This article is an answer to the Case – Hepatomegaly with a Palpable Hepatic Mass
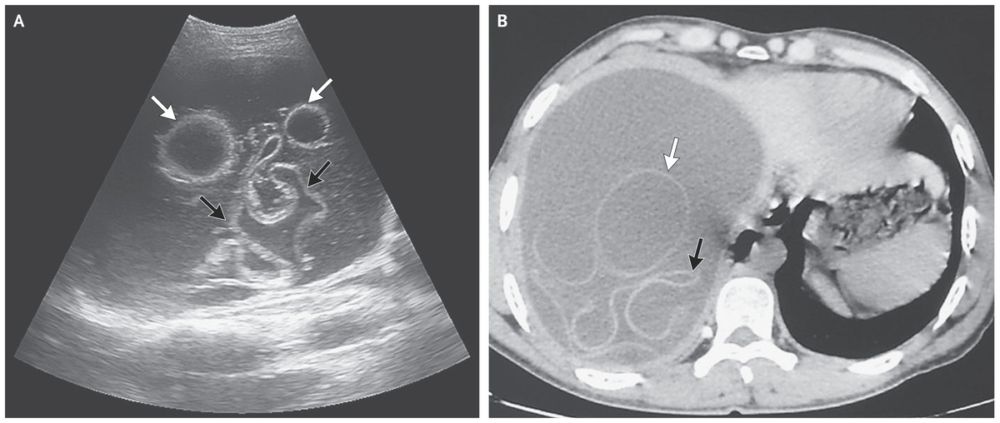
Ultrasonography (Panel A) and computed tomography (Panel B) of the abdomen revealed a large cyst in the right lobe of the liver, containing hydatid membranes (black arrows) and daughter vesicles (white arrows).
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay indicated an anti-echinococcus IgG antibody index of 16.7 in the patient’s blood (normal value, ≤11).
Hydatid disease is caused by the echinococcus tapeworm. Dogs are the definitive host; the infection is transmitted when eggs shed in their stool are ingested by humans or other animals.
The patient underwent laparotomy, during which the cysts were removed in their entirety with no spillage of their contents. Echinococcus granulosis was detected. A follow-up ultrasound examination 2 months after surgery showed no sign of recurrence.
References
- Sebastian Gallo-Bernal, Alexis M. Cahalane, Michael S. Gee. (2022) Percutaneous Image-Guided Drainage of Abdominal Fluid Collections in Children: Technical Considerations and Clinical Scenarios. Digestive Disease Interventions 24.
- Erqiang Wang, Zhenyu Liao, Lianghai Wang, Yuan Liao, Xiaodan Xu, Ping Liu, Xian Wang, Jun Hou, Huijiao Jiang, Xiangwei Wu, Xueling Chen. (2021) A combination of pirfenidone and TGF-β inhibition mitigates cystic echinococcosis-associated hepatic injury. Parasitology 148:7, 767-778.