Table of Contents
Hyponatremia
Definition
- Excess free water relative to Na (serum Na < 135 mEq/L)
Symptoms
- Neurologic spectrum secondary to water shift in cells:
- Fatigue, lethargy, AMS (altered mental status) (usually starting <120 mEq/L), seizure, coma
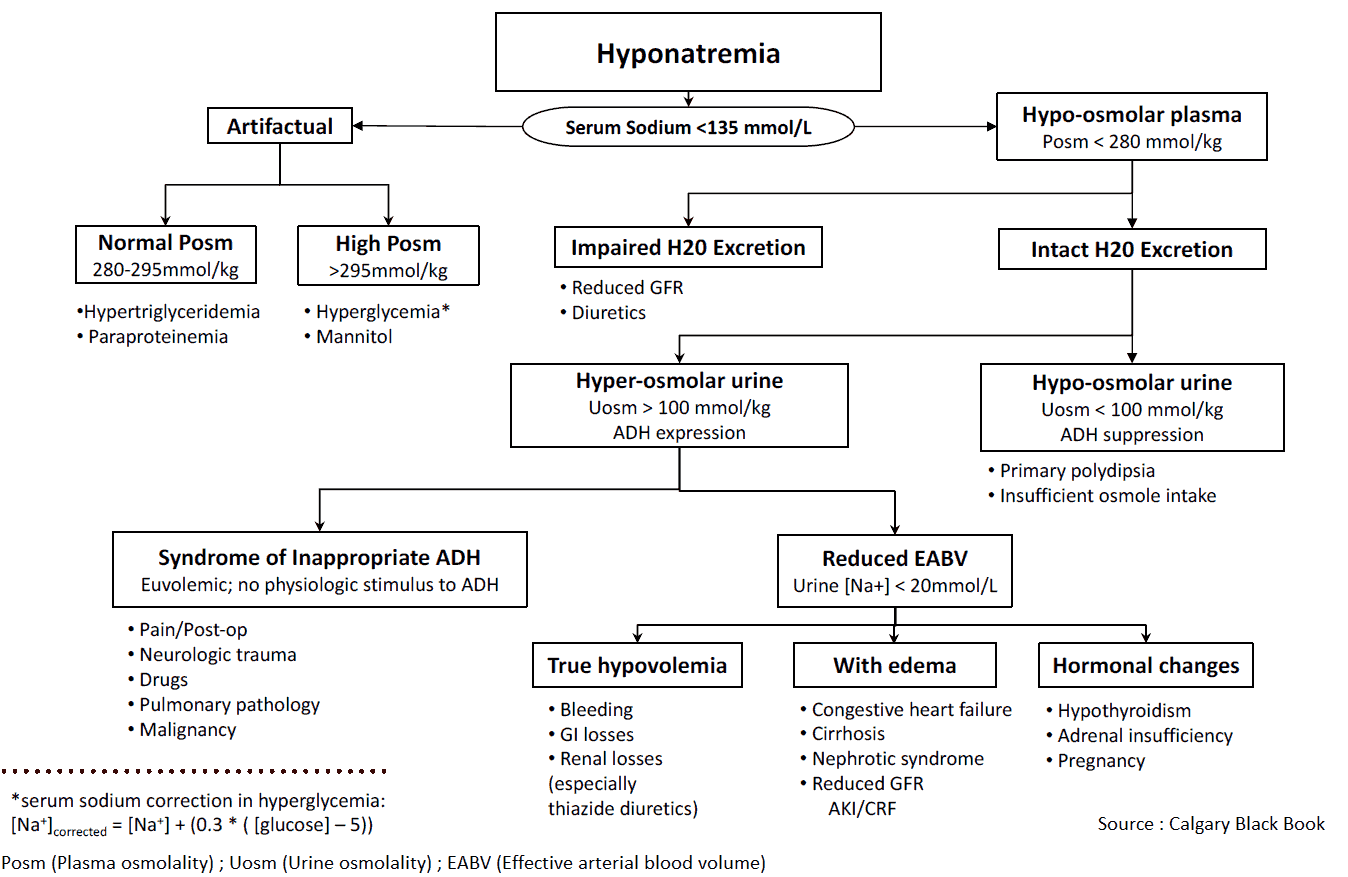
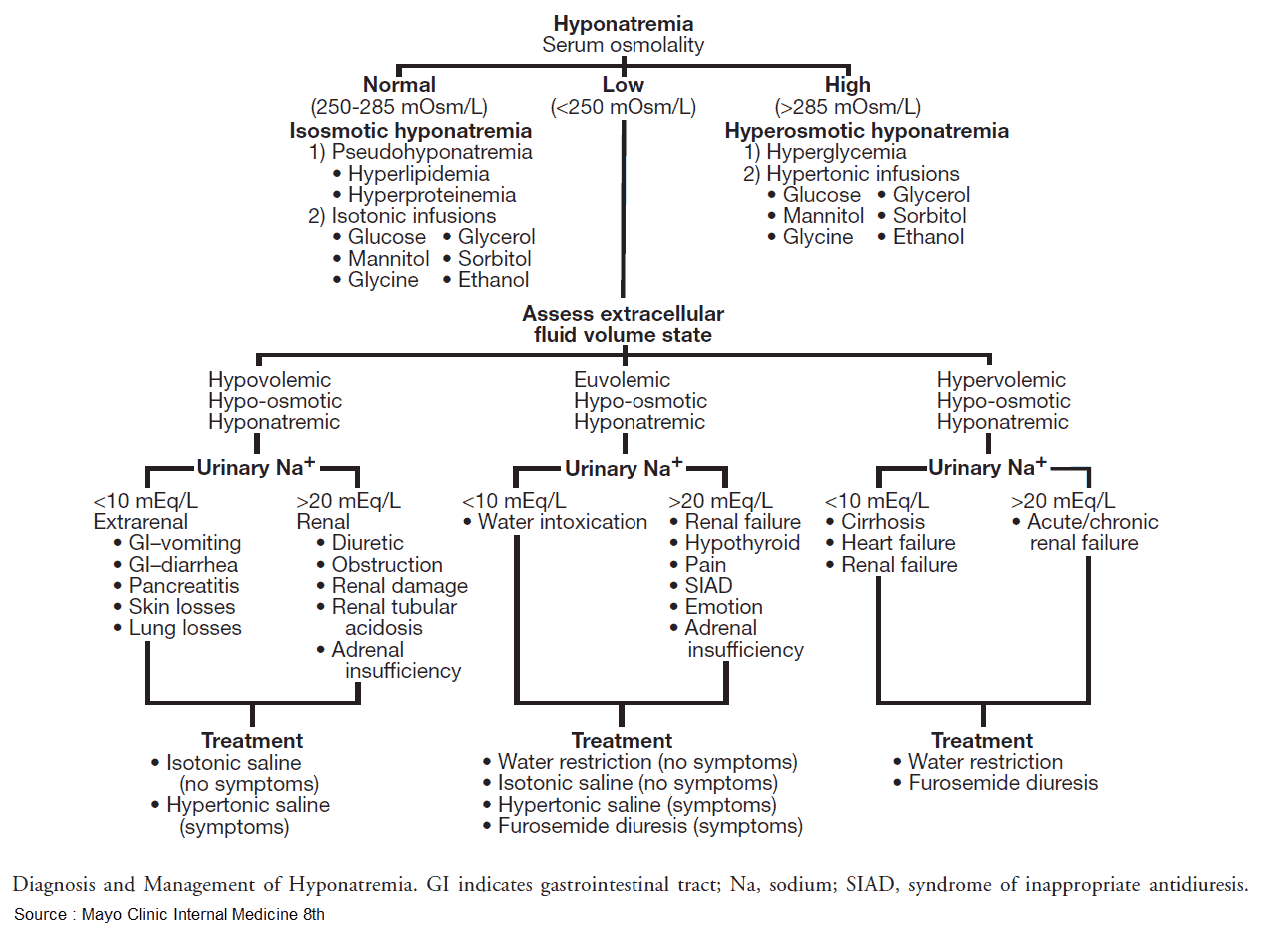
Diagnosis
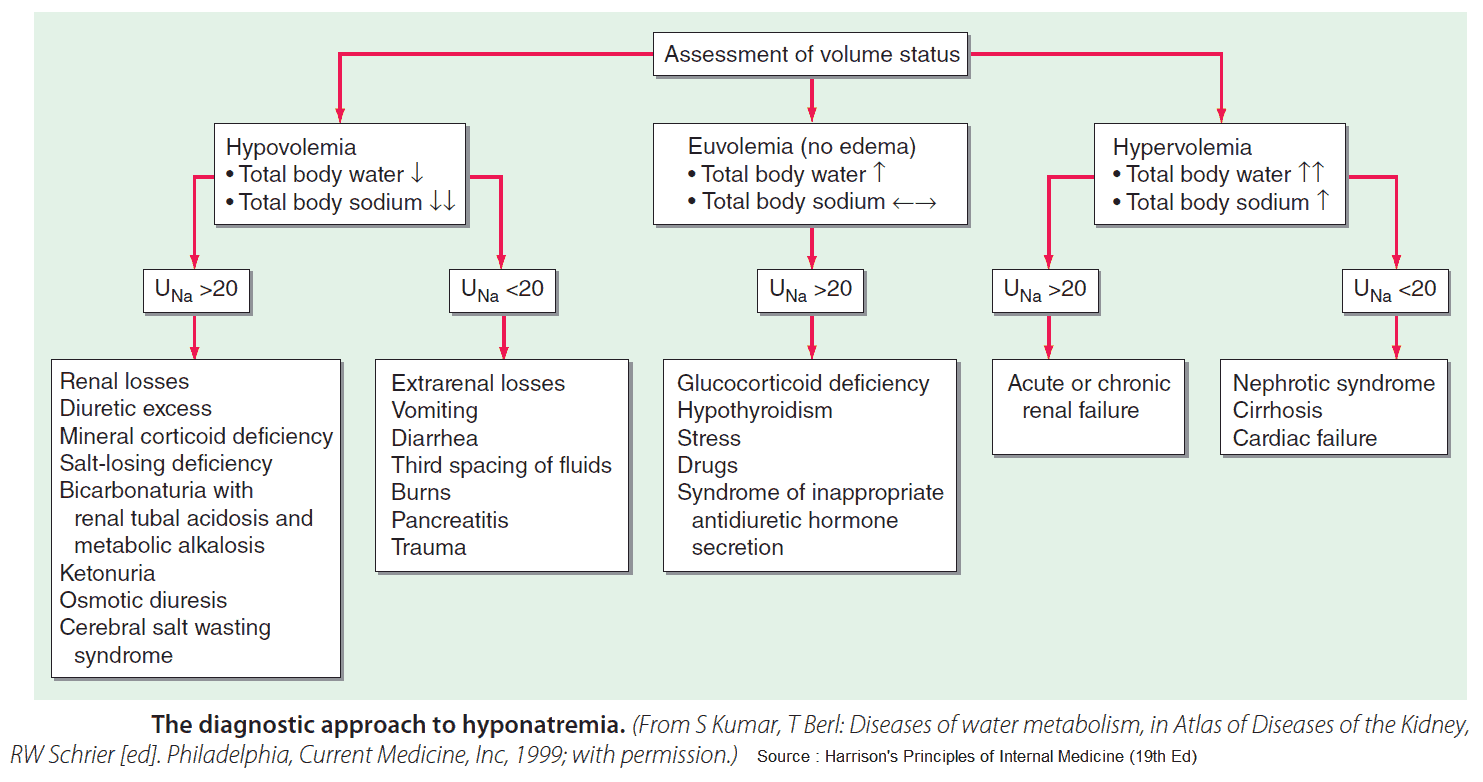
- Hypovolemic ? – check volume status (mucous membranes, skin turgor, pitting edema, BUN/Cr, U/S IVC, etc)
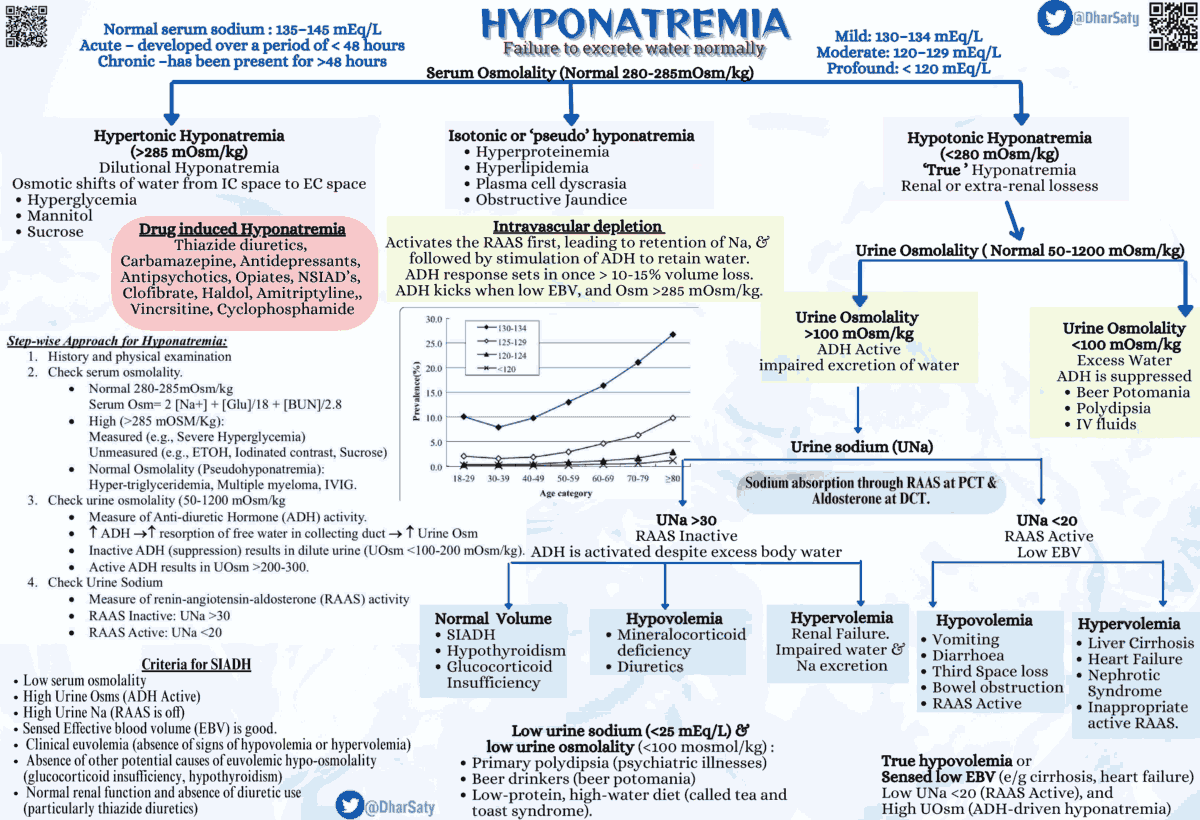
- Calculate plasma osmolality: 2[Na+] + [Glucose]/18 + [BUN]/2.8 + [Ethanol]/4.6
- Calculate osmolar gap: calculated osmolality – measured osmolality
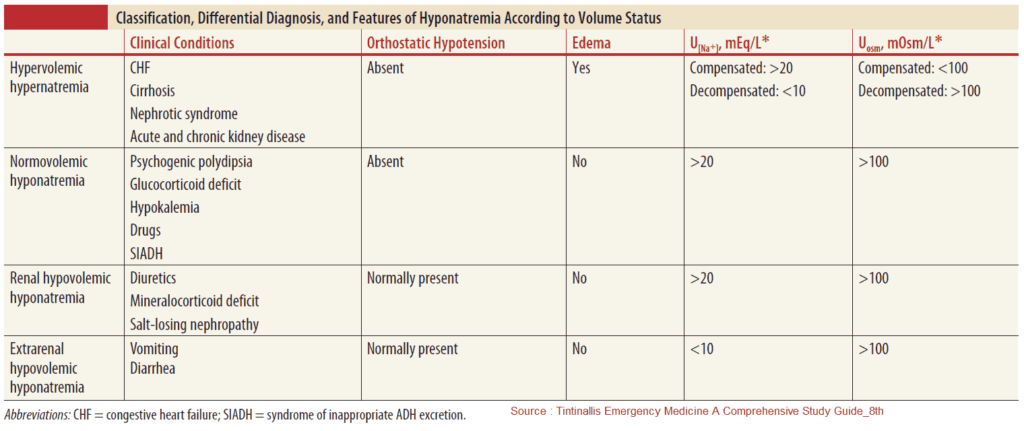
Differential Diagnosis:
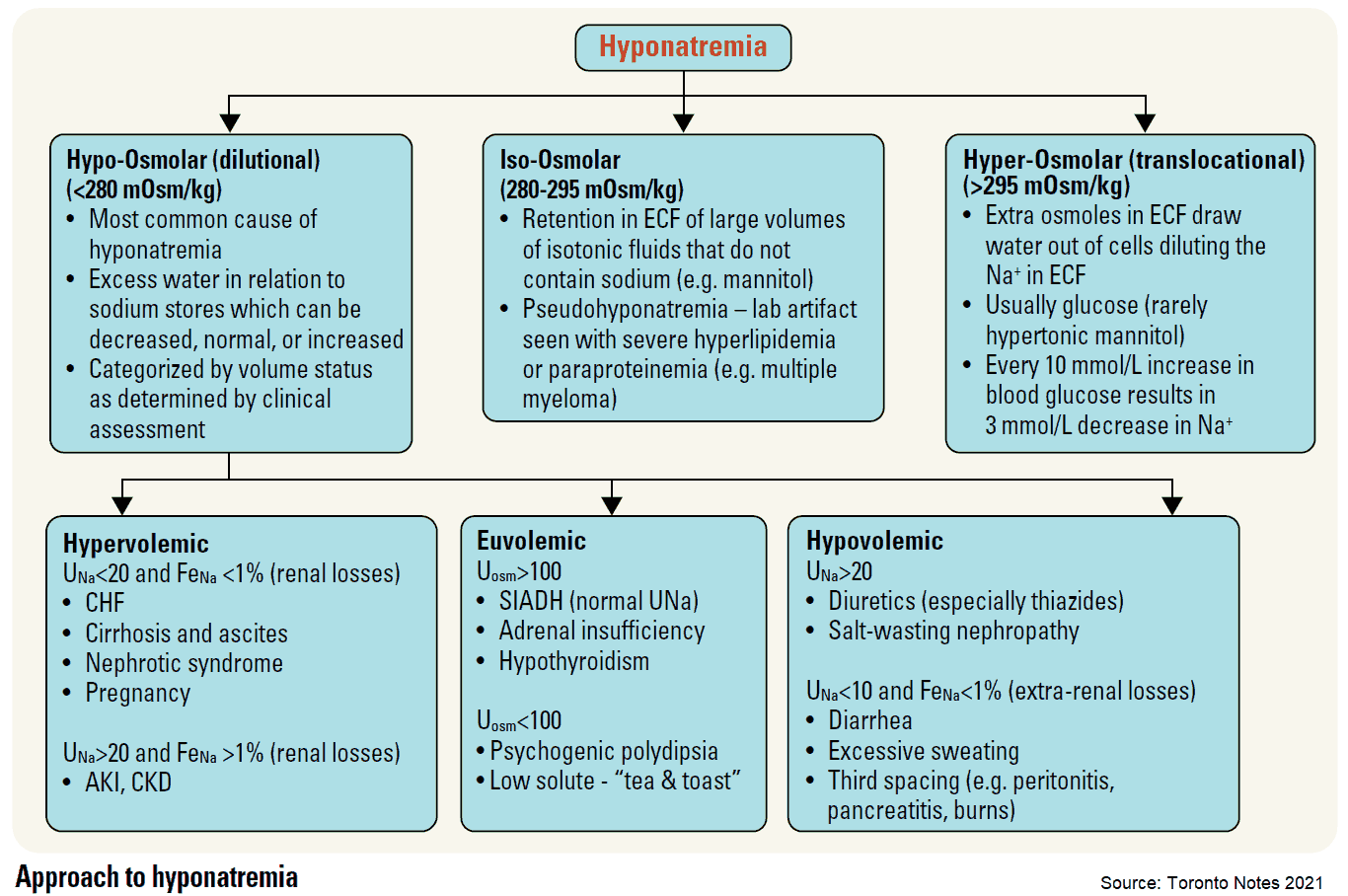
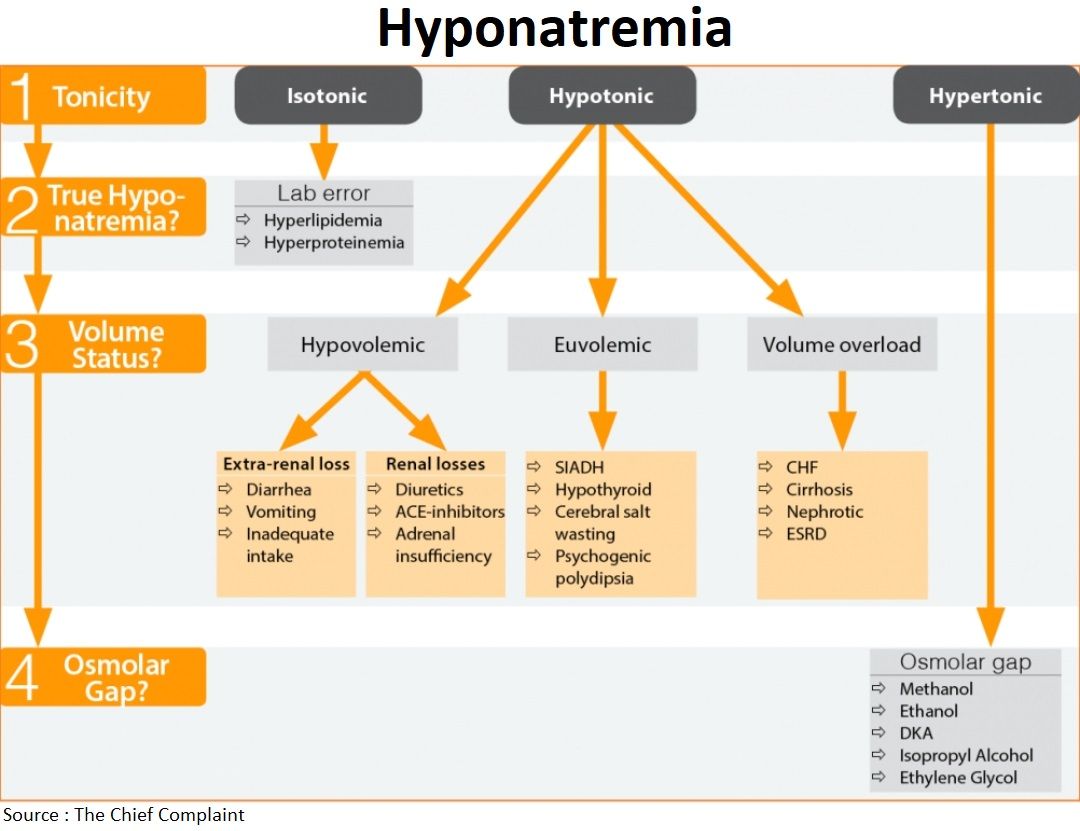
- Hypotonic (<280 mOsm/kg): most common type of hyponatremia
- Hypovolemic
- i. Extra-renal Na loss: (↓UNa)
- Diarrhea, vomiting (pancreatitis), inadequate intake, blood loss, excessive sweating (marathon runners), “third spacing” fluid sequestration
- ii. Renal Na loss: (↑UNa)
- Diuretics (loop, thiazides), ACE inhibitors, adrenal insufficiency, osmotic diuresis
- i. Extra-renal Na loss: (↓UNa)
- Euvolemic:
- SIADH (malignancy?), hypothyroid (check TSH), adrenal insufficiency (hyperkalemia), psychogenic polydipsia, beer potomania/“tea & toast” diet, cerebral salt wasting (trauma, stroke)
- Hypervolemic:
- CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, ESRD
- Hypovolemic
- Isotonic: usually lab “error” secondary to hyperlipidemia, hyperproteinemia
- Hypertonic (>295 mOsm/kg): unaccounted solute
- Glucose: every 100mg/dL > 100mg/dL → ↓[Na+] by 1.6 mEq/L
- Toxic Alcohols (EtOH, ethylene glycol, isopropyl alcohol, methanol)
- Calculate osmolal gap (measured – calculated) if suspected: normal<10
Hypertonic saline
– Use for AMS, seizure, coma
– Dose: 3% saline 100mls, repeat q 10min
– Rate of Na correction: 0.5 mEq/L/h
Management
- Hypertonic saline 3%
- Indication: Seizure, AMS (altered menal status), Coma
- Dose: 100 ml 3% saline, may repeat every 10 min until symptoms resolve
- Rate of correction
- 0.5 to 1 mEq/L/h or a total of 10 to 12 mEq/L per 24 hours
- Rapid correction ok ? :
- AMS / seizure / coma / focal neuro (use hypertonic saline)
- Hyponatremia <12-24 hours
- Max: Rise of 6mEq in first 6 hours in severely symptomatic patients
- Adverse effects
- Over rapid correction
- Consider DDAVP and free water replacement
- Central pontine myelinolysis
- Caused by too rapid correction of Na/osmolality
- Symptoms: AMS, dysphagia, seizures → locked-in state
- Over rapid correction
- Free water restriction
- Electrolyte replacement
- Watch for concurrent hypokalemia and hypophosphatemia
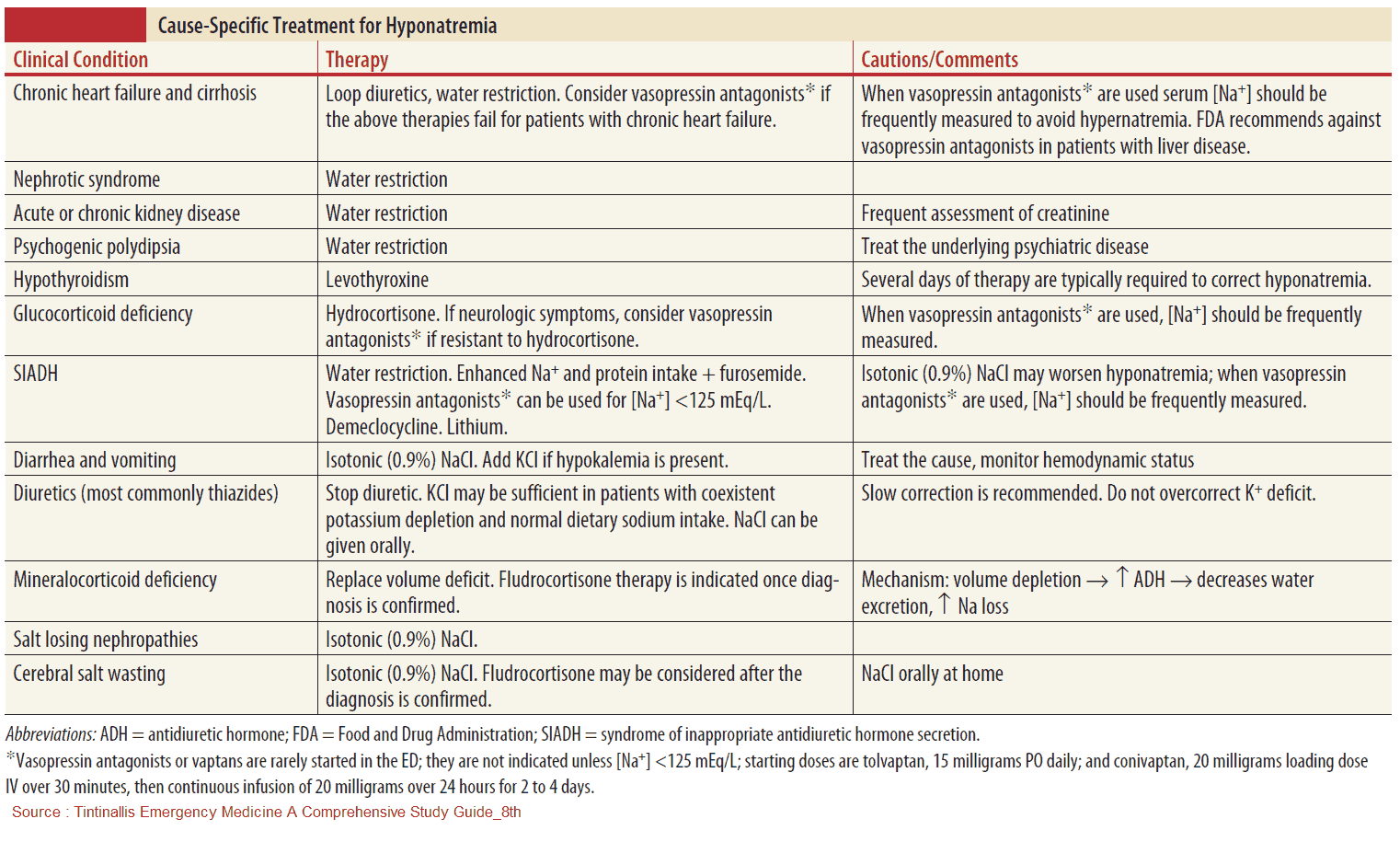
- Specific treatment
- Hypovolemic
- IV Normal Saline: repletes volume and Natrium
- Euvolemic
- No IV NS (Normal Saline): will worsen SIADH
- Free Water restriction <1L/day
- Treat underling cause
- Hypervolemic
- Free water restriction <1L/day + diuresis (monitor possible resulting electrolyte disturbances)
- Hypovolemic
Hypernatremia
Definition
- By definition dehydration: free water deficit (excess loss and inadequate intake) – serum Na > 145 mEq/L
- Often seen in elderly patients with dementia (unable to perform ADLs) as a result of decreased water intake
- Few symptoms until Na > 160 mEq/L
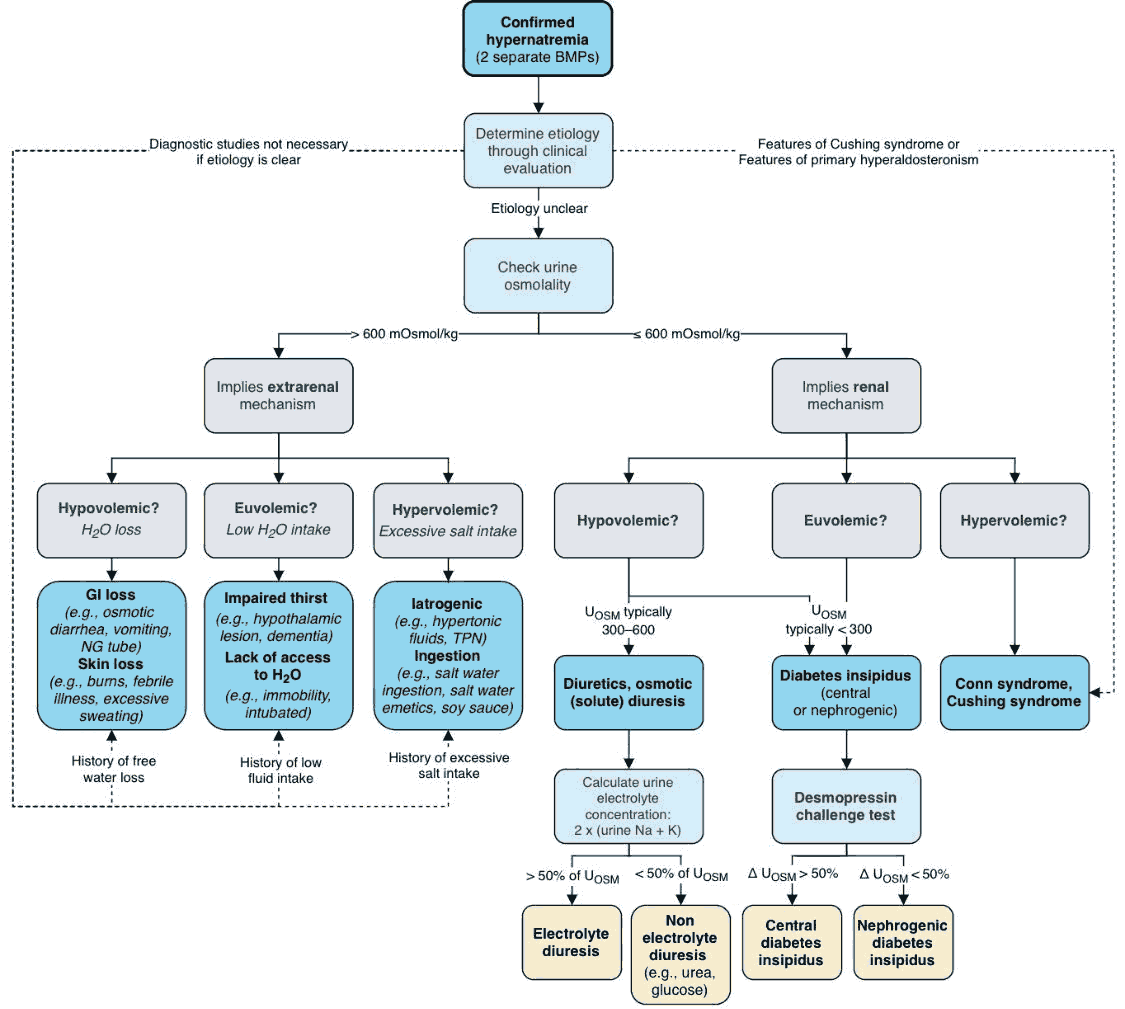
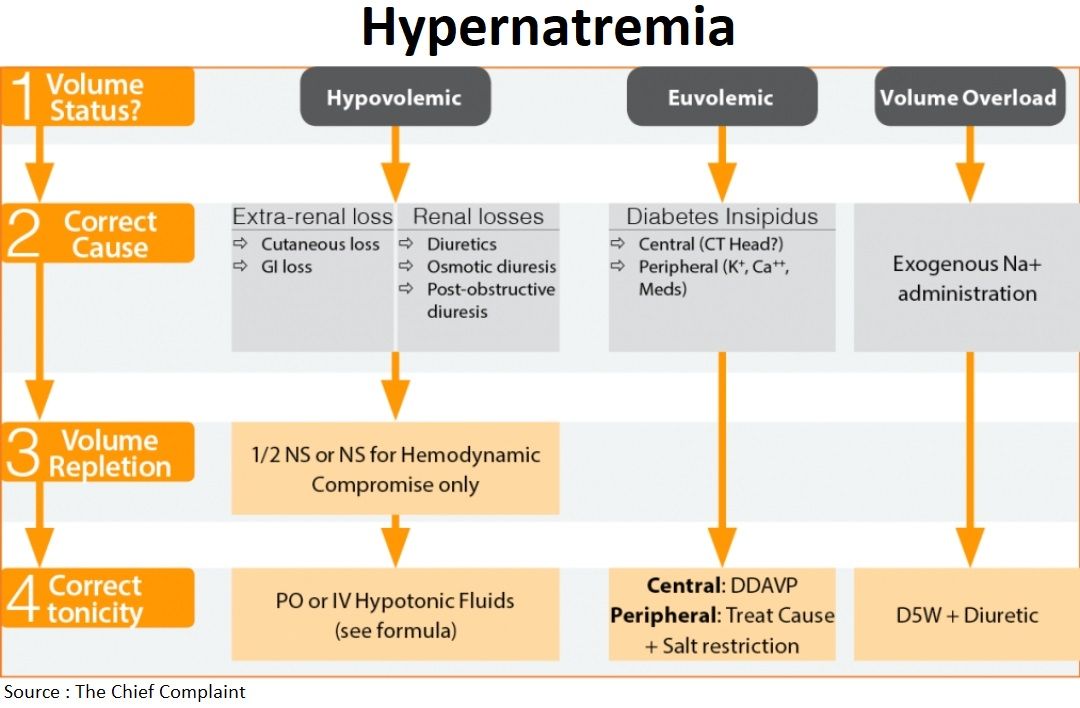
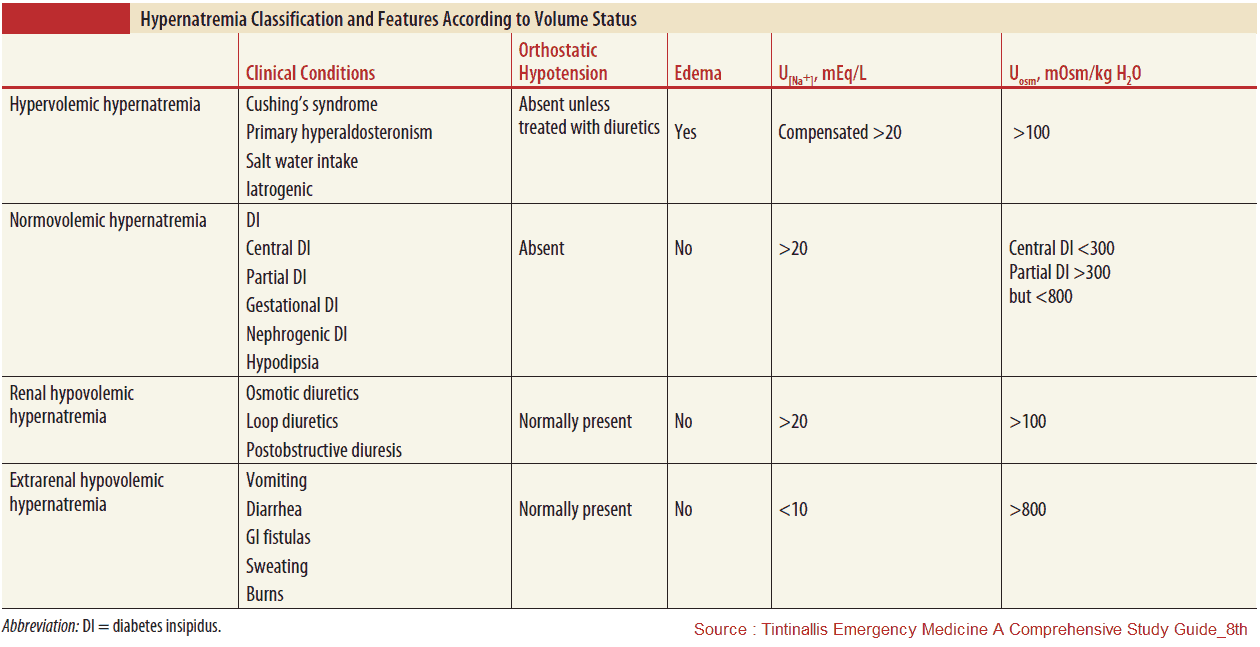
Diagnosis
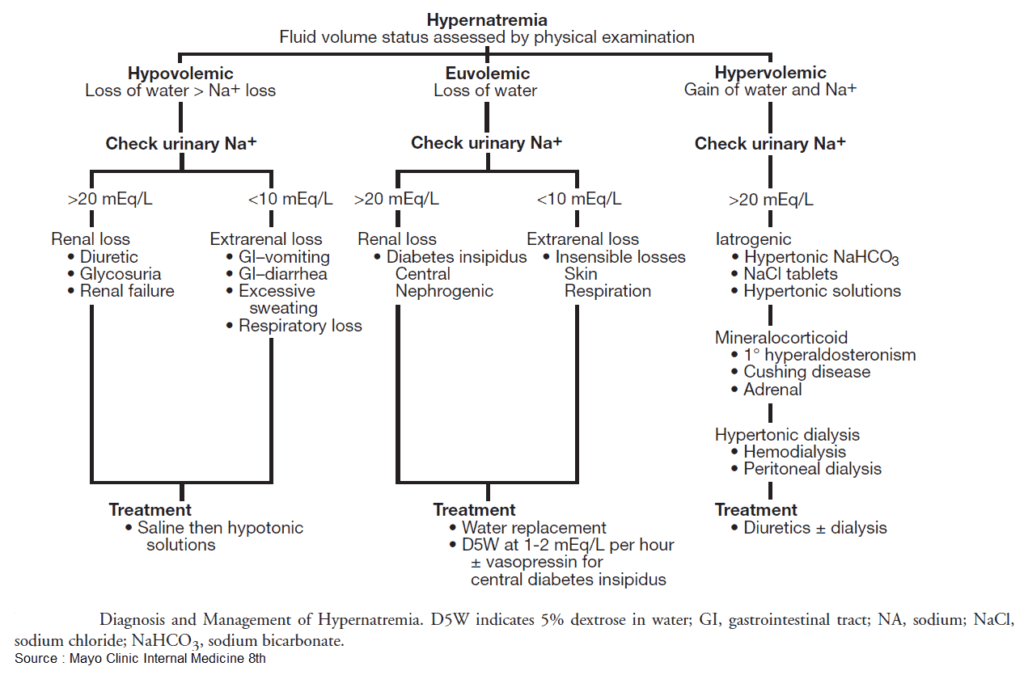
- Check fluid status (mucous membranes, skin turgor, pitting edema, BUN/Cr, U/S IVC, etc)
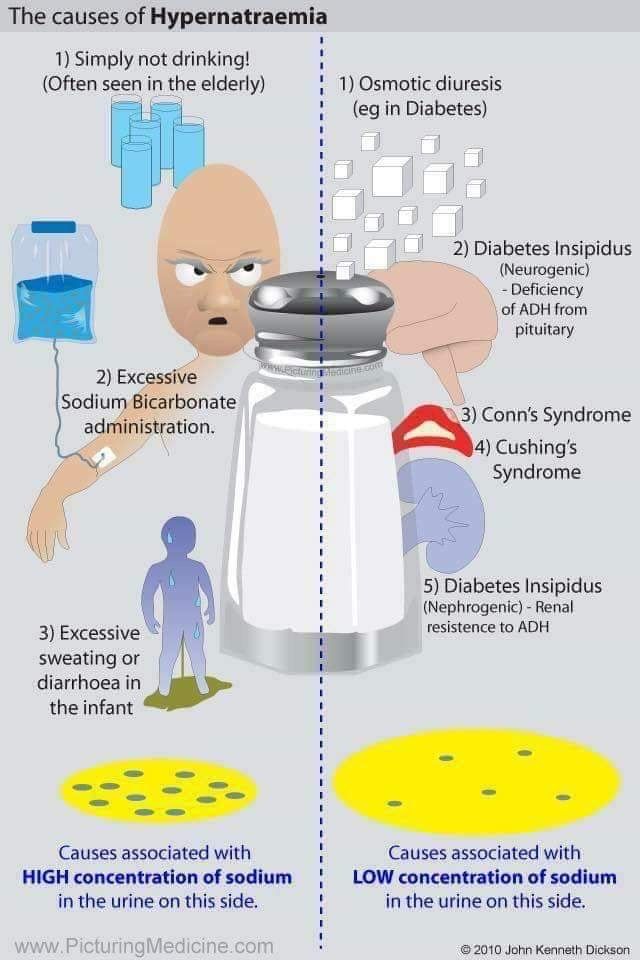
- Hypovolemic
- Renal losses: diuretics, osmotic diuresis (hyperglycemia, mannitol, urea), postobstructive diuresis
- Non-renal losses:
- i. Cutaneous loss: Insensible loss, burns, fever, sweating
- ii. GI loss: diarrhea (osmotic, lactulose), vomiting
- Euvolemic
- Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
- i. Central: trauma, post-op, tumor, hemorrhage/stroke, infection
- ii. Nephrogenic: Hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, drugs (demeclocycline, lithium)
- Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
- Hypervolemic
- Post-resus NaHCO3 administration or hypertonic saline
Management
- Hypovolemic or unstable
- Begin with volume resuscitation: Normal Saline
- Calculate free Water deficit (mdcalc.com)
- Free H2O deficit = TBW* x (Na/140 – 1)
- *TBW = 0.60 x ideal body weight (IBW), (x 0.85 if female or age>60)
- Half free water deficit should be given in first 12-24h
- Do not correct >12 mEq/L/day unless hypernatremia < 12-24 hours, otherwise can lead to cerebral edema
- Free H2O deficit = TBW* x (Na/140 – 1)
- If patient can tolerate PO then give PO free water
- If Hypervolemic give D5W + diuretic
- Diabetes Insipidus
- Central: DDAVP 1-2mcg IV q12h
- Nephrogenic: treat underlying condition