Table of Contents
Critical Diagnoses of Upper Abdominal Pain
General
- Work-up for upper abdominal pain begins with resuscitation and exclusion of critical diagnoses
- Then, through a detailed history and physical, consider all the causes of upper abdominal pain (see below)
- The differential may then come down to Gallstone etiology vs Gastritis/PUD → will need further imaging based on suspicion (US abdomen)
Resuscitate
- IV/O2/Monitor, IV Fluids, Labs as needed, pregnancy test
Rule Our Critical diagnoses of Upper Abdominal Pain:
- AAA, Mesenteric Ischemia, Perforation, SBO, ectopic pregnancy
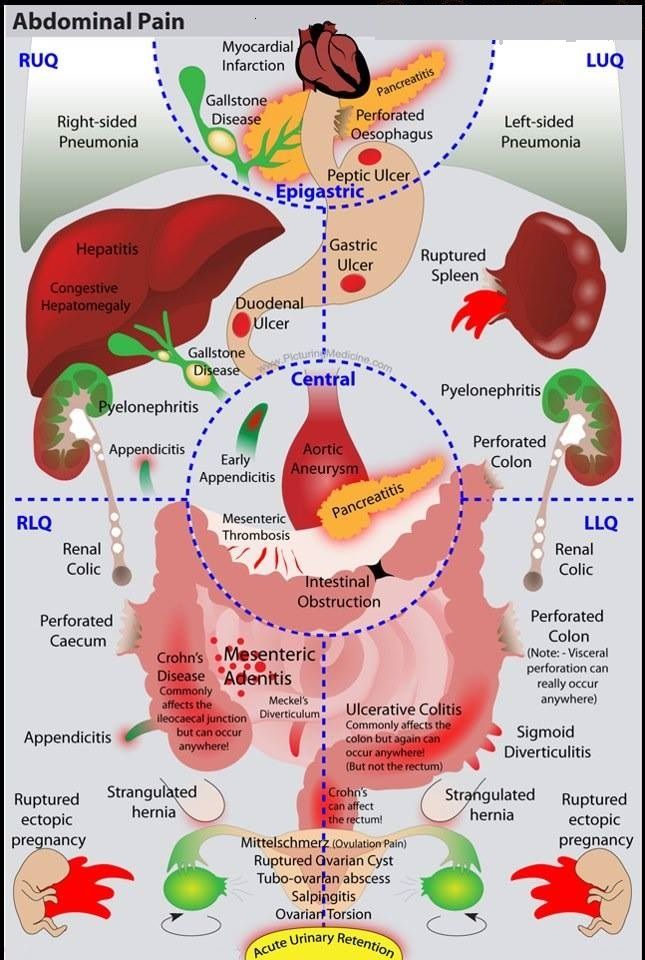
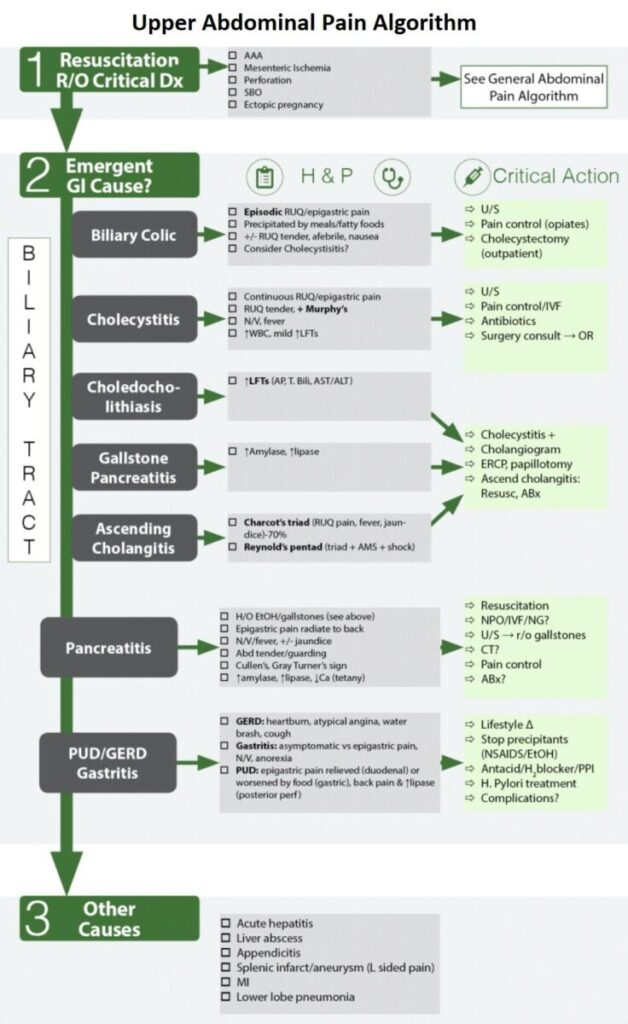
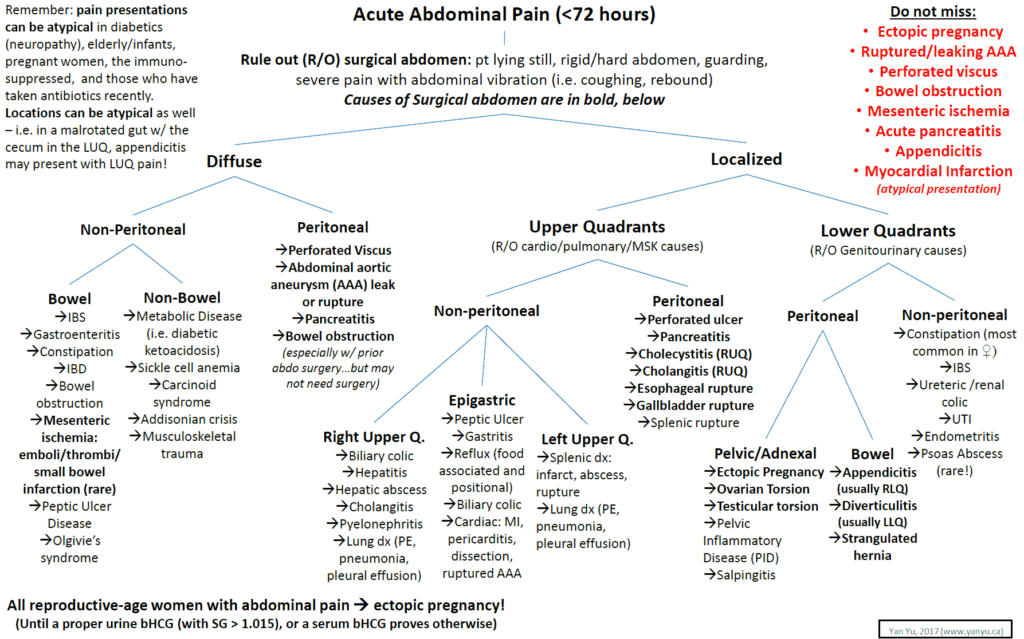
Emergent Gastrointestinal ( GI ) Causes of Upper Abdominal Pain
1. Billiary Tract Disease
General:
- The goal is to find the location of the stone and its associated complications → Is it still in the gallbladder (symptomatic cholelithiasis), in the cystic duct (cholecystitis), or in the CBD (choledocholithiasis, gallstone pancreatitis, ascending cholangitis)
Cholelithiasis
- Prevalence of 10% in US, usually asymptomatic (symptoms develop in 2%/yr)
BILIARY COLIC
- Symptomatic cholelithiasis → obstruction of cystic duct by gallstones
- Clinical: Episodic pain in Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ), minutes to hours, resolves spontaneously
- Precipitated by meals/fatty foods
- Treatment: Recurrent biliary colic → pain control, elective outpatient cholecystectomy
CHOLECYSTITIS
- Clinical (vs biliary colic, may be difficult to distinguish)
- Pain longer in duration (>6 hours), localizes to RUQ, ↑ N/V/F (more nausea, vomitus)
- Murphy’s sign:
- Localized peritonitis over gallbladder → arrest of inspiration on gallbladder palpation with pain
- Highest LR+ of PE/lab values
- Diminished in elderly
- Course
- 1/3 will worsen→ complications (cholangitis, perforation)
- 1/2 will improve spontaneously (7-10days)
- Laboratory: ↑ WBC, mild ↑ LFTs
- Radiology
- RUQ U/S (sensitivity 84-97%, specificity up to 100%)
- Findings: Gallstones, pericholecystic fluid, gallbladder wall thickening (>3mm), sonographic Murphy’s
- HIDA scan: non-visualization of contrast in gallbladder (cholecystitis) or intestine (choledocholithiasis)
- Treatmentof Cholecystitis
- NPO/IVF/Abx (antibiotics) (broad spectrum)
- Semi-urgent Cholecystectomy, laparoscopic (at 24-48h) with CBD exploration or ERCP if CBD stone of concern
- Complications of Cholecystitis: gallbladder perforation, emphysematous cholecystitis, gangrenous cholecystitis, cholangitis, gallstone ileus
CHOLEDOCHOLITHIASIS
- Define: Gallstone lodged in common bile duct
- Clinical: similar presentation to cholecystitis except elevated LFTs (↑Alk Phos, ↑T. Bili)
- Radiology: RUQ U/S
- Dilated CBD (>6mm)
- Common bile duct stone?
- ERCP
- Diagnose and treat common duct stones (with sphincterectomy)
- R/O other causes of obstruction (tumors…)
GALLSTONE PANCREATITIS
- Elevated amylase, lipase
- ERCP to decompress biliary tree
ASCENDING CHOLANGITIS
- CBD obstruction causing infection proximal to obstruction → sepsis (↑ mortality)
- Charcot’s triad (RUQ pain, fever, jaundice)
- Reynold’s pentad (Charcot + hypotension + AMS)
- Treatment
- Conservative (NPO, IVF, broad-spectrum Abx → elective ERCP at resolution)
- If failure of conservative tx (15%)→ emergent surgery (Percutaneous vs ERCP)
2. Acute Pancreatitis
Etiology of Acute Pancreatitis:
- Gallstones (35%), Alcohol (30%)
- Idiopathic (10%),ERCP complications (4%), Tumors, Drugs (furosemide, sulfa, thiazides, valproate, tetracyclines…), infection (viral, mycoplasma), blunt trauma (1.5%), scorpion, hypercalcemia, elevated triglycerides ( hypertriglyceridemia )
Symptoms and Signs of Acute Pancreatitis
- Epigastric pain radiating to back
- Nausea/ Vomitus /fever, +/- jaundice
- Abdominal tenderness / guarding, Cullen’s (peri-umbilical ecchymosis), Gray Turner’s (flank bruising)
Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis:
- Lipase
- Levels peak (12-36h), duration (2 weeks)
- Test of choice, better sensitivity and specificity over amylase → lipase level 3x normal, more specific
- If high suspicion for pancreatitis and lipase negative → CT scan
- Level of lipase not predictive of severity of pancreatitis
- Amylase
- Less specific, duration (1 week)
- Not used: many false positives and false negatives
- Many sources: bowel, uterus, pancreas
- Amylase: level 3x normal, not specific
- CT A/P
- Unsure of diagnosis (high index of suspicion and lipase low)
- Will see acute and chronic changes on CT
- Rule out surgical issues
- Staging system (Balthazar) → help stage and predict which patients will develop severe complication: necrotizing pancreatitis (Radiology 1994;193(2):297)
- Unsure of diagnosis (high index of suspicion and lipase low)
- RUQ U/S → diagnose gallstone pancreatitis
Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis
- Resuscitation
- NPO / bowel rest / IVF/ NG suction
- Fluid resuscitation (up to 10L/day → maintain adequate UOP)
- Antibiotics
- Meta-analysis→ prophylactic antibiotics for necrotizing pancreatitis decreased sepsis
- and mortality
- Save for sickest pts → Imipenem/meropenem (Ann Surg. 2006;243(2):154)
- Necrotizing Pancreatitis
- Antibiotics (Imipenem), CT A/P, Urgent surgical consultation, ICU
- Fluid collections→ CT or U/S guided drainage
- Infected pancreatic collections →benefit from early surgery
- Gallstone Pancreatitis
- RUQ US to diagnose
- MRCP if not sure of obstructive etiology
- Treatment: ERCP (but may cause pancreatitis)
Complications of Acute Pancreatitis
- NECROTIZING PANCREATITIS
- Pancreatitis → necrosis/liquefaction of tissue → local/systemic complications
- Greatest life-threatening complication of pancreatitis (mortality up to 50%)
- Predisposes to sepsis, multi-organ failure and death
- Predictive factors:
- Hemorrhage? (Gray-Turner, Cullen’s→ delayed 48h),
- Pancreatic enzymes (low levels more consistent with necrosis),
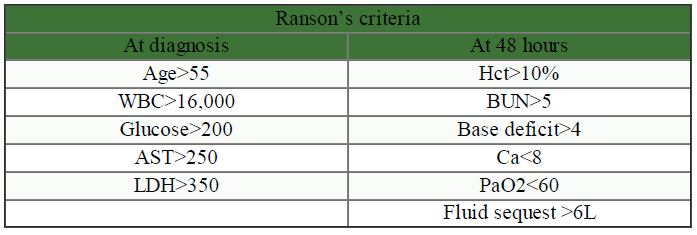
- ↑ Severity of pancreatitis (↑ Ranson’s)
- i. Hemoconcentration: Hct >47% at 48h has high sensitivity and may need CT early in course (Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:2130-4)
- Treatment
- ✓ Antibiotics (Imipenem), CT A/P, Urgent surgical consultation, ICU
- ✓ Fluid collections→ CT or U/S guided drainage
- ✓ Infected pancreatic collections → benefit from early surgery
- SEPSIS
- Responsible for most mortality associated with AP
- See Sepsis algorithm
- PSEUDOCYST
- Drainage → >6cm after 6 wks observation, or causing sx (abd pain, gastric outlet obstruction, biliary obstruction)
- Other
- ↓ Ca, ↑ glucose, ↑ TG, GI hemorrhage, ascites, pleural effusion, ARDS, renal failure
3. Gastritis , GERD , Peptic Ulcer Disease
General:
- If patient stable→ often considered default diagnosis when work-up negative and excluded lifethreats (MI, perforation…)
- Empiric therapy given with abdomen re-check
Clinical
- GERD: Heartburn, atypical angina, water brash, cough
- Gastritis: Asymptomatic vs epigastric pain, N/V, anorexia
- PUD: Epigastric pain relieved (duodenal) or worsened (gastric) by food; back pain & ↑ lipase (post perforation)
Treatment
- Lifestyle change (↑ Head of bed), stop precipitants (NSAIDS / alcohol)
- H. Pylori treatment, antacid / H2 blocker / PPI
Complications:
- Peptic Ulcer Disease:
- Hemorrhage, Perforation, Intractable pain, Obstruction
- Posterior perforation → may present like pancreatitis (back pain, ↑ enzymes, vomiting…)
Other Causes of Upper Abdominal Pain
- Consider other causes above and below the area of tenderness
- Acute hepatitis, liver abscess, appendicitis, splenic infarct/aneurysm (L sided pain), MI, lower lobe pneumonia