ECG Intepretation
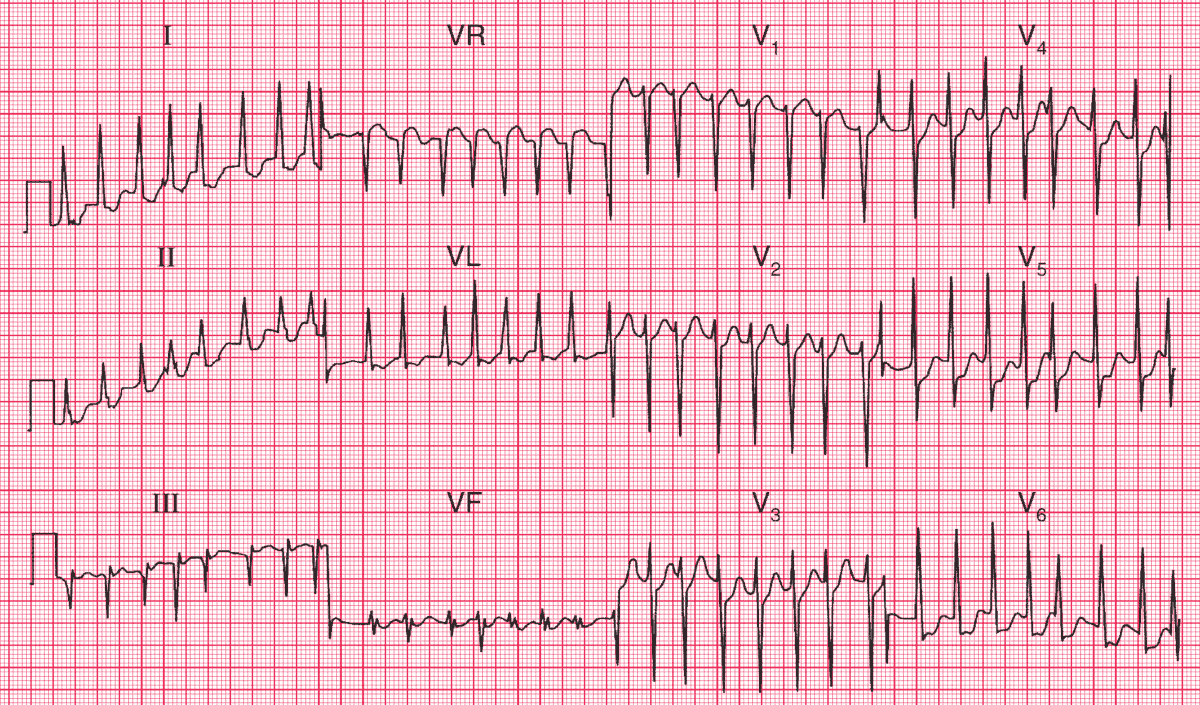
- Atrial fibrillation
- Normal axis
- Ventricular rate of up to 200/min
- Widespread ST segments depression, most prominent in leads V4-V6, with reciprocal ST elevation in aVR, suggesting subendocardial ischemia, probably demand ischemia because of the fast heart rate
- Normal T waves
What to do ?
Ischaemia may have been the cause of the atrial fibrillation, or the rapid ventricular rate itself may be responsible for the ischaemic changes. The things to think about are rheumatic heart disease (particularly with mitral stenosis), thyrotoxicosis, alcoholism, and other forms of cardiomyopathy.
Immediate treatment of the heart failure with diuretics may be necessary, but the ventricular rate is best controlled by digoxin, which can be given intravenously if necessary. DC cardioversion may be necessary if the patient is in severe heart failure.
Remember that a patient with atrial fibrillation probably needs anticoagulants on a long-term basis. Echocardiography confirmed that this patient had mitral stenosis.
- READ MORE: Management of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) with Rapid Ventricular Response (RVR)
- Similar Cases: