COPD (Emphysema and Chronic Bronchitis): From Diagnosis to Treatment
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined as a condition in which there is chronic obstruction to airflow due to chronic bronchitis with or without emphysema
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined as a condition in which there is chronic obstruction to airflow due to chronic bronchitis with or without emphysema
Peptic ulcer disease most commonly occurs in the duodenum, followed by the stomach, esophagus, and jejunum in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, or after a gastroenterostomy, or in a Meckel's diverticulum with ectopic gastric mucosa.
The leukemias are a group of conditions characterized by the malignant proliferation of leukocytes in the bone marrow. The cells spill out into the blood stream and may infiltrate other organs...
Asthma is a disease of the airways characterized by an increased responsiveness of the tracheobronchial tree to many different stimuli. It is manifested by paroxysms of shortness of breath, cough, and wheezing
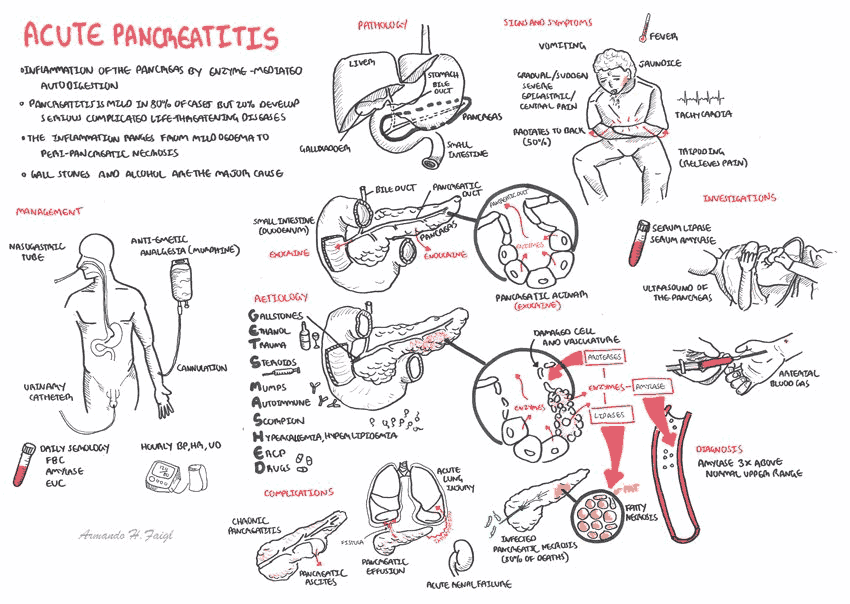
The causes of pancreatitis can be recalled from the mnemonic GET SMASH'D: gallstones, ethanol, trauma, steroids, mumps, autoimmune diseases, scorpion stings, hypertriglyceridemia, and drugs (e.g., azathioprine or diuretics).
By quality of pain the chest pain can be categorized into: pleuritic, dull central chest pain, chest wall tenderness...
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) causes tall R waves in left sided and deep S waves in right sided leads. Always look for ‘strain’ pattern in left sided leads...
Characteristic features of Atrial Flutter are: Atrial rate around 300/min; ‘Sawtooth’ baseline; AV block (commonly 2:1, but can be 3:1, 4:1 or variable). You should always suspect atrial flutter with 2:1 block when a patient has a regular tachycardia with a ventricular rate of about 150/min.
In patients with typical symptoms and diagnostic laboratory tests, CT or MR imaging is not required to confirm the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. CT or MR imaging are primarily used to detect complications of acute pancreatitis...
Sensory neurologic deficits include: Hyperesthesias (increased pain, touch, or vibration); Hypalgesia (decreased sensitivity to painful stimuli); Paresthesia (abnormal sensation of the skin like tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness); Anesthesia (complete loss of pain, temperature, touch, and vibration sense). Sensory and Motor Neurologic Deficits can result from disease occurring anywhere along the pathway from the skin or muscle to the brain and back.