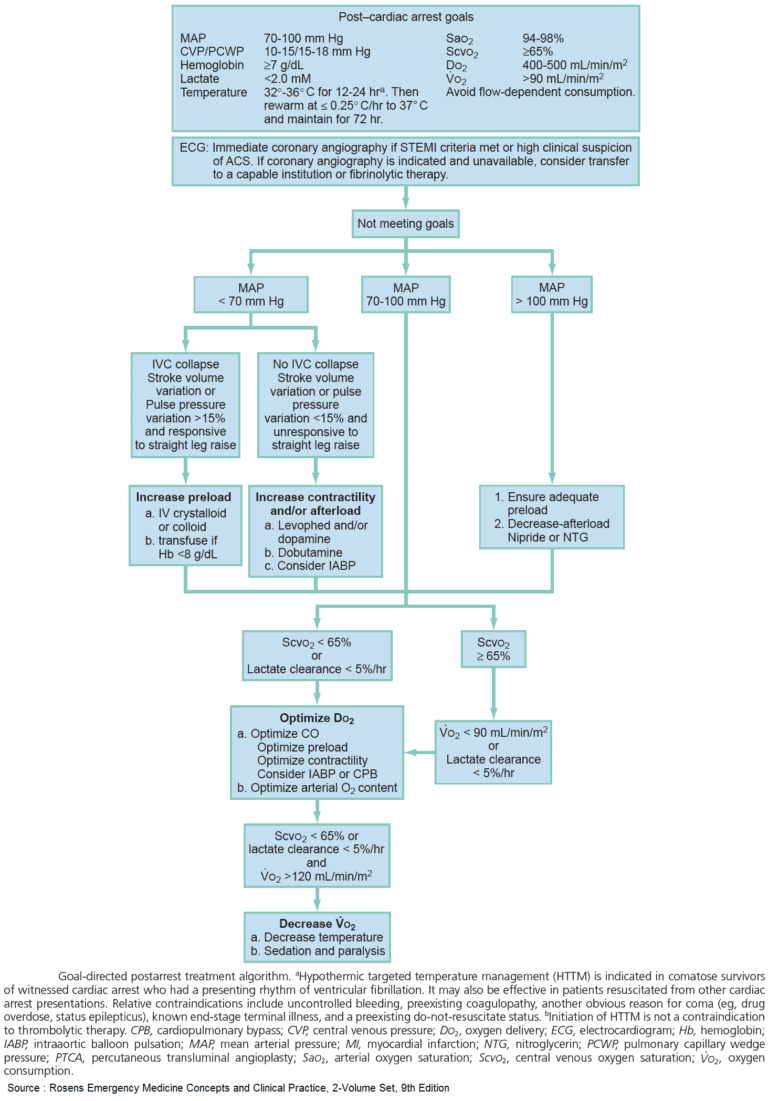
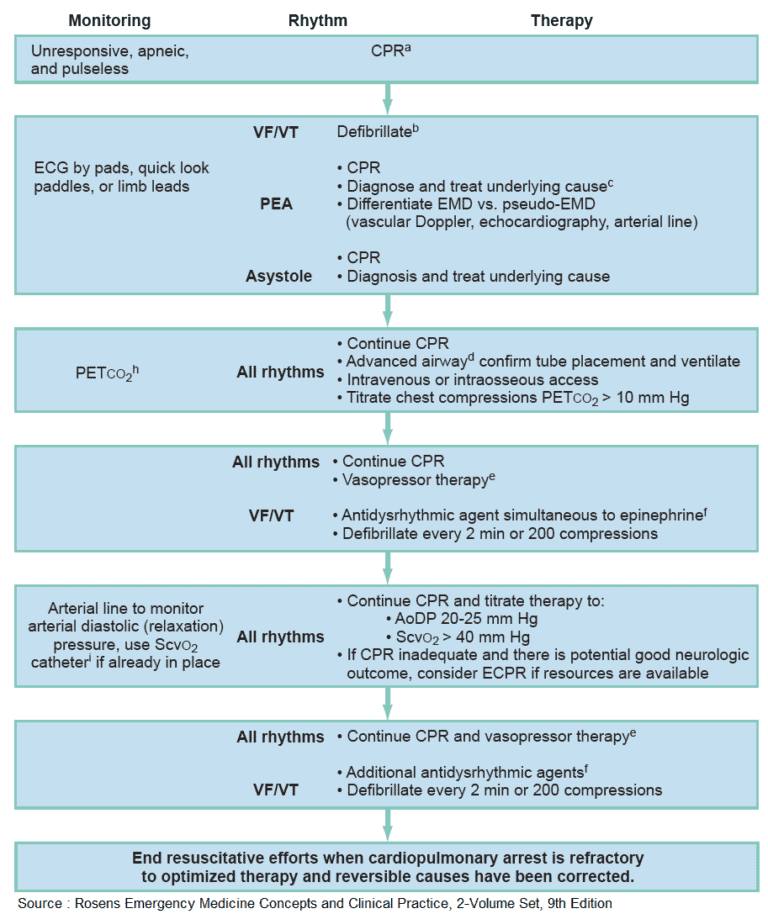
Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Thrombolytics
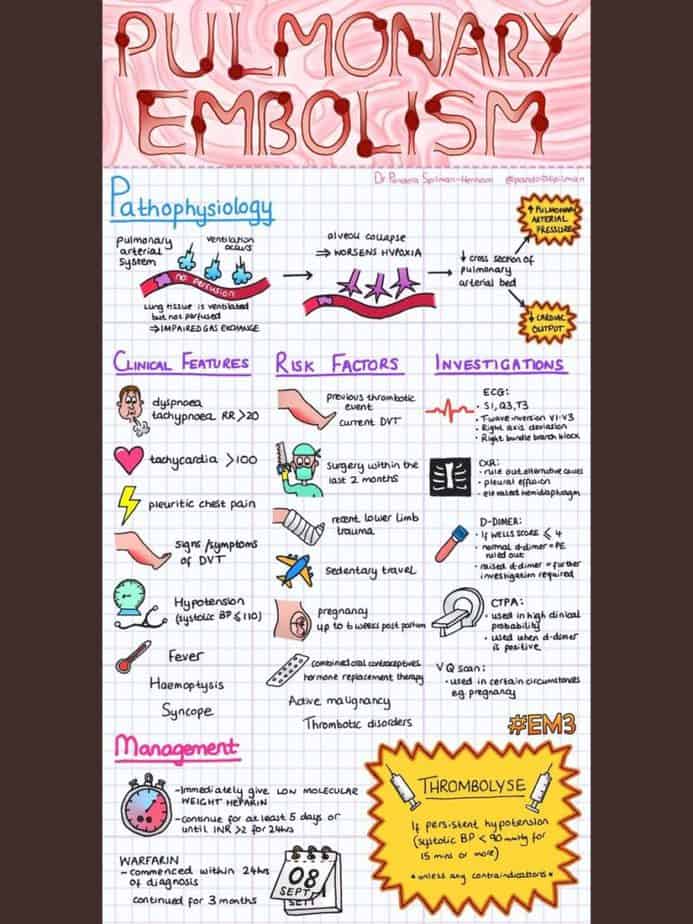
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is responsible for more than 250,000 annual hospitalizations in the United States, with significant risk for morbidity…