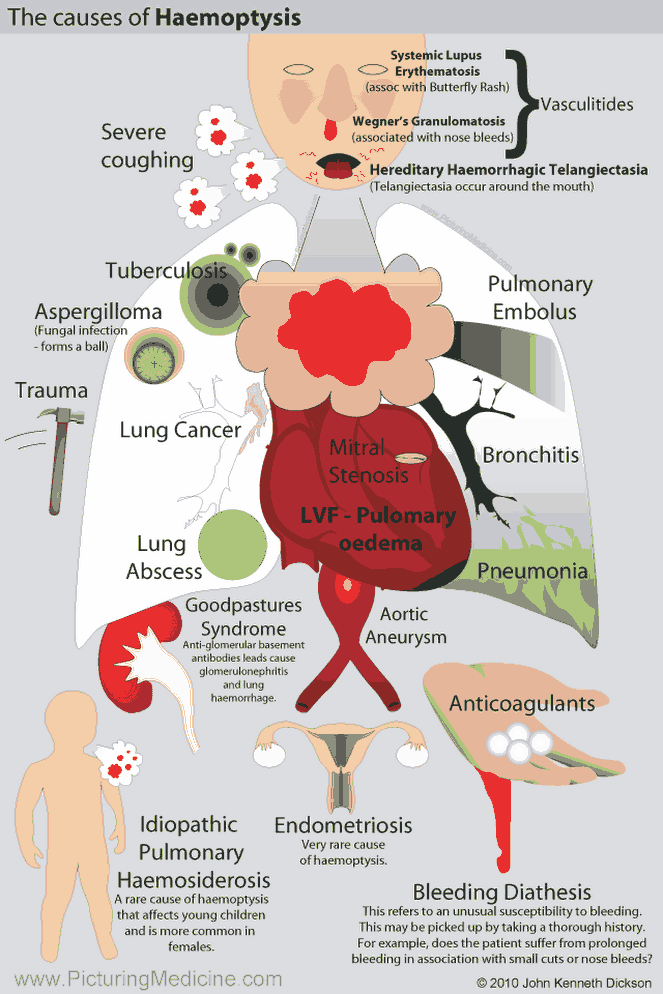
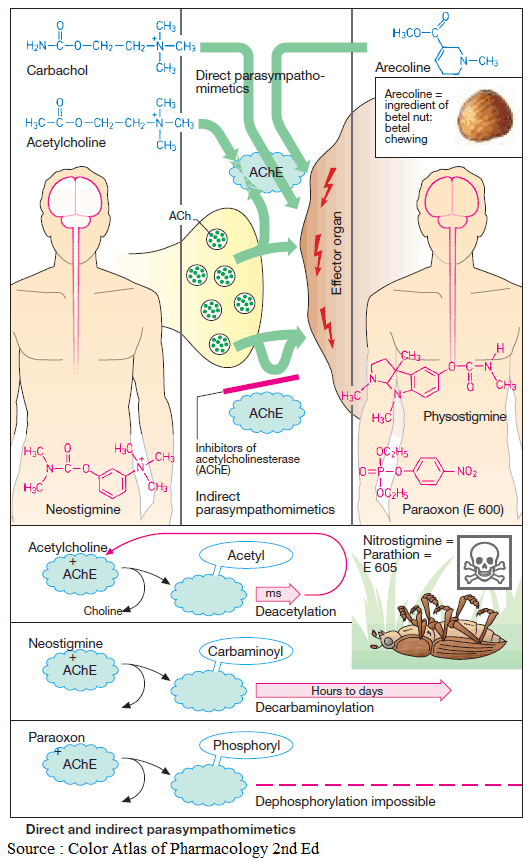
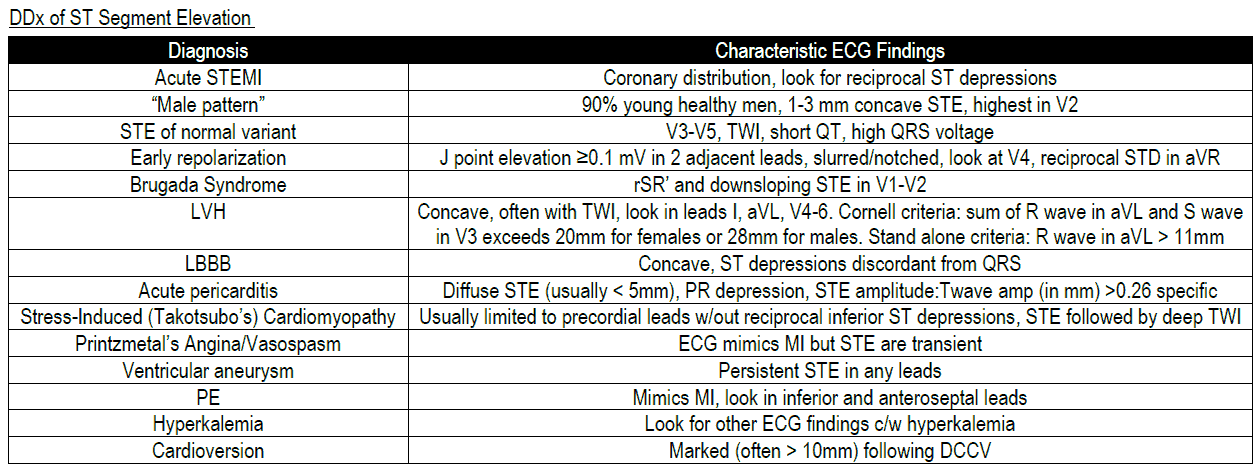
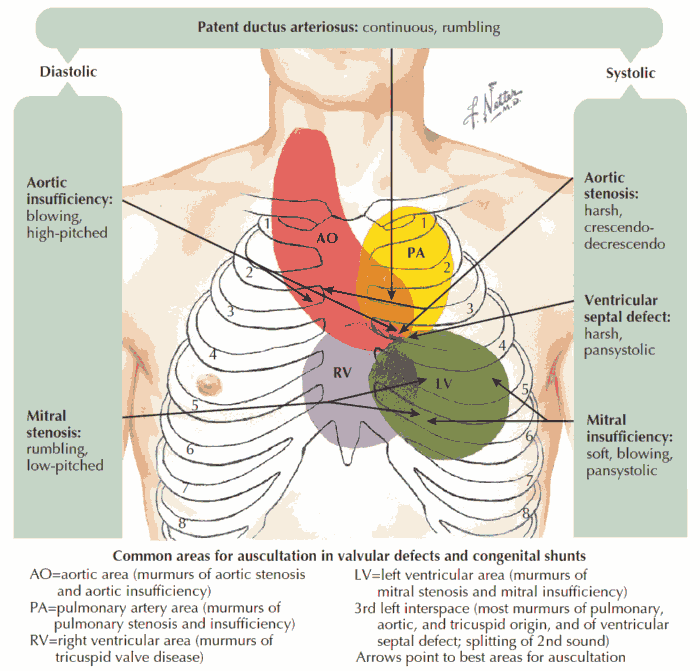
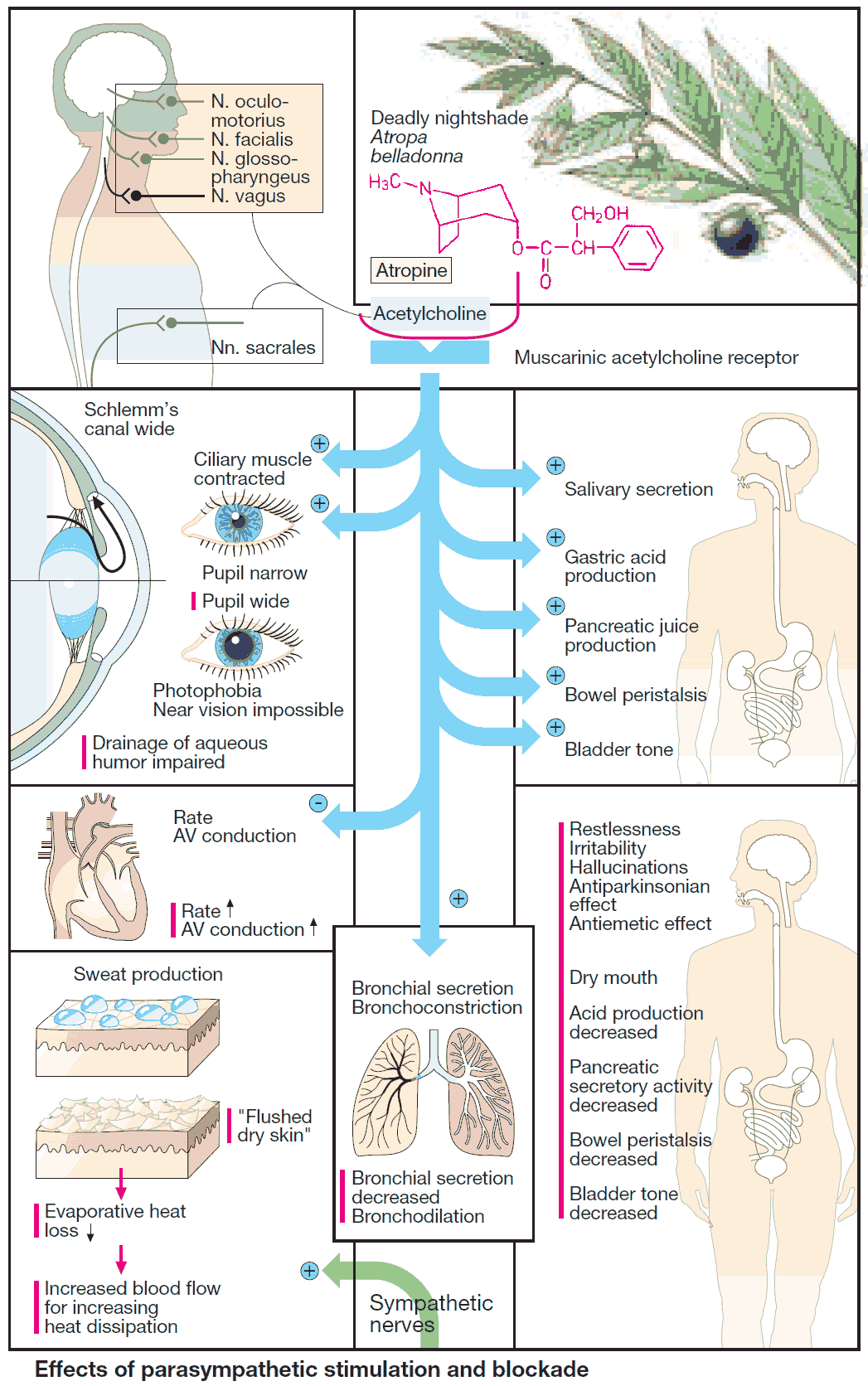
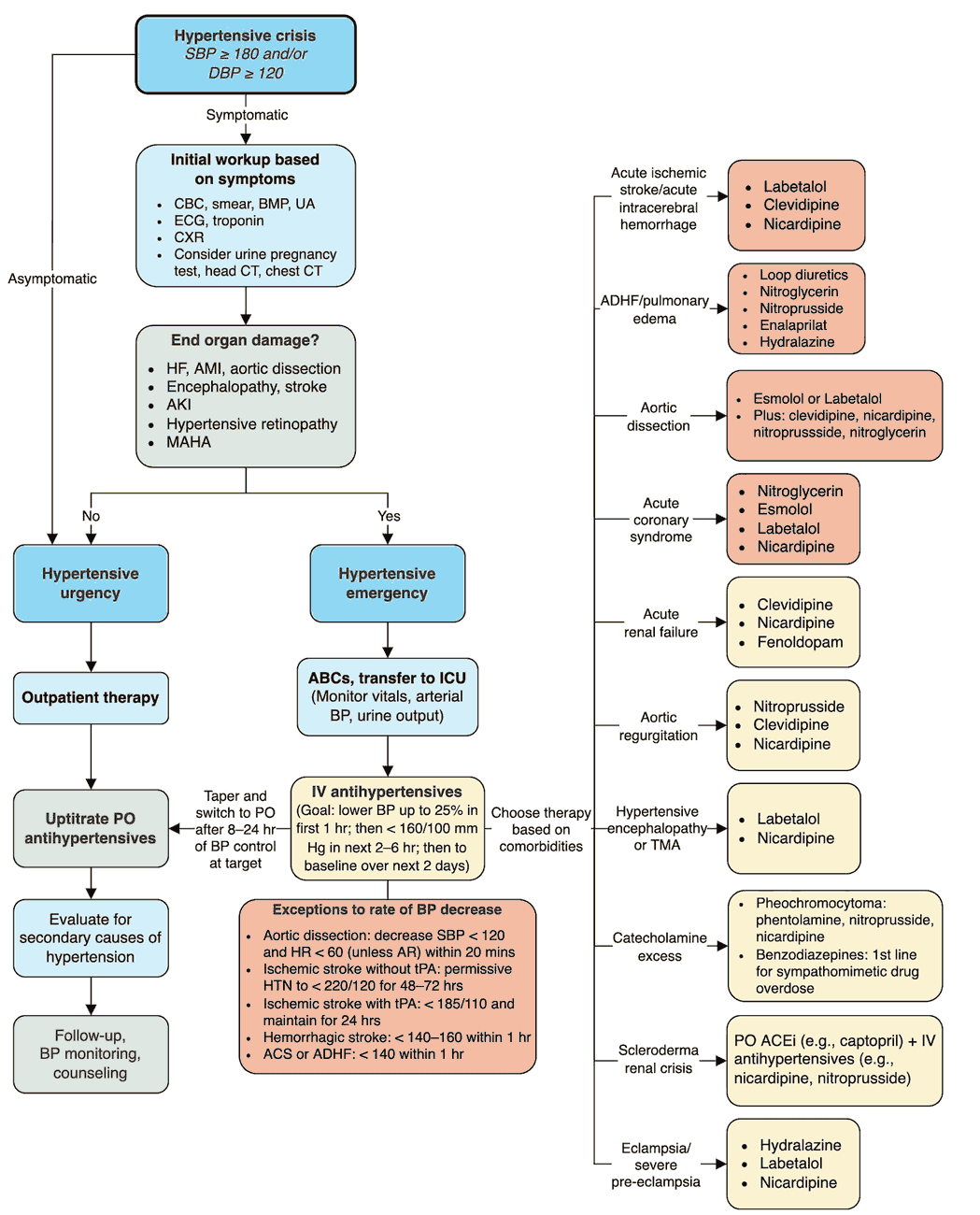
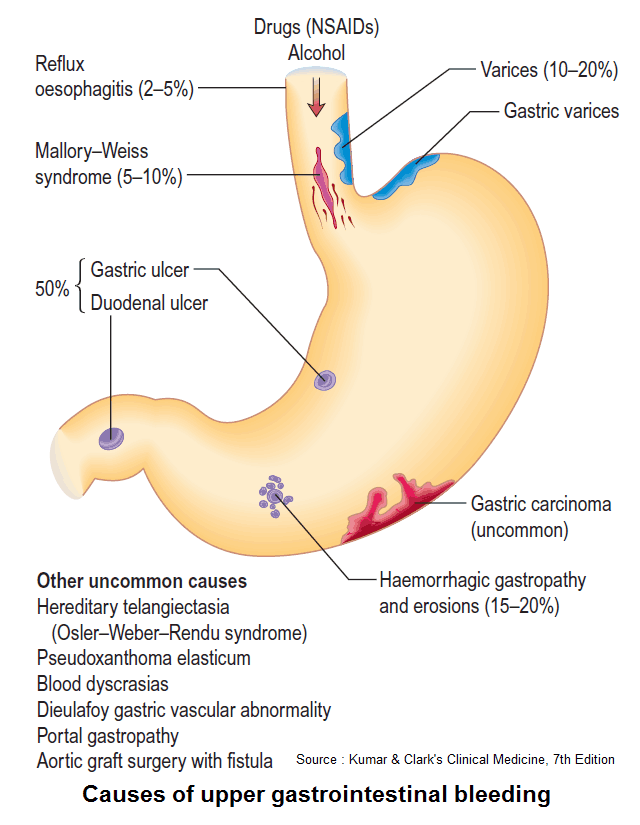
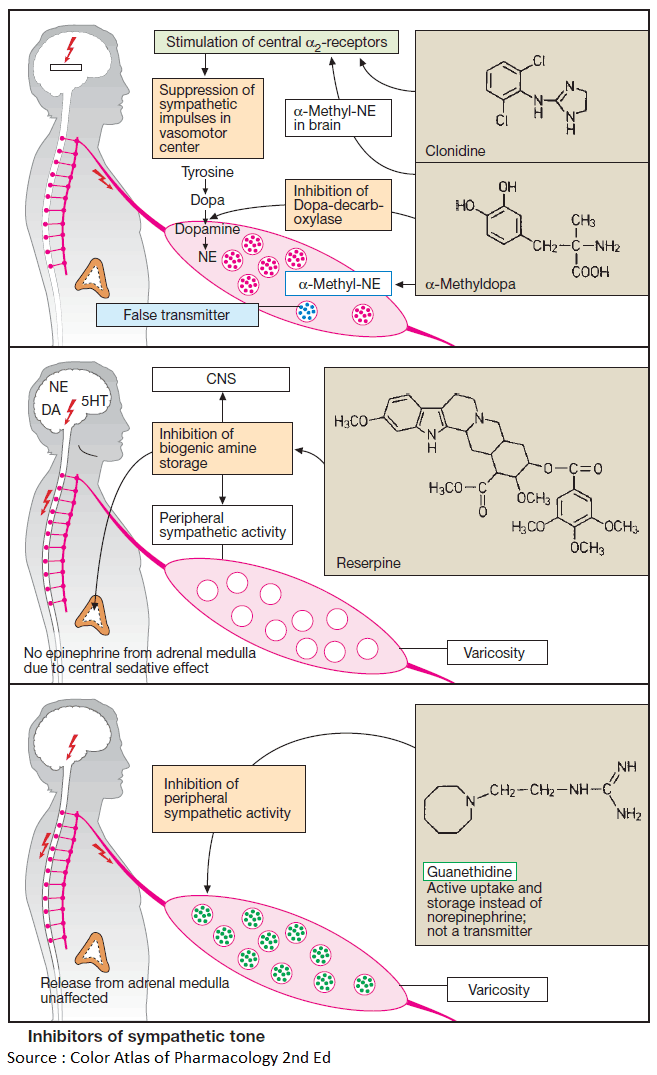
Cough and Hemoptysis – Differential Diagnosis, Examination and Investigations
Coughing is a nonspecific reaction to irritation anywhere in the respiratory tract from the pharynx to the lungs, and it is the most common manifestation of lower respiratory tract disease. Any cough that persists for over 3 weeks merits further investigation in the absence of an obvious cause.