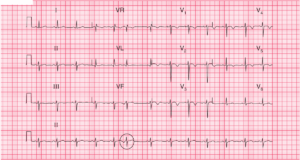
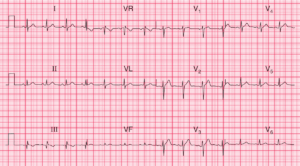
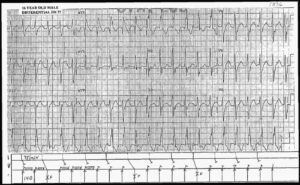
The rhythm is irregularly irregular at a rate of 186 bpm. There are only three supraventricular rhythms that are irregularly irregular:
- sinus arrhythmia, in which there is one P-wave morphology and a stable PR interval;
- multifocal atrial tachycardia (rate > 100 bpm) or multifocal atrial rhythm or wandering atrial pacemaker (rate < 100 bpm), in which there are three or more P-wave morphologies without any dominant P wave;
- atrial fibrillation, in which there are no organized P waves seen.
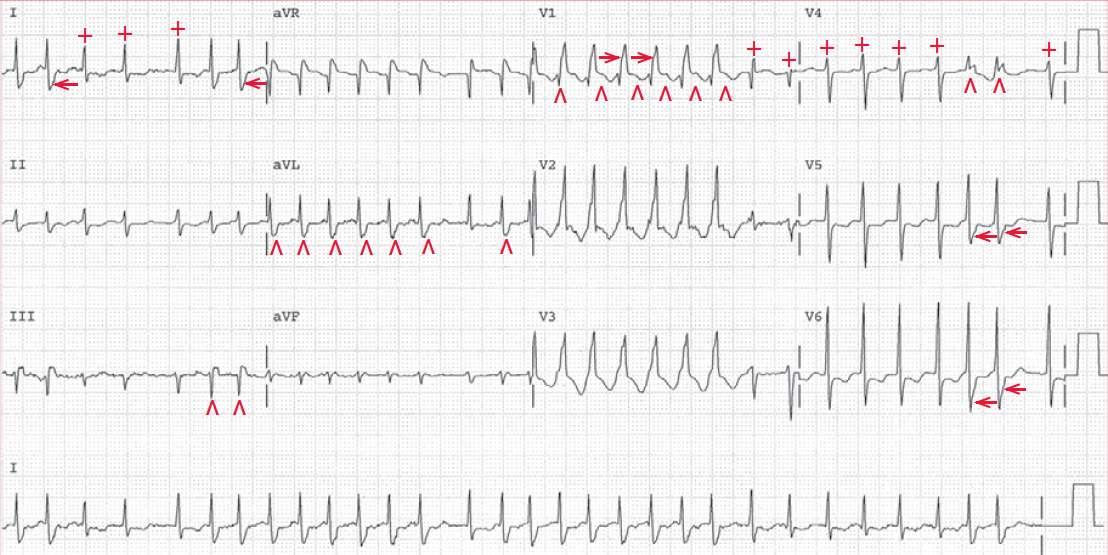
In this ECG, there are no P waves seen before or after any QRS complex. Hence this is atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response. The QRS complexes have two different widths and morphologies.
The narrow complexes (+) have a duration of 0.08 second and have a normal morphology. The wide QRS complexes (^) have a duration of 0.12 second and these QRS complexes have a right bundle branch block morphology (RSR′ in V1 [→] and broad S wave in leads I and V5–V6 [←]).
It can be seen that the wide QRS complexes with a right bundle branch block pattern are associated with shorter RR intervals (or faster rate). Hence this is a rate-related right bundle branch block.
As the symptoms with atrial fibrillation are usually due to the rapid ventricular response rate, initial therapy is slowing the ventricular rate. As the ventricular rate is due solely to AV nodal conduction, initial therapy is directed at AV nodal blockade to slow conduction through this structure and thereby slow the ventricular rate.
This can be achieved with an AV nodal blocking agent, including a b-blocker, calcium-channel blocker (verapamil or diltiazem), or digoxin. Adenosine blocks the AV node, but its effect is very brief and hence this is not a therapeutic agent in this arrhythmia.
- READ MORE:
- SIMILAR CASES:
- ECG Case 71: Atrial fibrillation with RVR, LAFB and Acute Anterolateral STEMI
- ECG Case 59: Atrial Fibrillation with Rapid Ventricular Response (RVR) and Diffuse Subendocardial Ischemia
- ECG Case 122: Atrial Fibrillation with Rapid Ventricular Response
- ECG Case 116: Atrial Fibrillation with a Rapid Ventricular Rate and Ischemic Changes