Don’t Stress the Stress Test in Suspected ACS
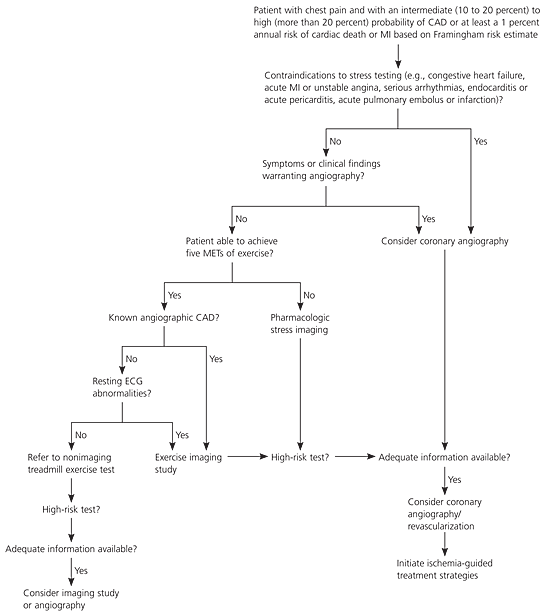
The goal of a cardiac stress test is to identify the patient with obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), typically defined as stenosis of 50% or more of a coronary artery on angiography.

The goal of a cardiac stress test is to identify the patient with obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), typically defined as stenosis of 50% or more of a coronary artery on angiography.
Correct classification of stones is important since it will impact treatment decisions and outcome. Urinary stones can be classified according to the following aspects: stone size, stone location, X-ray characteristics of stone, aetiology of stone formation, stone composition (mineralogy), and risk group for recurrent stone formation.
VAD (Ventricular assist device) patients are a special challenge for the EP. Through a careful assessment of the VAD, physical exam, MAP, ECG, and echo, the EP can resuscitate the good VAD that has gone bad.
Infections due to fungi are usually confined to the skin or mucous membranes: local or superficial mycosis. However, in immune deficiency states, internal organs may also be affected: systemic or deep mycosis. Mycoses are most commonly due to dermatophytes, which affect the skin, hair, and nails following external infection.
Rule Out Emergent Diagnosis and Causes of Stridor in Children: Epiglottitis, Retropharyngeal Abcsess, Bacterial Tracheitis, Foreign Body Aspiration
In 2009, “highly sensitive” troponin assays became available. These assays can detect the presence of troponin at much lower serum levels compared to traditional troponin assays. “Highly sensitive” troponins have a higher sensitivity and negative predictive value, but lower specificity, when compared with traditional troponin assays.
The therapeutic principle applicable to both Tuberculosis and Leprosy is combined treatment with two or more drugs. Combination therapy prevents the emergence of resistant Mycobacteria and Mycobacterial Infections.
Always begin with ABCs and decide whether or not to emergently intubate. Begin fluid resuscitation if not in overt CHF and check/correct hypoglycemia. At minimum, these neonates will get a septic work-up including labs, antibiotics and possibly LP, then admission.
Patients with acute life-threatening cardiac or pulmonary conditions frequently present with feelings of panic or impending doom in association with chest pain. This may even be in the setting of a stressful situation and mislead the EP to feel confident that anxiolytic therapy and reassurance is all that may be needed.
Benzodiazepines modify affective responses to sensory perceptions; specifically, they render a subject indifferent towards anxiogenic stimuli, i.e., anxiolytic action. Furthermore, benzodiazepines exert sedating, anticonvulsant, and muscle-relaxant (myotonolytic) effects.