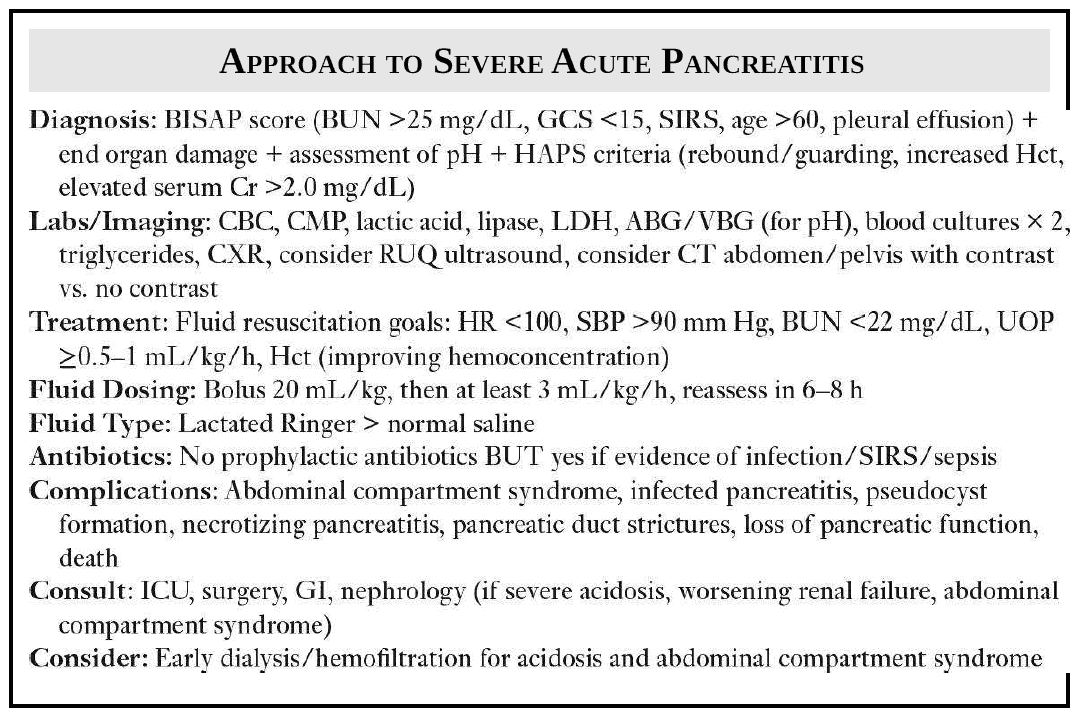
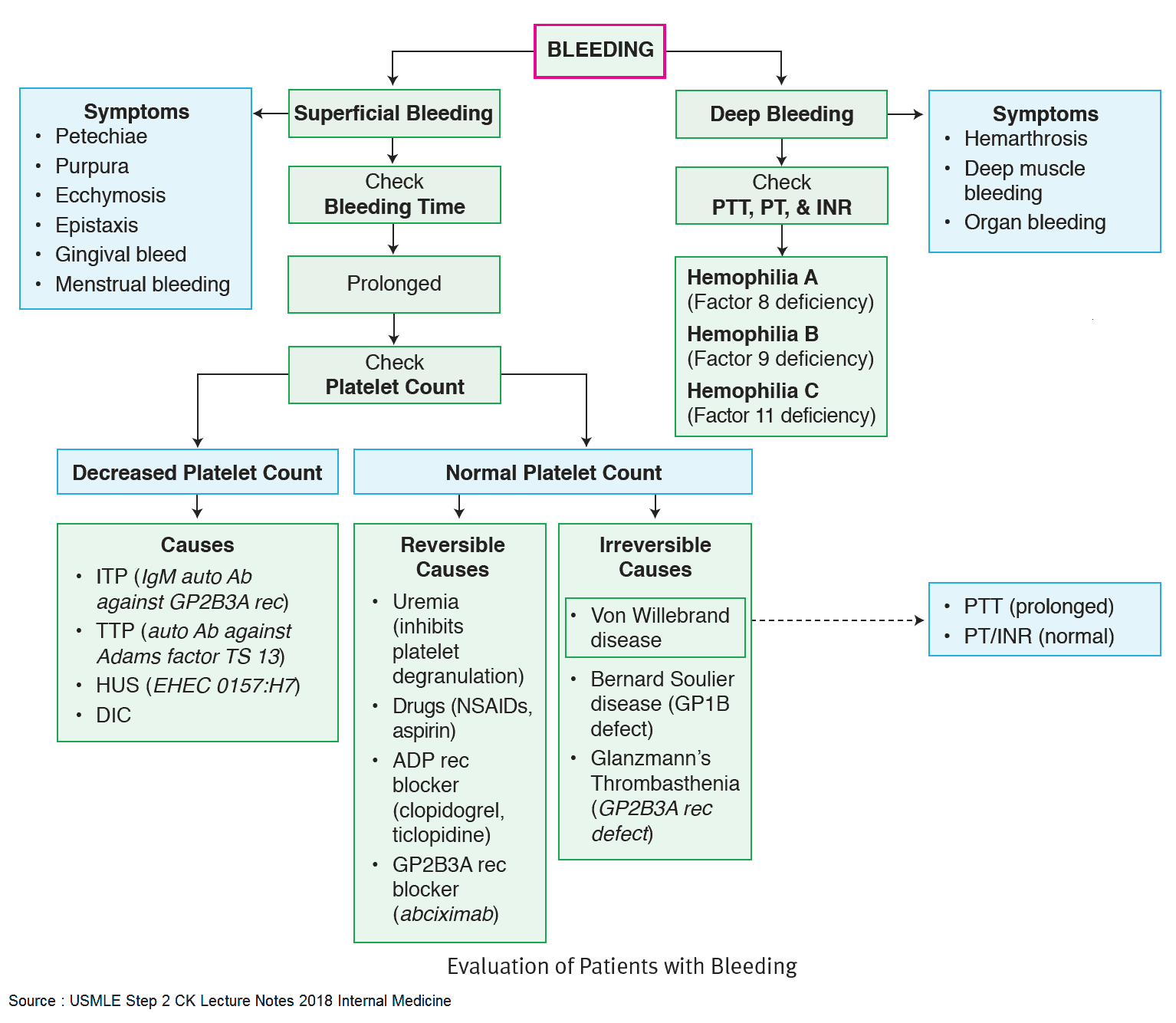
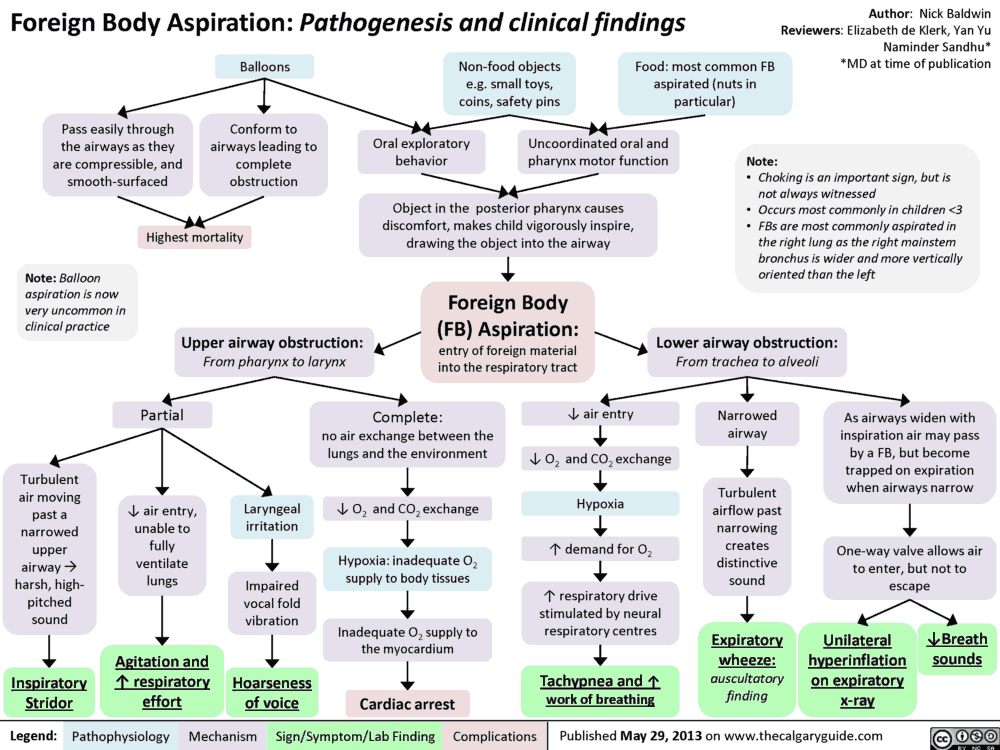
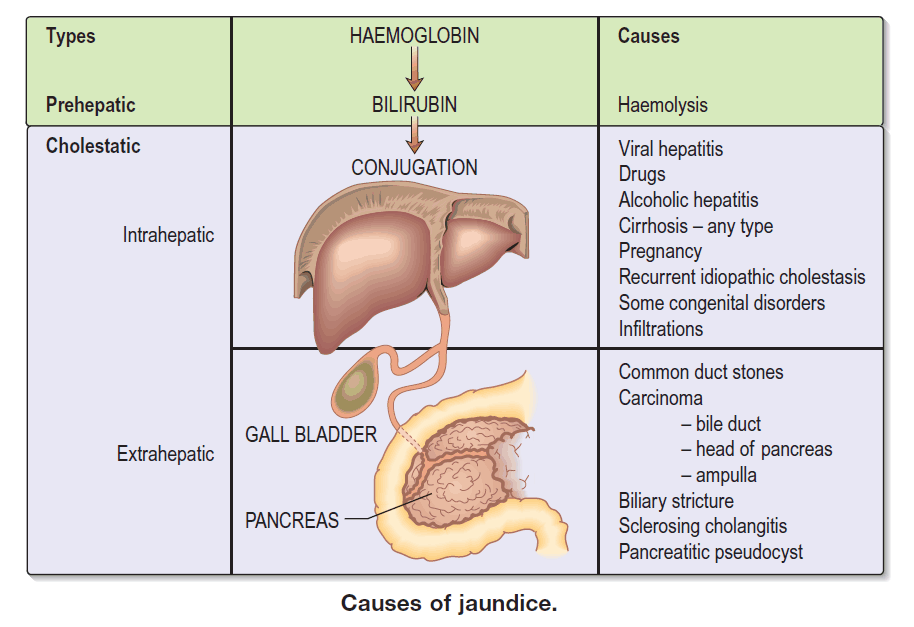
The Pain in Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis occurs when there is irreversible and progressive destruction of the pancreas. While the etiology of the pain in chronic pancreatitis is not well understood, it is most likely due to: chronic inflammation, altered nociception and tissue ischemia