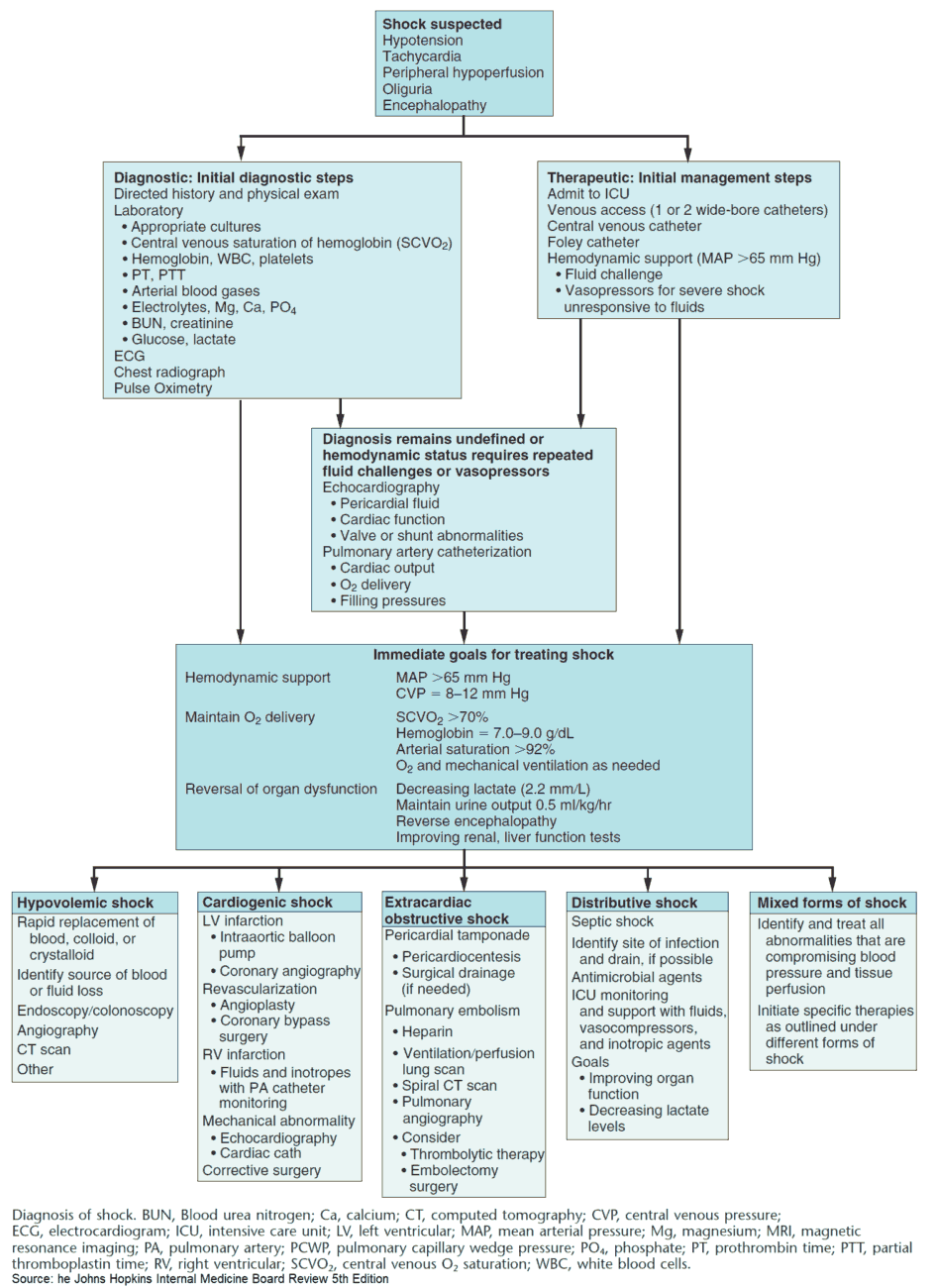
The goal for the patient in shock is rapidly identifying that the patient is in shock, finding the cause of shock and treating the cause while simultaneously resuscitating the patient.
Read Also : Approach to Undifferentiated Shock
Clinical Presentation
- Ill appearing/AMS
- Tachycardia
- Hypotension
- Met acidosis (lactate>4 mg/dl or Base def <-5)
- Tachypnea (RR>22 or PCO2<32)
- Oliguria: UOP<0.5 ml/kg/h
- Base deficit, lactate and sublingual capnometry (SLCO2) can help identify patients in early shock and are a predictor of mortality
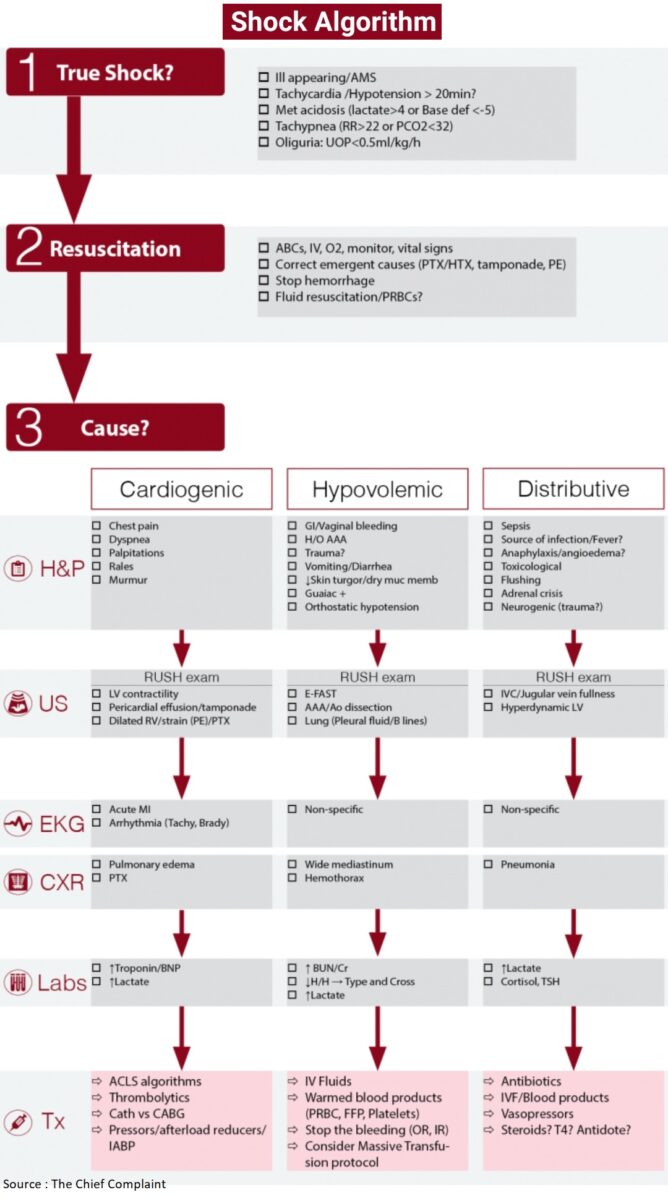
Resuscitation
- ABCs
- IV/O2/Cardiac monitor
- Foley
- Crystalloids
- 20ml/kg boluses
- Caution in CLOCK (CNS, Liver, Older, Children, Kidney disease)
- Antibiotics empirically
- Blood (before Pressors)
- Vasopressors (from α→β: PNEDDI)
- Phenylephrine
- Norepinephrine
- Epinephrine
- Dopamine
- Dobutamine
- Isoproterenol
Causes and Classification of Shock
- Hypovolemic ( Low CVP (Central Venous Pressure), Low CI (Cardiac index), High SVR (systemic vascular resistance) )
- Volume depletion type
- Vomiting/Diarrhea, Heat stroke, Burns, decreased intake
- 3rd Spacing – Pancreatitis, Burns
- Hemorrhagic type
- GI bleed/Vaginal bleed
- AAA rupture/Dissection
- Trauma
- Volume depletion type
- Cardiogenic (High CVP, Low CI-cardiac index, High SVR)
- Cardiomyopathy
- MI/Ischemia
- Arrhythmias
- Tachy (AF/VT), Slow (Brady, blocks)
- Mechanical
- Valve defect, atrial myxoma, ruptured ventricular aneurysm
- Obstructive
- Massive PE, tension PTX, constrictive pericarditis, cardiac tamponade,
- pulmonary HTN
- Cardiomyopathy
- Distributive (Low CVP, High CI, Low SVR)
- Sepsis/SIRS
- Anaphylaxis, Toxic shock
- Drugs
- Addisonian crisis
- Myxedema coma
- Neurogenic shock
Assesment of Shock
- Correct emergent and reversible causes
- Tension PTX → needle thoracostomy
- Cardiac tamponade → pericardiocentesis/thoracotomy
- Arrhythmia → shock
- Vital signs
- Shock index: HR (Heart Rate)/SBP (Systolic Blood Pressure) > 0.9 abnormal
- SIRS: HR>90; RR>20; Temp<36 or >38; WBC<4 or >12 (>10% bands); PaCO2 <32
- Pediatrics assessment
- Pediatric assessment triangle
- Work of breathing
- General appearance
- Circulation to skin
- Pediatric assessment triangle
- RUSH protocol for sonography (Read more about RUSH Exam)
- The Pump: Pericardial effusion, LV contractility, RV strain
- The Tank: IVC/Jugular vein fullness, FAST, Lung (PTX, Pleural fluid, B lines)
- The Pipes: AAA, Ao Dissection, DVT