This article is an answer to the Case – Headache after Motor Vehicle Accident
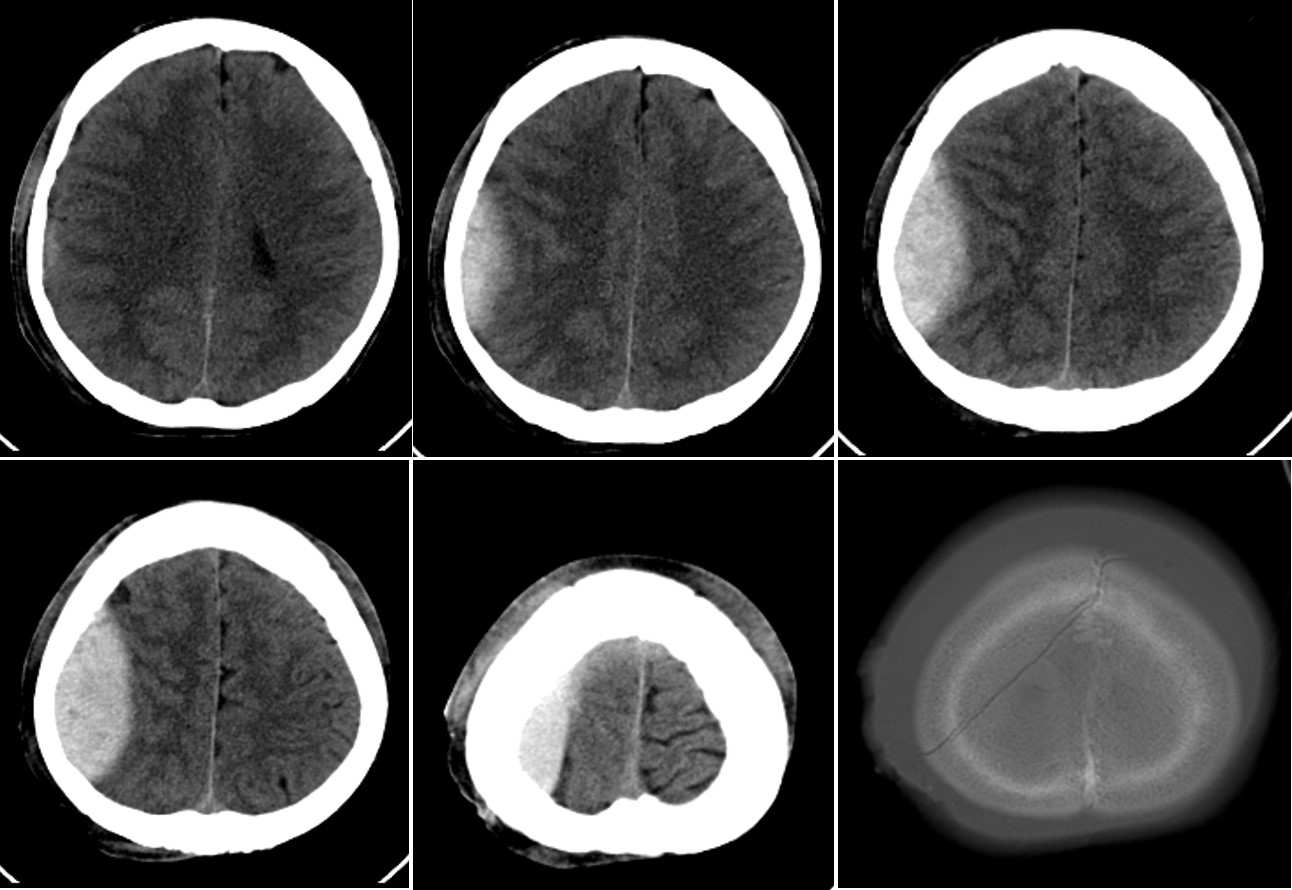
CT scan findings
- A lens-shaped hemorrhage in the right fronto-occipital region
- It does not cross the suture
- Compression effect to the brain parenchyma
- Effacement of ipsilateral cerebral sulci
- No significant midline shift
- On bone window, a skull fracture is seen
Diagnosis: Traumatic Right Epidural (Extradural) Hemorrhage
Discussion:
- Epidural (Extradural) Hemorrhage is a collection of blood that forms between the inner surface of the skull and the endosteal layer.
- They are usually associated with a history of head trauma and frequently associated skull fracture.
- The source of bleeding is usually arterial, most commonly from a torn middle meningeal artery
- EDHs are generally unilateral in more than 95% of cases, however, bilateral or multiple EDHs are reported.
- Supratentorial location: temporoparietal (60%), frontal (20%) and parieto-occipital (20%) infratentorial location (5%) in posterior fossa
- Management is craniotomy with evacuation of blood
- Surgical intervention if
- EDH larger than 30 cm3, regardless of GCS
- EDH with GCS <9
Progress of patient: Craniotomy and evacuation done
SIMILAR CASE: Traumatic Epidural Hematoma