Table of Contents
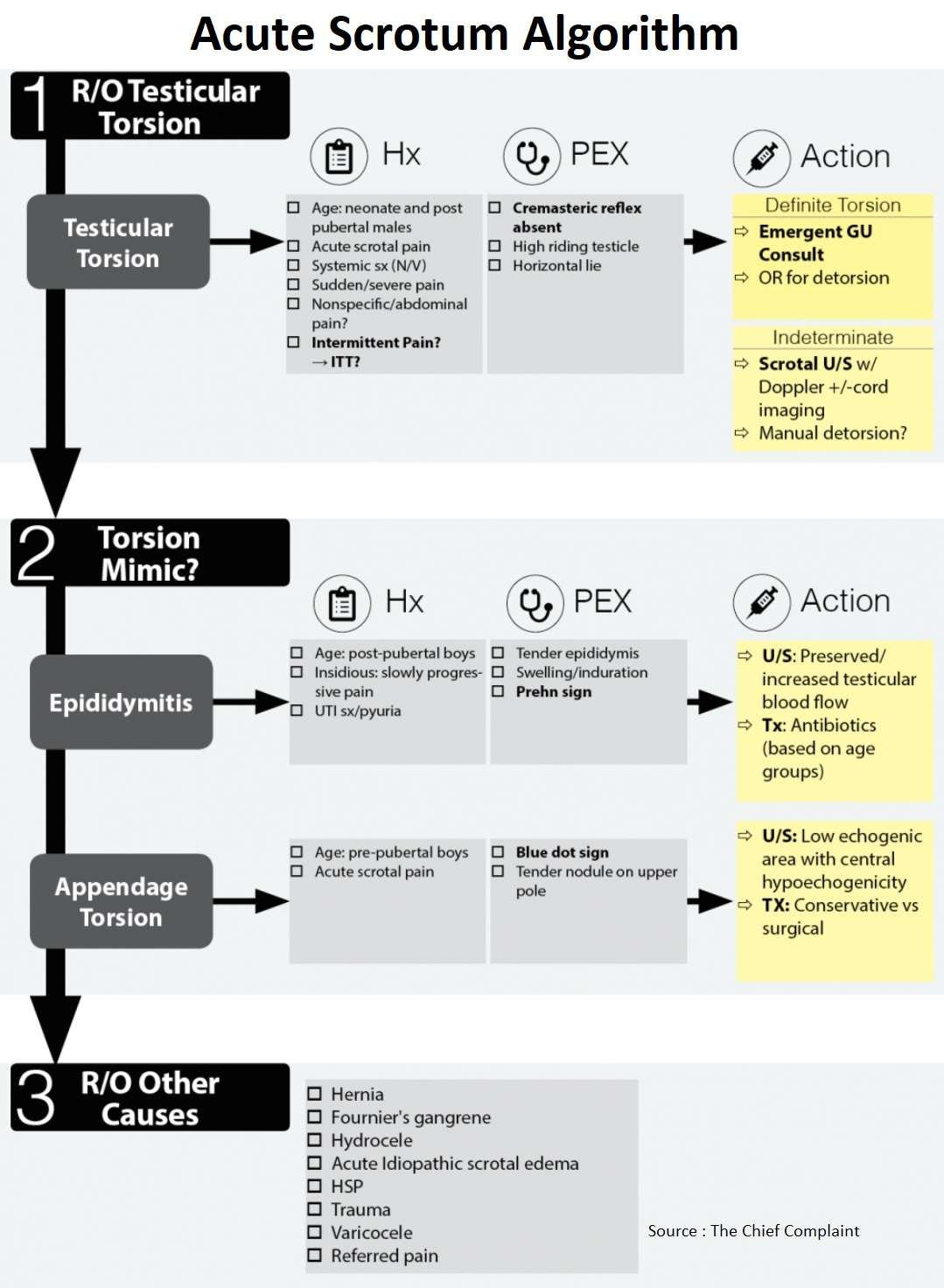
- The general approach to acute scrotal pain is to work-up the patient for testicular torsion by first risk stratifying them based on age group, history and physical.
- Based on the patient’s pre-test probability → call GU emergently or obtain testicular U/S.
- The U/S will also help in the evaluation of other serious causes of testicular pain such as appendage torsion and epididymitis.
- The etiology of acute scrotal pain varies among different age groups, the most common being: (Journal of Pediatric Surgery 1995;30(2):277-82)
- 0-1 yo: Testicular torsion
- 3-13 yo: Appendage torsion
- 13 yo: Epididymitis
Rule Out Testicular Torsion
History
- Age
- Torsion can occur at any age, and up to 39% of cases occur in adulthood (J Urol 1990;143:62)
- Adults with torsion may have a lower salvage rate (likely because of the severity of cord twisting) (J Urol 2002;167:2109)
- Presentation of Testicular Torsion
- Acute scrotal pain – Sudden/severe pain
- Systemic symptoms (N/V)
- Nonspecific/abdominal pain
- Pitfall: Intermittent Testicular Torsion (torsion-detorsion)
- Intermittent Testicular Torsion should be considered in patients who present with recurrent, rapid onset, severe pain with spontaneous resolution.
- Hyperperfusion of testis can occur after detorsion or intermittent torsion and give a false diagnosis of epididymitis on U/S.
- Whirlpool sign (caused by twisting of the spermatic cord) on spermatic cord imaging can help identify these patients along with horizontal lie of the testis (J Ultrasound Med 2006;25:563-574)
- Horizontal lie of testis is the only physical exam finding significantly associated with bell clapper deformity (Spec 100%) (J Urology 2005;174:1532-35)
- GU should be contacted if intermittent torsion suspected for future surgical fixation to prevent future pain and infarction.
Physical Exam for Testicular Torsion
- Cremaster reflex (J Urol 1984;132(1):89-90)
- Most sensitive physical exam finding is the cremasteric reflex (sensitivity100%) in one series of 245 patients
- If you see scrotum rising when you stroke the inner thigh → less likely there is torsion (other series have confirmed these findings)
- Disclaimer: Cannot rely solely on presence of reflex, must interpret in context of other clinical findings.
- Absence of cremasteric reflex is meaningless, kids normally lack this reflex.
- High riding testicle
- Horizontal lie
Salvage rates for Torsion (Am Fam Physician 2006;74:1739-43)
- <6 hours: 90-100%
- 2-24 hours: 36-50%
- >24 hours: 0-10%
Diagnostic work up for Testicular Torsion
- Based on pre-test probability of torsion
- Definite Torsion: GU consult for emergent evaluation, especially if <4hours
- Indeterminate: U/S +/- GU consulting
- Color Doppler U/S
- Sensitivity and specificity to diagnose torsion across multiple studies are 85-100% and 75-100%, respectively. (J Urol 2004;172:1692-1695)
- U/S is not perfect in ruling-out torsion and multiple studies have shown false negatives → must look for intra-testicular (not peripheral) flow
- Pitfall: Emergent surgical exploration should still be considered for those at high risk for torsion despite negative U/S
- Cord Imaging:
- Rotated spermatic cord “whirlpool sign” is a highly sensitive and specific sign for torsion, especially when vascular flow is present on Doppler U/S.
- Manual detorsion
- Procedure: Detorse from inside to out → like opening a book
- 30-80% success rate
- If successful, relief of ischemia can convert a urologic emergency into an elective surgical procedure and will salvage the testes
Rule Out Torsion Mimics
- Epididymitis
- Appendage Torsion
1. Epididymitis
Clinical Presentation of Epididymitis
- Age: post-pubertal boys
- Insidious onset: slowly progressive pain
- UTI symptoms / pyuria
- Tender epididymis with swelling/induration
- Prehn sign (physical lifting of the testicles relieves the pain of epididymitis but not pain caused by testicular torsion)
Etiology of Epididymitis
- Varies by age groups
- Pre-pubertal: Chemical irritation secondary to reflux of sterile urine (STD? → child abuse?)
- Young males: STD
- Older male: STD vs urinary pathogens (reflux from BPH)
- Special Case:Child with Epididymitis? (J Urol. 1987;138:1100-3)
- Will need GU follow up for upper tract imaging and VCUG (voiding cystourethrogram) because of the known association with urinary tract pathology
Work-up for Epididymitis
- Urine Neisseria gonorrhoeae/Chlamydia trachomatis (CT/GC)
- US – shows preserved/increased testicular blood flow
Treatment of Epididymitis (based on age group)
• Empiric antibiotics to cover most likely etiology (STD vs urinary pathogens)
• Children: Antibiotics against coliforms
• Adults: Neisseria gonorrhoeae/Chlamydia +/- coliforms
2. Appendage Torsion
- Clinical Presentation of Appendage Torsion
- Age: pre-pubertal boys
- Acute scrotal pain
- Physical exam: Blue dot sign, tender nodule on upper pole
- Work up for Appendage Torsion
- Clinical diagnosis
- US – Low echogenic area with central hypoechogenicity
- Treatment of Appendage Torsion
- Conservative: Rest, ice, anti-inflammatories → slow recovery and pain may last weeks to months
- Surgical: excision of appendix testes → not necessary but is safe and pts can resume activity in days
Rule out Other Causes
- Hernia
- Fournier’s gangrene
- Hydrocele
- Acute Idiopathic scrotal edema
- HSP (Henoch-Schonlein Purpura)
- Trauma
- Varicocele
- Referred pain (nephrolithiasis, appy etc…)
More Algorithms
- Pregnant Vaginal Bleeding Algorithm
- Blunt Chest Trauma Algorithm
- Penetrating Chest Trauma Algorithm
- Blunt Chest Trauma Algorithm
- Penetrating Chest Trauma Algorithm
- Cervical Spine Trauma Clearance Algorithm
- Blunt Head Trauma Algorithm
- Hypothermia Algorithm
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm
- Low Back Pain Algorithm and Differential Diagnosis
- Sepsis Algorithm and Differential Diagnosis
- Vertigo Algorithm and Differential Diagnosis
- Burns Algorithm
- Headache Algorithm
- Shock Algorithm
- Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea) in the Emergency Department
References
- Torsion of the Spermatic Cord in Adults. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S002253471739866X
- Adult Testicular Torsion. https://www.auajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1016/S0022-5347%2805%2965096-3
- Sonographic Differential Diagnosis of Acute Scrotum. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.7863/jum.2006.25.5.563
- The importance of the cremasteric reflex in acute scrotal swelling in children. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6726967/
- Testicular Torsion (Am Fam Physician. 2006 Nov 15;74(10):1739-1743). https://www.aafp.org/afp/2006/1115/p1739.html
- ULTRASONOGRAPHY OF THE SPERMATIC CORD IN CHILDREN WITH TESTICULAR TORSION: IMPACT ON THE SURGICAL STRATEGY. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15371792/