Table of Contents
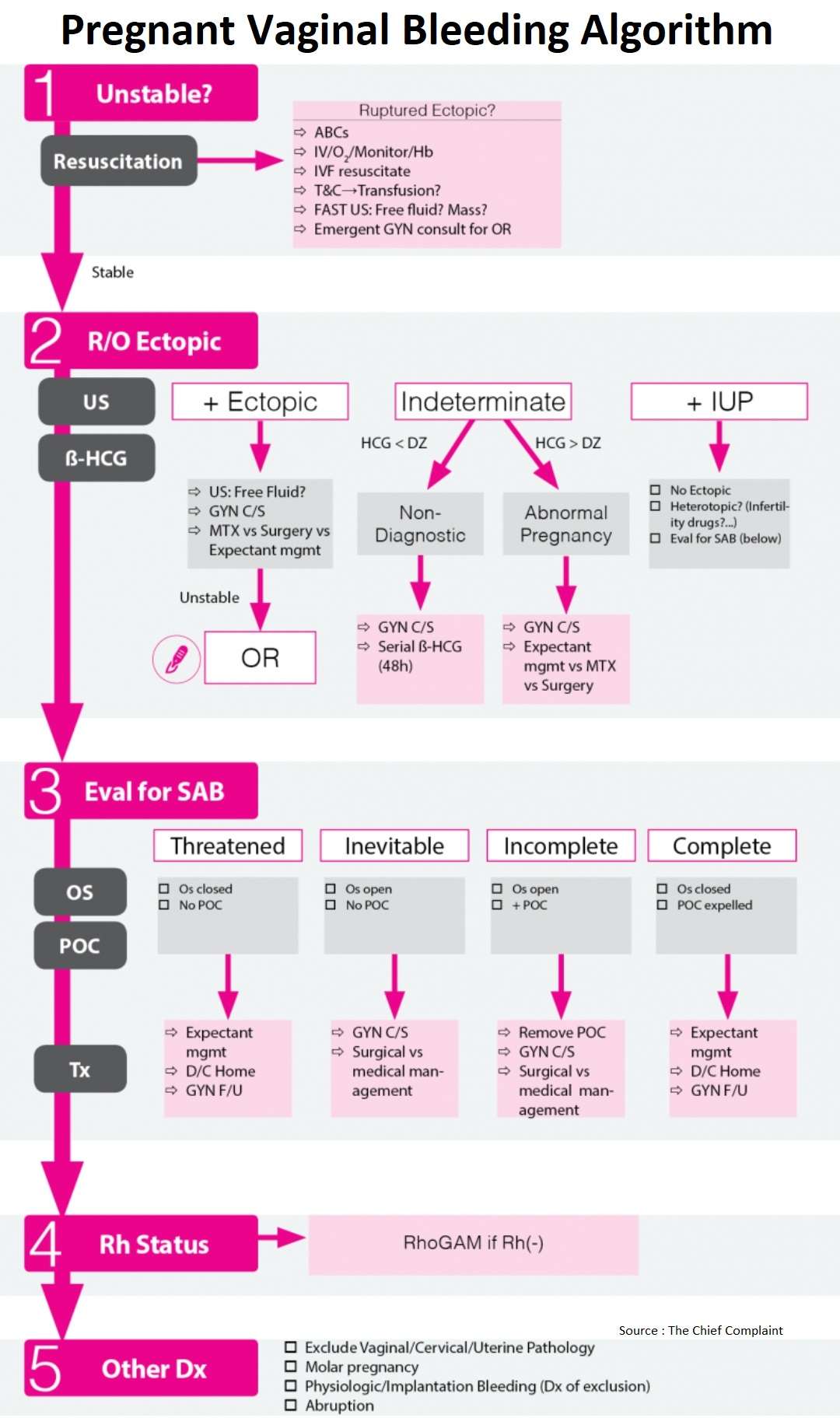
1. General Approach and Resuscitation
General
- Start with initial resuscitation and ABCs depending on stability of the patient
- Then rule-out ectopic pregnancy using pelvic ultrasound and HCG level
- If ultrasound shows Intrauterine Pregnancy and no concern for ectopic, then evaluate for Spontaneous Abortion based on os and POC on exam
- Final steps are to consider RhoGAM and other benign causes for vaginal bleeding
Unstable patient
- Treat as ruptured ectopic
- Clinical: Severe abdominal pain, peritonitis, hypotension/shock
- FAST US: Intraperitoneal free fluid, complex adnexal mass
- Type and Cross vs transfusion
- Emergent Gyn consult for OR
2. Rule Out Ectopic Pregnancy
Work-up
- Based on results of Ultrasound → 3 possibilities:
- If Ultrasound shows ectopic, Gyn consult for operative vs conservative management
- If Ultrasound shows Intrauterine Pregnancy and no concern for heterotopic, eval for SAB
- If Ultrasound indeterminate, classify into non-diagnostic or abnormal pregnancy based on ß- HCG level
| Gestational Age | Transabdominal Landmarks | Transvaginal Landmarks | Beta-HCG Levels |
| 4-5 Weeks | +/- Gestational Sac | Gestational Sac | 1000 |
| 5 Weeks | Gestational Sac +/- Yolk Sac | Gestational Sac, Yolk Sac +/- Fetal Pole | 1000-2000 |
| 6 Weeks | Yolk Sac and Fetal Pole | Yolk Sac and Fetal Pole with Cardiac Activity | 10000-20000 |
Intrauterine Pregnancy
Ultrasound criteria for Intrauterine Pregnancy
- See table for normal US appearance in pregnancy
- Gestational sac + “double decidual sac” sign is earliest sign of pregnancy, although most believe it is the yolk sac
Pitfall: Pseudosacs
- Pseudosacs are false sacs that can be confused with gestational sacs
- Pseudosacs can occur in 10-20% of ectopic pregnancies
- Centrally located → compared to eccentric location of true gestational sacs
Management
- Ectopic?
- IUP in uterus essentially rules-out ectopic pregnancy unless concerned about heterotopic pregnancy
- Heterotopic (ectopic + IUP) incidence:
- General population: 1:4,000-30,000
- Incidence in assisted reproduction: 1 in 100, therefore cannot exclude ectopic and further work-up needed in this population
- Miscarriage
- See Eval for Spontaneous Abortion section → patient is, at minimum having a threatened miscarriage
Indeterminate: Non Diagnostic
Discriminatory Zone (DZ):
- Definition: β-HCG level at which it is assumed that all viable intrauterine pregnancies can be visualized by ultrasound
- Level varies by institution and by experience of ultrasonographer
- DZ level
- Discriminatory zone for ß-HCG for transvaginal ultrasound is classically 1500-3000 (depending on institution)
- New evidence shows discriminatory zone may actually be higher, even greater than 3500 in one study (Obstet Gynecol 2013;121:65–70) (N Engl J Med 2013;369:1443)
- Caution in using a strict β-HCG cutoff to rule out a viable gestation
Indeterminate Ultrasound below Discriminatory Zone (DZ):
- Ddx: early viable IUP vs nonviable IUP vs ectopic
- If patient stable:
- Gyn consult
- Serial ß-HCG
- Ultrasound repeat when ß-HCG above DZ
- OK to discharge home if patient stable and reliable
- Pitfall: Low ß-HCG
- Ultrasound should still be obtained if ß-HCG is below discriminatory zone because may still be able to diagnose both IUP and ectopic (Level C ACEP Recommendation)
Indeterminate: Abnormal Pregnancy
General
- Definition: Indeterminate U/S + β-HCG above the discriminatory zone
- Ddx: Recent spontaneous AB, multiple gestation, molar pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, viable or non-viable pregnancy
- Indeterminate U/S + ß-HCG > DZ: Diagnostic of ectopic pregnancy? (Fertil Steril 1998;70:972-981)
Follow up
- Follow-up needed in abnormal pregnancy because of increased likelihood of ectopic (Level B ACEP Recommendation Ann Emerg Med 2003;41:123)
- Serial β-HCG
- Standard approach for serial ß-HCG is a rise of 66% at 48hours (considered normal) although:
- A normal rise may be seen in up to 15% of ectopics and an abnormal rise (<66%) may be seen in 15% of IUPs (Obstet Gynecol 1981;58:162-6)
- Serial ß-HCG values at 48h: (Level B ACEP Recommendation Ann Emerg Med 2003;41:123)
- 66% increase: IUP, Ectopic (15%)
- Plateau: nonviable IUP, Ectopic Pregnancy (EP)
- <66% increase: Ectopic, non-viable IUP, nl IUP(15%)
- Decreasing: SAB, resolving ectopic
- Ectopic pregnancy can resolve spontaneously by tubal abortion or regression, but >90% of women with ectopic and ß-HCG>2,000 will require surgery (CMAJ 2005;173(8);905-912)
Ectopic Pregnancy
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- U/S signs suggestive of ectopic pregnancy (Ma OJ, First Trimester Pregnancy. In: Emergency Ultrasound, McGraw Hill. 2003, pp. 239)
- Definite: Extra-uterine embryo with cardiac activity (seen in 15-20% of ectopic pregnancies)
- Suggestive: Free pelvic or Intra-peritoneal fluid, tubal ring, complex adnexal mass
- Incidence of heterotopic (ectopic + IUP) in
- General population: 1:4,000-30,000
- Incidence in assisted reproduction: 1 in 100, therefore cannot exclude ectopic and further work-up needed in this population
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Unstable
- Treat as ruptured ectopic
- Clinical: Severe abdominal pain, peritonitis, hypotension/shock ⇒ FAST US: Intraperitoneal free fluid, complex adnexal mass
- Type and Cross vs transfusion
- Emergent GYN consult for OR
- Stable
- Expectant management
- Indication: unknown location pregnancy or suspected ectopic with low/declining β-HCG
- Contraindications: Risk factors for rupture (increasing abdominal pain), not able to follow-up, and lack of timely access to medical care
- Methotrexate
- See table for indications
- Surgery
- Indications: Hemodynamic instability, contraindications to methotrexate, suspicion or risk factors for rupture, or failed medical therapy
- Expectant management
Indications for Medical Therapy for Ectopic Pregnancy
□ Hemodynamically stable
□ Patient desires future fertility
□ Ability to return for follow-up
□ No contraindications to Methotrexate
□ Unruptured mass <3.5cm
□ No fetal cardiac activity
□ Quantitative ß-hCG < 6,00015,000
3. Evaluation for Spontaneous Abortion
General
- Evaluate for spontaneous abortion in the patient with an IUP and vaginal bleeding
- Classify into type of Spontaneous Abortion based on cervical OS and POC (Products of Conception)
Classification
- Threatened miscarriage
- Os closed and no POC
- Inevitable
- Os open and no POC
- Incomplete
- Os open and POC on exam in os
- Complete
- Os closed and POC expelled
Incidence of miscarriage: (BMJ 1997;315:32-4)
- 21% of pregnant patients bleed before 20th week
- 57% of those will miscarry
- 80% of those will miscarry before 12 weeks
- 57% of those will miscarry
- After detection of fetal cardiac activity, <5% of pregnancies with normal sonographic appearance will abort (Ann Emerg Med 2003;41:123,)
4. Rhogam ?
- Indication
- RhoGAM 50 mcg for Rh(-) women at time of first trimester pregnancy loss (Level B ACEP Recommendation Ann Emerg Med 2003;41:123,)
- No recommendations for after first trimester, but standard dose is 300 mcg IM
5. Non Emergent Causes of Vaginal Bleeding
MOLAR PREGNANCY
- Diagnosis by U/S showing “snowstorm” pattern or cystic structures
- Treatment is surgical evacuation with close monitoring of ß-HCG levels
IMPLANTATION BLEEDING
- Definition: spotting from implantation of embryo around the time of expected menses
ANEMBRYONIC PREGNANCY
- Development of a gestational sac without embryonic structures
- They may present with vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain
- The diagnosis is confirmed with ultrasound. Treatment is misoprostol and/or uterine aspiration
ROUND LIGAMENT SYNDROME
- Usually presents with abdominal or low back pain, not vaginal bleeding
- Normal occurrence due to growth of the uterus
- The majority have pain on the right side as the uterus tilts to that side
References
- Clinical Policy: Critical Issues in the Initial Evaluation and Management of Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department in Early Pregnancy. https://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(12)00406-4/fulltext
- Reevaluation of discriminatory and threshold levels for serum β-hCG in early pregnancy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23262929/
- Diagnostic Criteria for Nonviable Pregnancy Early in the First Trimester. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejmra1302417
- Serum human chorionic gonadotropin measurement in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy when transvaginal sonography is inconclusive. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0015028298002787
- Clinical policy: critical issues in the initial evaluation and management of patients presenting to the emergency department in early pregnancy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12514693/
- A method of screening for ectopic pregnancy and its indications. https://europepmc.org/article/med/6454867
- Diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy. https://www.cmaj.ca/content/173/8/905
- Incidence and outcome of bleeding before the 20th week of pregnancy: prospective study from general practice. https://www.bmj.com/content/315/7099/32.short