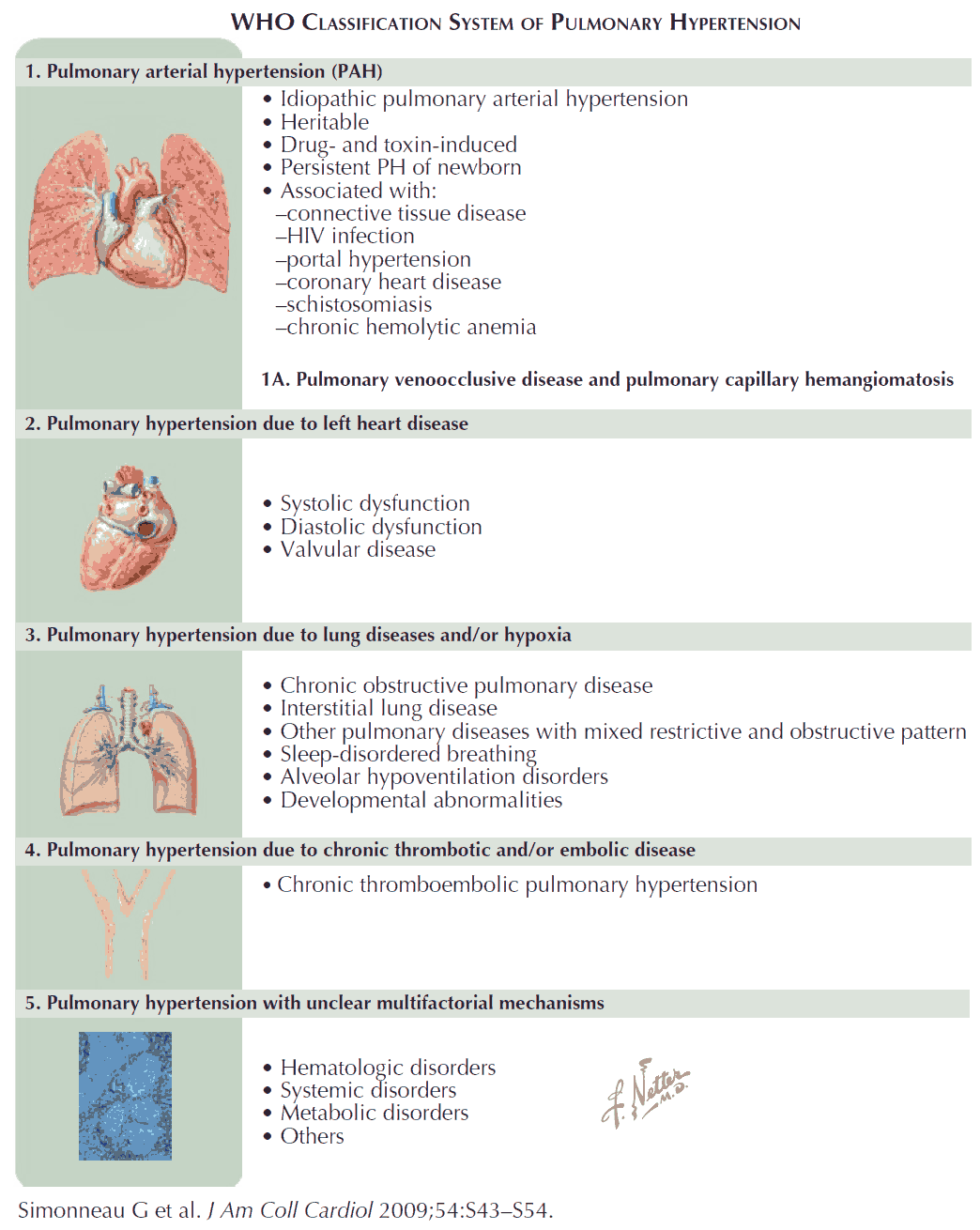
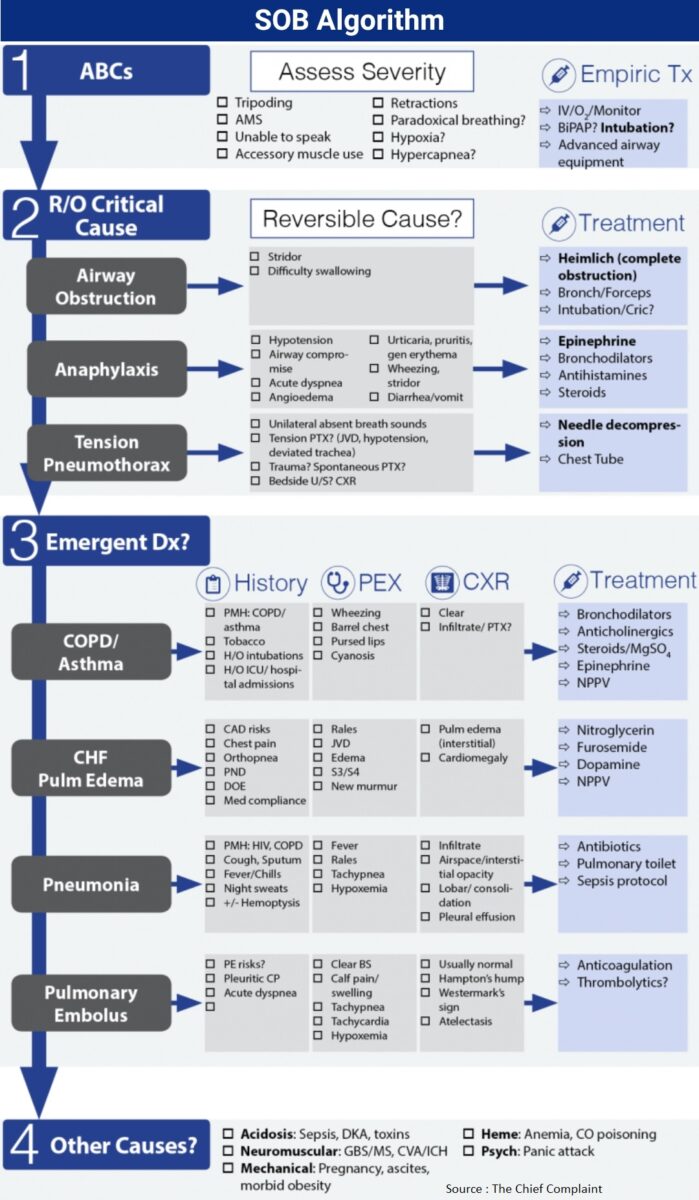
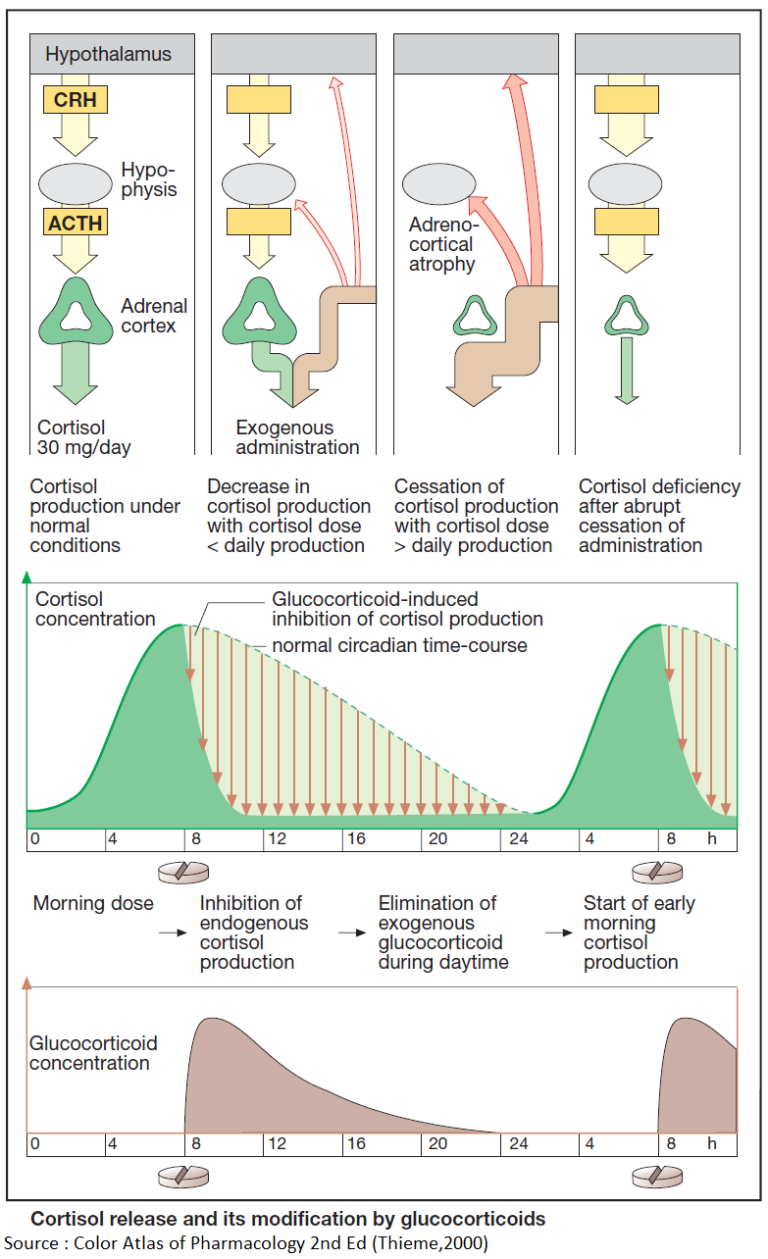
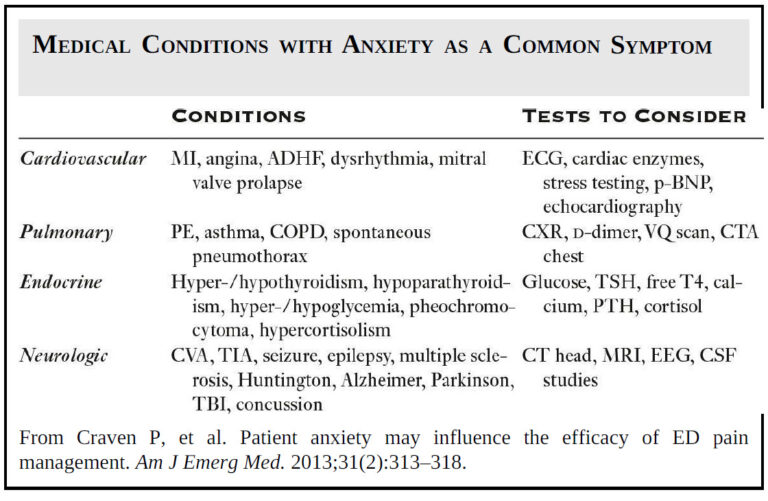
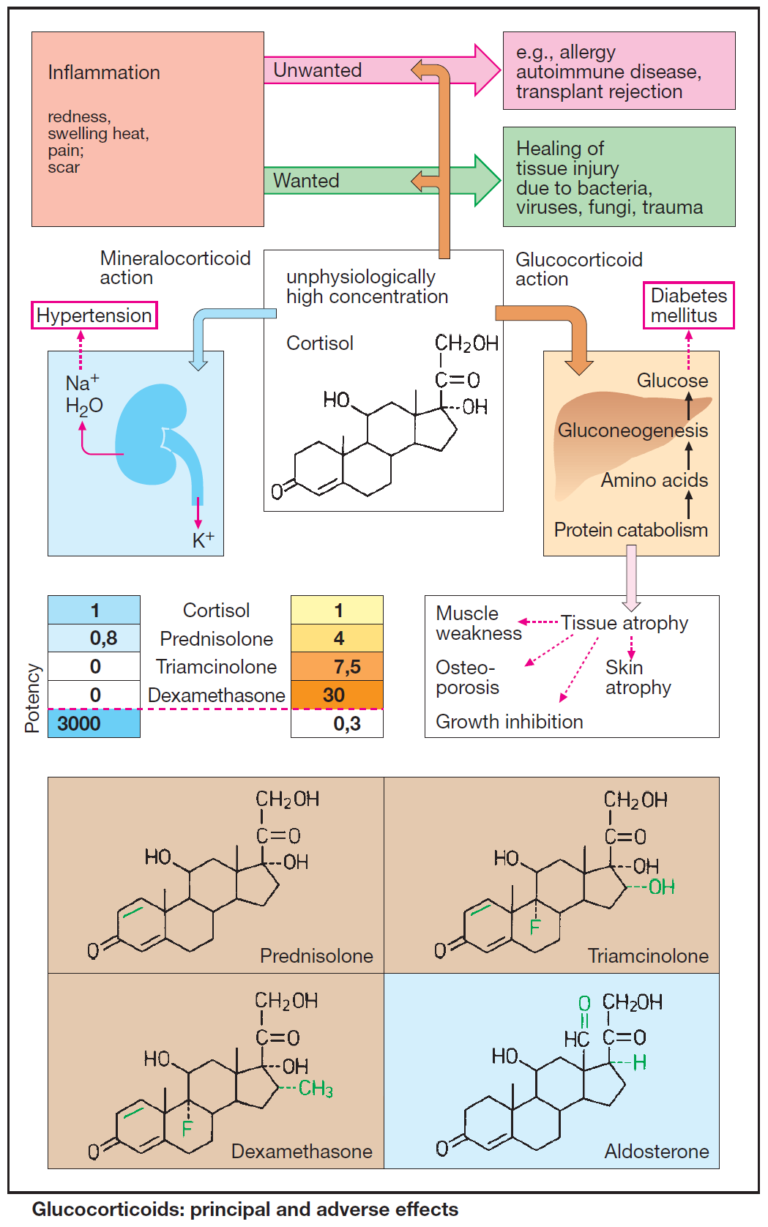
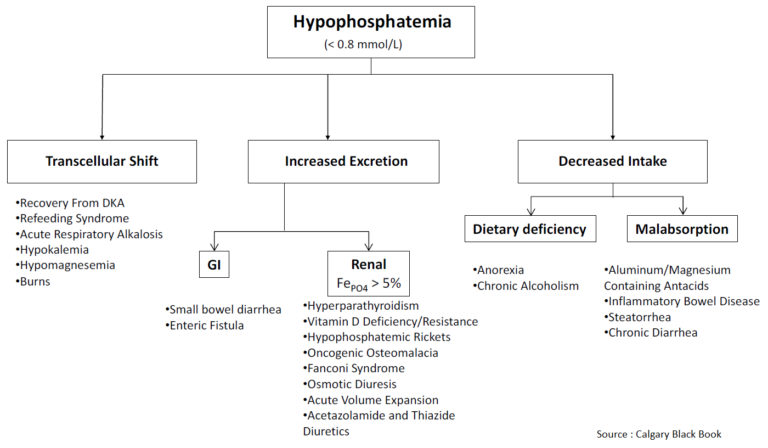
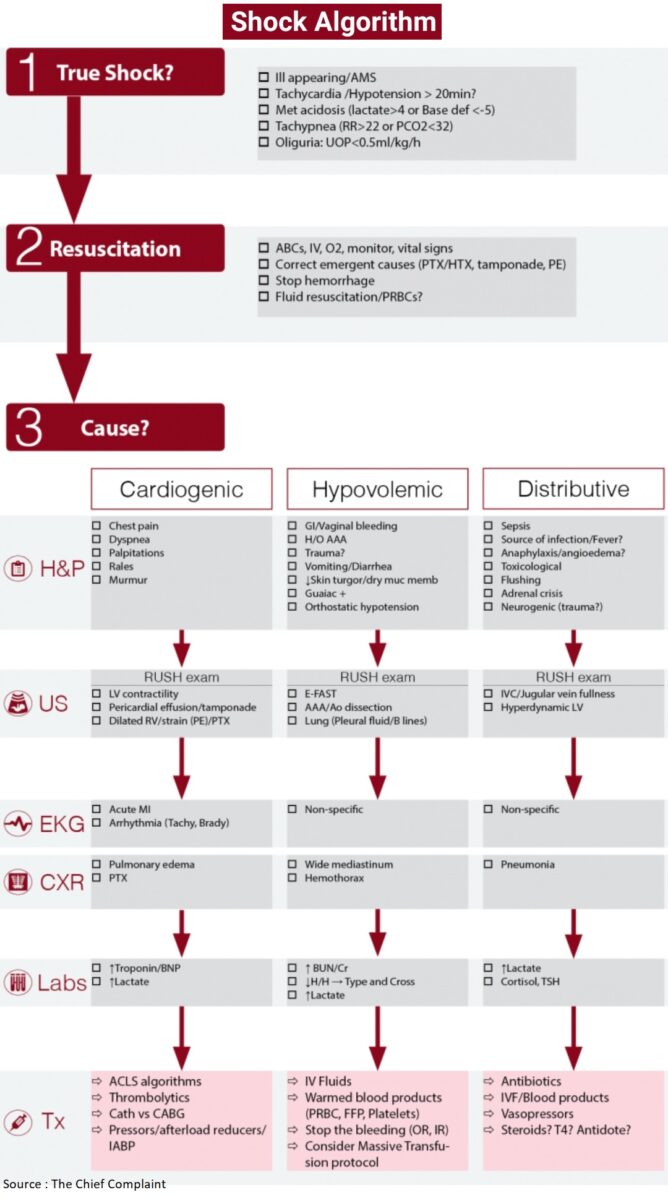
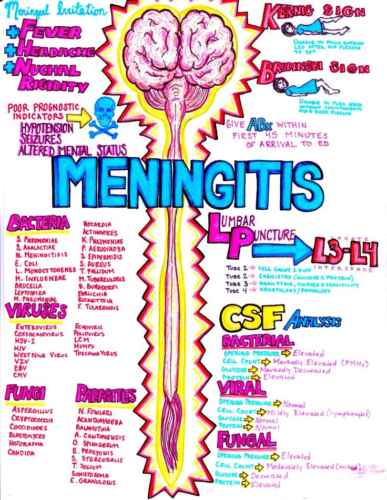
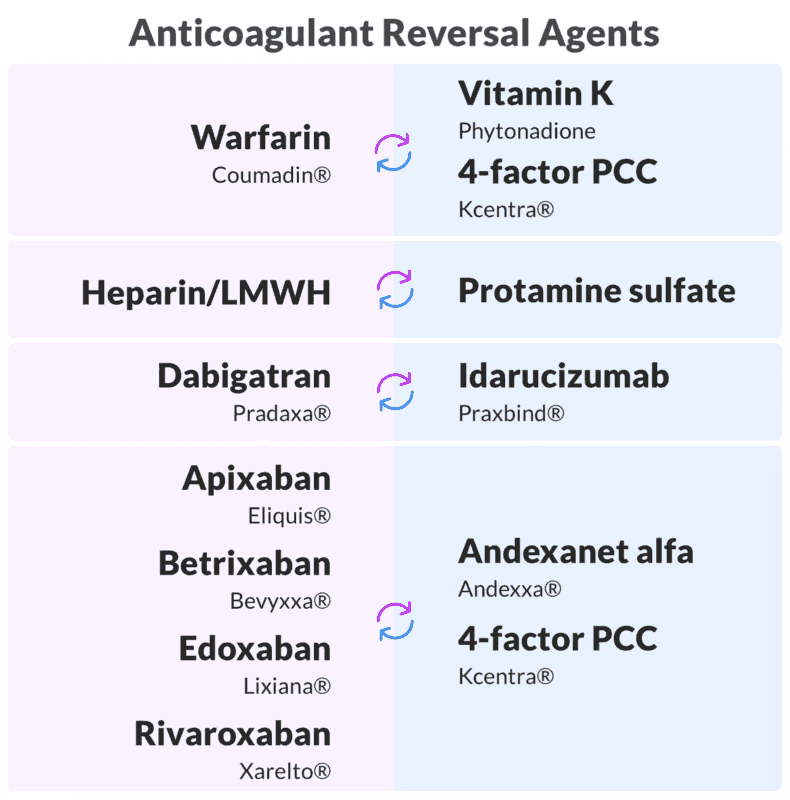
Acute Illnesses that Lead to Rapid Deterioration in Pulmonary Hypertension
Sudden deterioration in RV function can rapidly lead to shock, cardiovascular collapse, and death. In the ED, it is important to rapidly recognize and treat common precipitants of acute decompensation. These include sepsis, tachyarrhythmias, hypoxia, pulmonary embolism (PE), and the abrupt withdrawal of vasodilator medications.